Abstract
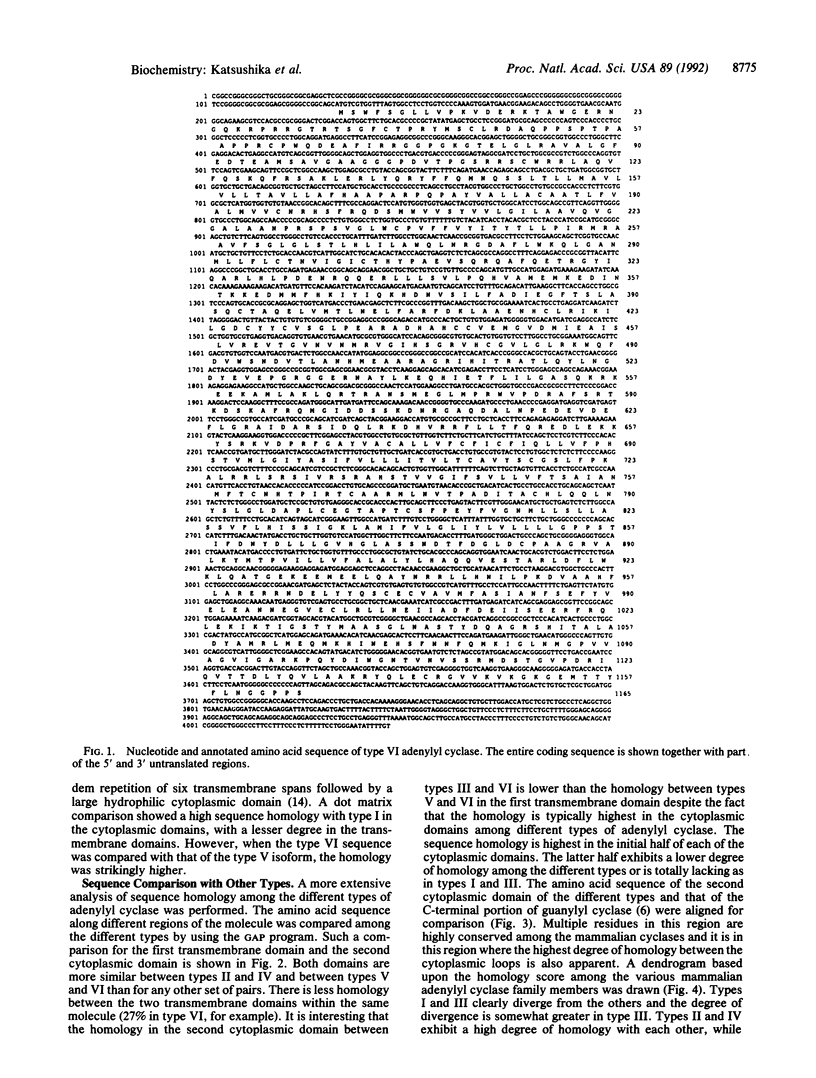
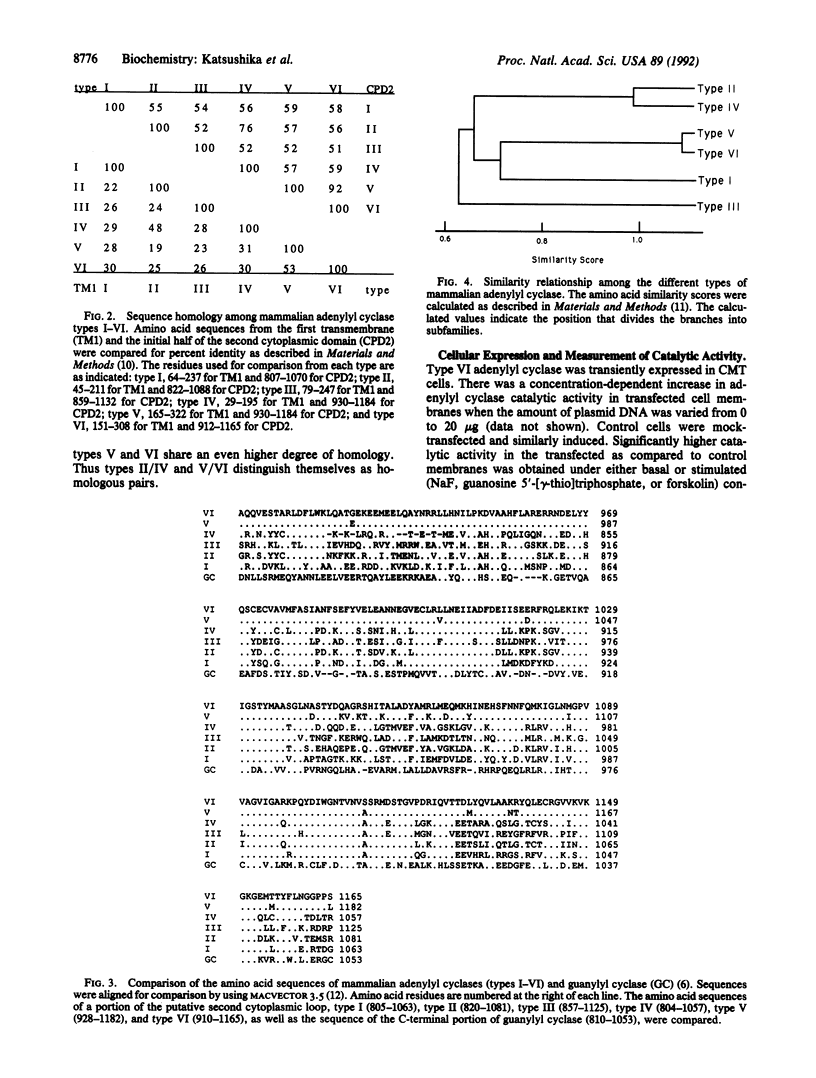
A sixth member of the mammalian adenylyl cyclase family has been isolated from a canine cardiac cDNA library. This isoform is more highly homologous to type V than to the other adenylyl cyclase types; sequence similarity is apparent even in the transmembrane regions where the greatest divergence among the types exists. Type VI mRNA expression is most abundant in heart and brain; however, unlike type V, a low level of expression is also observed in a variety of other tissues examined. Type VI adenylyl cyclase can be stimulated by NaF, guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate, and forskolin but not by Ca2+/calmodulin, whereas it is inhibited by adenosine and its analogues. Comparison of both their structural and biochemical properties suggests that types V and VI constitute a distinct subgroup of the mammalian adenylyl cyclase family.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakalyar H. A., Reed R. R. Identification of a specialized adenylyl cyclase that may mediate odorant detection. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1403–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.2255909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Beiderman B., Steinberg F., Brothers V. M. Three adenylate cyclase phenotypes in S49 lymphoma cells produced by mutations of one gene. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;22(1):204–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Garbers D. L., Chang M. S., Lowe D. G., Chin H. M., Goeddel D. V., Schulz S. A membrane form of guanylate cyclase is an atrial natriuretic peptide receptor. