Abstract
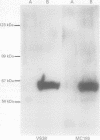
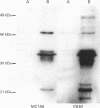
AIMS: To characterise the 64 kDa intracellular antigen present on normal and neoplastic plasma cells detected by monoclonal antibody VS38 and by another antibody, MC186, of similar reactivity. METHODS: The VS38 monoclonal antibody was used to screen a bacterially expressed peripheral blood cDNA library, and the immunocytochemical staining of the two antibodies was compared with those raised specifically to the protein identified as the VS38 antigen. RESULTS: A partial cDNA encoding the VS38 antigen was cloned and shown to be identical to the human p63 gene. p63 is a non-glycated, reversibly palmitoylated type II transmembrane protein which is found in rough endoplasmic reticulum. Antibody MC186 also recognised this protein and both VS38 and MC186 together with two antibodies raised to p63 gave identical immunostaining patterns. CONCLUSIONS: The VS38 antigen was identified as the rough endoplasmic reticulum protein p63. While it is not exclusively expressed on plasma cells, the presence of p63 distinguishes plasma cells from other lymphoid cells because of their high secretory activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. C., Park E. K., Bates M. P., Leonard R. C., Hardy R., Schlossman S. F., Nadler L. M. Antigens on human plasma cells identified by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1132–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman T. G., Cabin D. E., Vickers S., Deutschman C. S., Delgado E., Sussman M. M., Bulkley G. B. Molecular biology of circulatory shock. Part II. Expression of four groups of hepatic genes is enhanced after resuscitation from cardiogenic shock. Surgery. 1990 Sep;108(3):559–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. J., Hickey W. F., Mezitis S. G., Stieber A., Lavi E., Gonatas J. O., Gonatas N. K. Monoclonal antibody 2H1 detects a 60-65 KD membrane polypeptide of the rough endoplasmic reticulum of neurons and selectively stains cells of several rat tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 May;39(5):635–643. doi: 10.1177/39.5.2016513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E., Görlich D., Kostka S., Otto A., Kraft R., Knespel S., Bürger E., Rapoport T. A., Prehn S. A tetrameric complex of membrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jun 1;214(2):375–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortsch M., Griffiths G., Meyer D. I. Restriction of docking protein to the rough endoplasmic reticulum: immunocytochemical localization in rat liver. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;38(2):271–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortsch M., Meyer D. I. Immunochemical analysis of rough and smooth microsomes from rat liver. Segregation of docking protein in rough membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Aug 1;150(3):559–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Ulrich B. L., Sabatini D. D. Proteins of rough microsomal membranes related to ribosome binding. I. Identification of ribophorins I and II, membrane proteins characteristics of rough microsomes. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):464–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden M. D., Fishleder A. J., Tubbs R. R., Park H. Immunophenotypic spectrum of plasma cell leukemia. Cancer. 1989 Mar 1;63(5):859–862. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890301)63:5<859::aid-cncr2820630511>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan P. D., Walker L., Hardie D., Richardson P., Khan M., Johnson G. D., Ling N. R. An antigenic study of human plasma cells in normal tissue and in myeloma: identification of a novel plasma cell associated antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jul;65(1):112–119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Miguel J. F., González M., Gascón A., Moro M. J., Hernández J. M., Ortega F., Jimenez R., Guerras L., Romero M., Casanova F. Immunophenotypic heterogeneity of multiple myeloma: influence on the biology and clinical course of the disease. Castellano-Leones (Spain) Cooperative Group for the Study of Monoclonal Gammopathies. Br J Haematol. 1991 Feb;77(2):185–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb07975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer A., Ericsson M., Bächi T., Griffiths G., Hauri H. P. Characterization of a novel 63 kDa membrane protein. Implications for the organization of the ER-to-Golgi pathway. J Cell Sci. 1993 Mar;104(Pt 3):671–683. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.3.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer A., Rohrer J., Hauri H. P., Kornfeld S. Retention of p63 in an ER-Golgi intermediate compartment depends on the presence of all three of its domains and on its ability to form oligomers. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):25–39. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer A., Rohrer J., Jenö P., DeMaio A., Buchman T. G., Hauri H. P. A reversibly palmitoylated resident protein (p63) of an ER-Golgi intermediate compartment is related to a circulatory shock resuscitation protein. J Cell Sci. 1993 Mar;104(Pt 3):685–694. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.3.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer A., Rohrer J., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Kornfeld S. Reassessment of the subcellular localization of p63. J Cell Sci. 1995 Jun;108(Pt 6):2477–2485. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.6.2477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanks J. H., Banerjee S. S. VS38 immunostaining in melanocytic lesions. J Clin Pathol. 1996 Mar;49(3):205–207. doi: 10.1136/jcp.49.3.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaper-Cortenbach I. C., Admiraal L. G., Kerr J. M., van Leeuwen E. F., von dem Borne A. E., Tetteroo P. A. Flow-cytometric detection of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase and other intracellular antigens in combination with membrane antigens in acute lymphatic leukemias. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1639–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazzari P. L., Gobbi M., Dinota A., Bontadini A., Grassi G., Cerato C., Cavo M., Pileri S., Caligaris-Cappio F., Tura S. Normal and neoplastic plasma cell membrane phenotype: studies with new monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Oct;70(1):192–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong A. W., Lee J. C., Stone M. J. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody having selective reactivity with normal and neoplastic plasma cells. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):238–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turley H., Jones M., Erber W., Mayne K., de Waele M., Gatter K. VS38: a new monoclonal antibody for detecting plasma cell differentiation in routine sections. J Clin Pathol. 1994 May;47(5):418–422. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.5.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel F., Hartmann E., Görlich D., Rapoport T. A. Segregation of the signal sequence receptor protein in the rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;53(2):197–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]