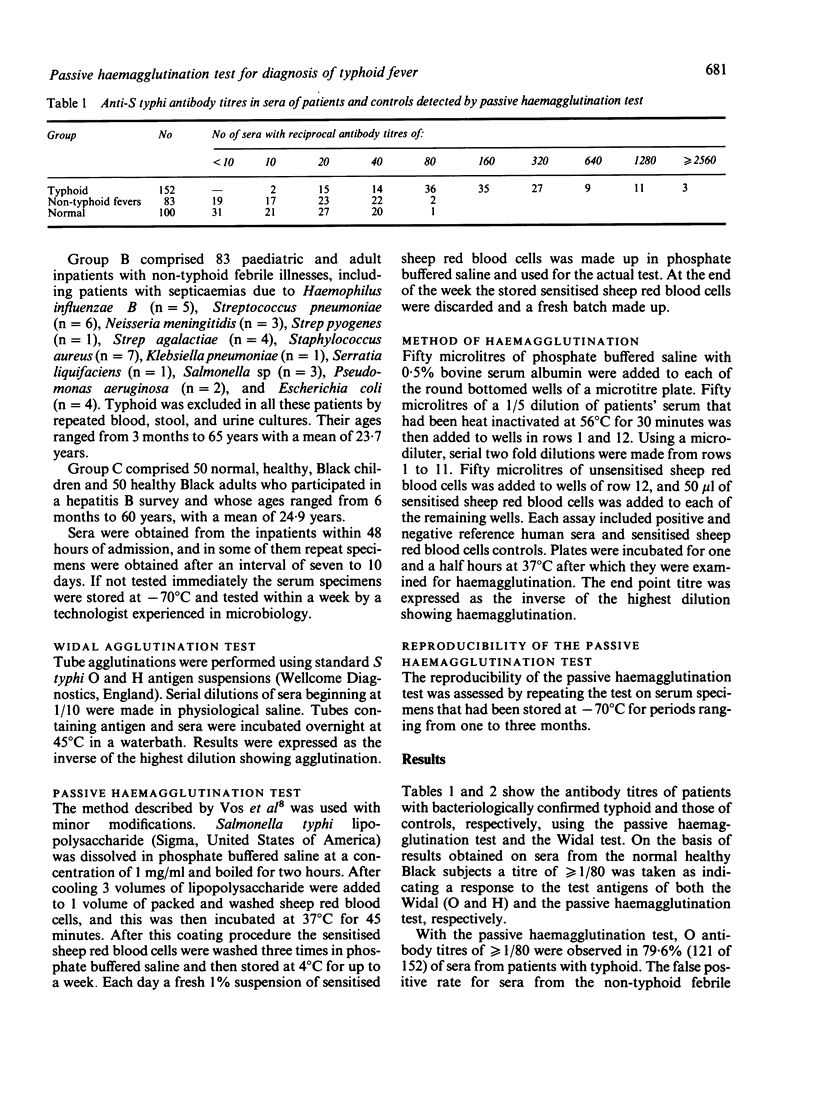
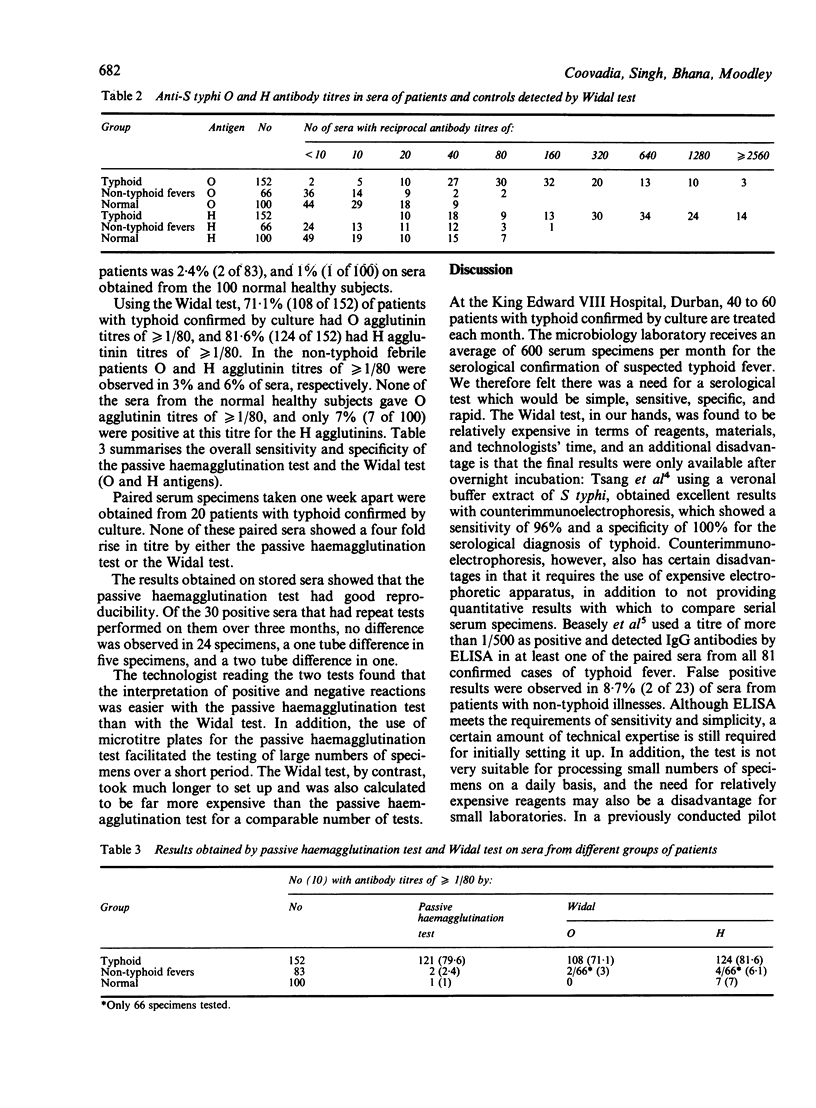
Abstract
A passive haemagglutination test, using sheep red blood cells sensitised with Salmonella typhi lipopolysaccharide, was compared with the Widal test for the serological diagnosis of typhoid fever in an endemic area. The results obtained on sera from 152 patients with bacteriologically confirmed typhoid and 183 patients who did not have typhoid were analysed in terms of sensitivity, specificity, simplicity, and rapidity of the respective tests. The passive haemagglutination test was found to be more sensitive (80%) than the S typhi O antigen (71%) but marginally less sensitive than the H antigen (82%) of the Widal test. The false positive rate on control sera was 1.2% and 6.6%, respectively, for the Widal O and H antigens, and 1.6% for the passive haemagglutination test. Our findings indicate that the passive haemagglutination test is comparable with the Widal test for the serological diagnosis of typhoid fever in endemic areas, but is more simple, rapid, and economic. The passive haemagglutination test may be a useful alternative to the Widal test for the serological diagnosis of typhoid fever in busy microbiology laboratories in areas in which the disease is endemic.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beasley W. J., Joseph S. W., Weiss E. Improved serodiagnosis of Salmonella enteric fevers by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):106–114. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.106-114.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie J. Antibodies and the Aberdeen typhoid outbreak of 1964. I. The Widal reaction. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Oct;79(2):161–180. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400052979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Grados O., Gilman R. H., Woodward W. E., Solis-Plaza R., Waldman W. Diagnostic value of the Widal test in areas endemic for typhoid fever. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Jul;27(4):795–800. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang T., Puthucheary S. D. Significance and value of the Widal test in the diagnosis of typhoid fever in an endemic area. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Apr;36(4):471–475. