Abstract
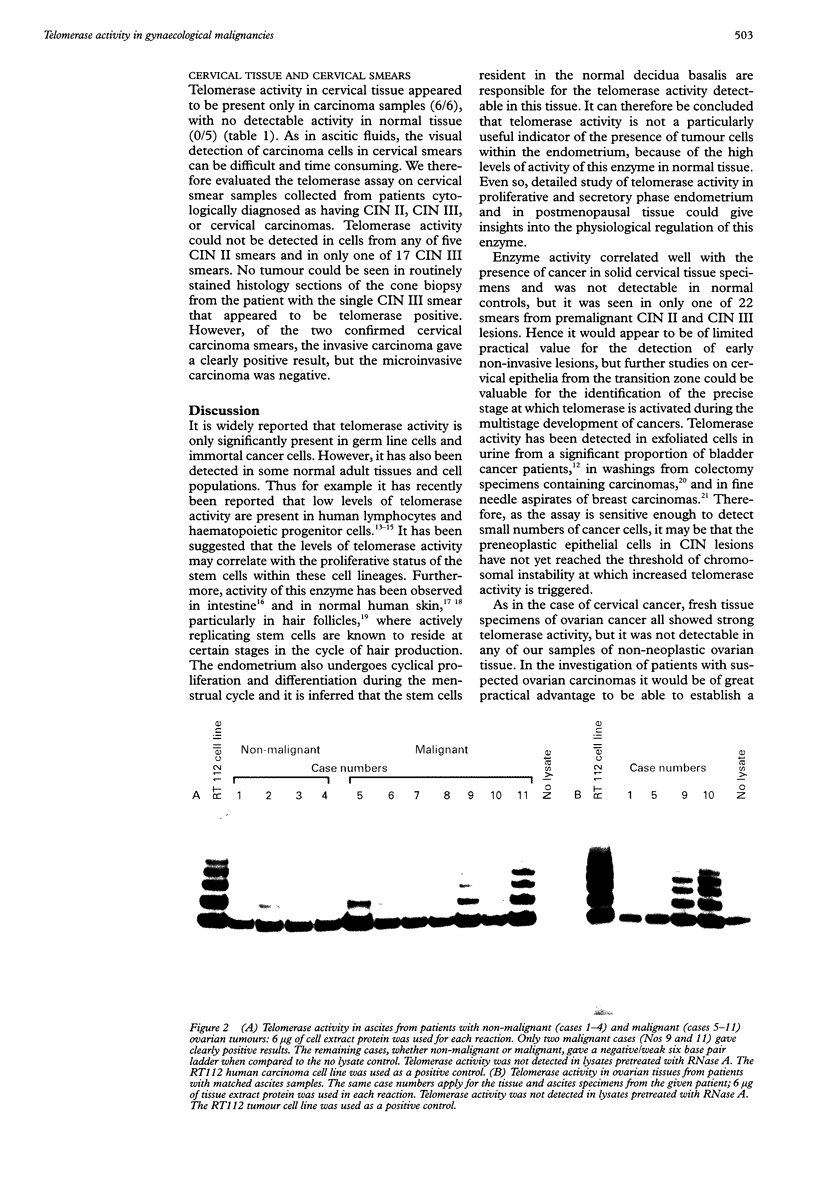
AIM: To evaluate whether increased telomerase activity can be clinically useful for detecting malignant cells in a variety of gynaecological specimens. METHODS: Telomerase activity was examined in frozen tissue samples of histologically confirmed lesions of the endometrium, ovary, and cervix. It was also assessed in exfoliated cells in cervical smears from patients with premalignant and malignant lesions and in ascitic fluid obtained from cases with malignant or non-malignant ovarian tumours. RESULTS: Solid tissues from carcinomas were telomerase positive in all specimens of endometrial (6/6) and cervical (6/6) origin, and in almost all from the ovary (12/13). Normal tissues from the cervix (0/5) and the ovary (0/5) were telomerase negative, but samples from normal endometrium were found to show telomerase activity, possibly due to the cyclical regenerative nature of this tissue. Conversely, dissociated cells in cervical smears from preneoplastic and frankly neoplastic lesions rarely showed detectable telomerase activity. Thus smears from patients with malignant tumours were only positive in one of two patients, whereas those from CIN-2 (0/5) and CIN-3 (1/17) lesions and from normal (0/10) samples were almost all negative. Telomerase activity was also scarcely detectable in cells obtained from ascitic fluid from patients with ovarian tumours. CONCLUSIONS: As in many other organs, telomerase activity is increased in solid tissue specimens from malignant tumours of the female reproductive tract, but it is not yet a reliable indicator of the presence of exfoliated cancerous or precancerous cells in clinical specimens from such lesions. Interpretation should be guarded until more extensive studies have been conducted. The data on solid tissues presented here confirm that activation of this enzyme is a major hallmark of the neoplastic process.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broccoli D., Young J. W., de Lange T. Telomerase activity in normal and malignant hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9082–9086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counter C. M., Avilion A. A., LeFeuvre C. E., Stewart N. G., Greider C. W., Harley C. B., Bacchetti S. Telomere shortening associated with chromosome instability is arrested in immortal cells which express telomerase activity. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1921–1929. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counter C. M., Hirte H. W., Bacchetti S., Harley C. B. Telomerase activity in human ovarian carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):2900–2904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.2900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90576-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W. Mammalian telomere dynamics: healing, fragmentation shortening and stabilization. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Apr;4(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B. Telomere loss: mitotic clock or genetic time bomb? Mutat Res. 1991 Mar-Nov;256(2-6):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(91)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiyama E., Yokoyama T., Tatsumoto N., Hiyama K., Imamura Y., Murakami Y., Kodama T., Piatyszek M. A., Shay J. W., Matsuura Y. Telomerase activity in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 1995 Aug 1;55(15):3258–3262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiyama K., Hirai Y., Kyoizumi S., Akiyama M., Hiyama E., Piatyszek M. A., Shay J. W., Ishioka S., Yamakido M. Activation of telomerase in human lymphocytes and hematopoietic progenitor cells. J Immunol. 