Abstract
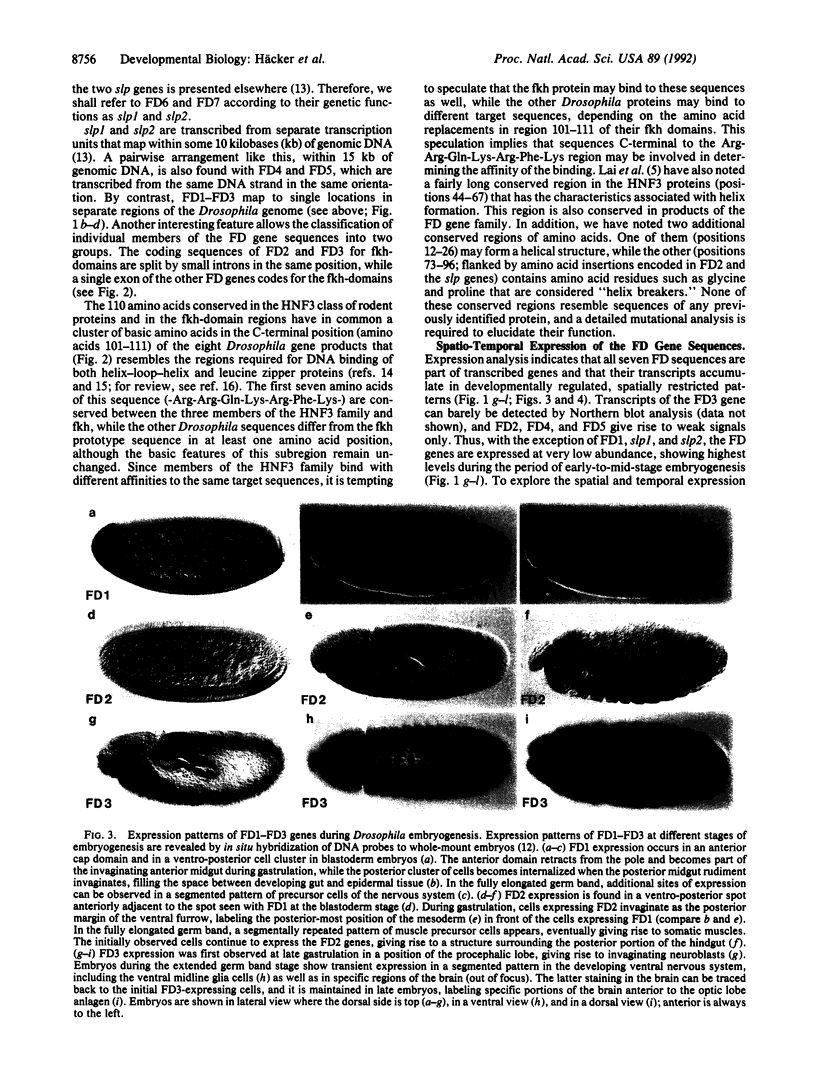
We have isolated seven Drosophila genes by means of low-stringency hybridization to a DNA probe containing the coding sequence for the protein domain shared by the rodent hepatocyte-enriched nuclear transcription factor HNF3A (alpha) and the product of the Drosophila region-specific homeotic gene fork head (fkh). The previously unreported genes encode a 110-amino acid conserved sequence, which we call the fork head (fkh) domain. Two of these fkh-domain-encoding genes ("FD genes") map to the sloppy paired locus (slp), which exerts segmentation gene function. The expression patterns of the other FD genes suggest that their protein products are likely to be involved in gut formation, mesoderm specification, and some specific aspects of neural development. The FD gene products presumably represent a family of transcription factors that, like the previously identified DNA-binding proteins, contribute to early developmental decisions in cell fates during embryogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumgartner S., Bopp D., Burri M., Noll M. Structure of two genes at the gooseberry locus related to the paired gene and their spatial expression during Drosophila embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1247–1267. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billin A. N., Cockerill K. A., Poole S. J. Isolation of a family of Drosophila POU domain genes expressed in early development. Mech Dev. 1991 Jun;34(2-3):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman K. G., Poole S. J., Weir M. P., Soeller W. C., Kornberg T. The invected gene of Drosophila: sequence analysis and expression studies reveal a close kinship to the engrailed gene. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):19–28. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côté S., Preiss A., Haller J., Schuh R., Kienlin A., Seifert E., Jäckle H. The gooseberry-zipper region of Drosophila: five genes encode different spatially restricted transcripts in the embryo. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2793–2801. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02575.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J., Hiromi Y. Homeotic genes and the homeobox. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:147–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossniklaus U., Pearson R. K., Gehring W. J. The Drosophila sloppy paired locus encodes two proteins involved in segmentation that show homology to mammalian transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):1030–1051. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Rosenfeld M. G. Mechanisms of complex transcriptional regulation: implications for brain development. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):183–196. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90257-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Smith E., Litvin O., Costa R. H., Darnell J. E., Jr HNF-3A, a hepatocyte-enriched transcription factor of novel structure is regulated transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1427–1436. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Tao W. F., Chen W. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):416–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A., Sakonju S. Characterization of two Drosophila POU domain genes, related to oct-1 and oct-2, and the regulation of their expression patterns. Mech Dev. 1991 Dec;36(1-2):87–102. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90075-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlodzik M., Fjose A., Gehring W. J. Molecular structure and spatial expression of a homeobox gene from the labial region of the Antennapedia-complex. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2569–2578. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C., Doyle H., Hoey T., Levine M. Molecular characterization of the zerknüllt region of the Antennapedia gene complex in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1268–1279. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh R., Aicher W., Gaul U., Côté S., Preiss A., Maier D., Seifert E., Nauber U., Schröder C., Kemler R. A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Krüppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90817-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jäckle H. The fork head domain: a novel DNA binding motif of eukaryotic transcription factors? Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):455–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90439-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jürgens G., Küttner F., Seifert E., Jäckle H. The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):645–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]