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.4.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockhill R. C., Rumans L. W., Lesmana M., Dennis D. T. Detection of Salmonella typhi D, Vi, and d antigens, by slide coagglutination, in urine from patients with typhoid fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):213–216. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.213-216.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder S. A. Interpretation of serologic tests for typhoid fever. JAMA. 1968 Oct 21;206(4):839–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senewiratne B., Senewiratne K. Reassessment of the Widal test in the diagnosis of typhoid. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):233–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehabi A. A. The value of a single Widal test in the diagnosis of acute typhoid fever. Trop Geogr Med. 1981 Jun;33(2):113–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivadasan K., Kurien B., John T. J. Rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever by antigen detection. Lancet. 1984 Jan 21;1(8369):134–135. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville P. C., Lewis M., Koornhof H. J., Alberts M., Alberts H. W., Raymond R. The Widal test in the diagnosis of typhoid fever in the transvaal. S Afr Med J. 1981 Jun 6;59(24):851–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang R. S., Chau P. Y. Serological diagnosis of typhoid fever by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 May 9;282(6275):1505–1507. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6275.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J. G., Buys J., Hanstede J. G., Hagenaars A. M. Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and passive hemagglutination method for quantification of antibodies to lipopolysaccharide and tetanus toxoid in rats. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):798–803. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.798-803.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicks A. C., Cruickshank J. G., Musewe N. Observations on the diagnosis of typhoid fever in an endemic area. S Afr Med J. 1974 Jul 6;48(32):1368–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