1995 Oct 15;155(8):3711–3715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiyama K., Hiyama E., Ishioka S., Yamakido M., Inai K., Gazdar A. F., Piatyszek M. A., Shay J. W. Telomerase activity in small-cell and non-small-cell lung cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Jun 21;87(12):895–902. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.12.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härle-Bachor C., Boukamp P. Telomerase activity in the regenerative basal layer of the epidermis inhuman skin and in immortal and carcinoma-derived skin keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jun 25;93(13):6476–6481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.13.6476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim N. W., Piatyszek M. A., Prowse K. R., Harley C. B., West M. D., Ho P. L., Coviello G. M., Wright W. E., Weinrich S. L., Shay J. W. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):2011–2015. doi: 10.1126/science.7605428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. The human telomere terminal transferase enzyme is a ribonucleoprotein that synthesizes TTAGGG repeats. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez R. D., Wright W. E., Shay J. W., Taylor R. S. Telomerase activity concentrates in the mitotically active segments of human hair follicles. J Invest Dermatol. 1997 Jan;108(1):113–117. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12285654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino T., Yoshida K., Bolodeoku J., Tahara H., Buley I., Manek S., Wells C., Goodison S., Ide T., Suzuki T. Telomerase activity in human breast cancer and benign breast lesions: diagnostic applications in clinical specimens, including fine needle aspirates. Int J Cancer. 1996 Aug 22;69(4):301–306. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19960822)69:4<301::AID-IJC11>3.0.CO;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara H., Kuniyasu H., Yokozaki H., Yasui W., Shay J. W., Ide T., Tahara E. Telomerase activity in preneoplastic and neoplastic gastric and colorectal lesions. Clin Cancer Res. 1995 Nov;1(11):1245–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. S., Ramirez R. D., Ogoshi M., Chaffins M., Piatyszek M. A., Shay J. W. Detection of telomerase activity in malignant and nonmalignant skin conditions. J Invest Dermatol. 1996 Apr;106(4):759–765. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12345811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng N. P., Levine B. L., June C. H., Hodes R. J. Regulated expression of telomerase activity in human T lymphocyte development and activation. J Exp Med. 1996 Jun 1;183(6):2471–2479. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Shay J. W., Piatyszek M. A. Modifications of a telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP) result in increased reliability, linearity and sensitivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Sep 25;23(18):3794–3795. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.18.3794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Sugino T., Goodison S., Warren B. F., Nolan D., Wadsworth S., Mortensen N. J., Toge T., Tahara E., Tarin D. Detection of telomerase activity in exfoliated cancer cells in colonic luminal washings and its related clinical implications. Br J Cancer. 1997;75(4):548–553. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1997.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Sugino T., Tahara H., Woodman A., Bolodeoku J., Nargund V., Fellows G., Goodison S., Tahara E., Tarin D. Telomerase activity in bladder carcinoma and its implication for noninvasive diagnosis by detection of exfoliated cancer cells in urine. Cancer. 1997 Jan 15;79(2):362–369. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0142(19970115)79:2<362::aid-cncr20>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]