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):78–83. doi: 10.1038/338078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein P. G., Schrader K. A., Bakalyar H. A., Tang W. J., Krupinski J., Gilman A. G., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning and characterization of a Ca2+/calmodulin-insensitive adenylyl cyclase from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10173–10177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman M. D., Copelas L., Gwathmey J. K., Phillips P., Warren S. E., Schoen F. J., Grossman W., Morgan J. P. Deficient production of cyclic AMP: pharmacologic evidence of an important cause of contractile dysfunction in patients with end-stage heart failure. Circulation. 1987 Feb;75(2):331–339. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.2.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao B. N., Gilman A. G. Cloning and expression of a widely distributed (type IV) adenylyl cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10178–10182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R. D., Gluzman Y. New host cell system for regulated simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3231–3240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Croop J., Housman D. Mammalian multidrug resistance gene: complete cDNA sequence indicates strong homology to bacterial transport proteins. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90594-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homcy C. J., Vatner S. F., Vatner D. E. Beta-adrenergic receptor regulation in the heart in pathophysiologic states: abnormal adrenergic responsiveness in cardiac disease. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:137–159. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa Y., Bianchi C., Nadal-Ginard B., Homcy C. J. Alternative promoter and 5' exon generate a novel Gs alpha mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8458–8462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa Y., Katsushika S., Chen L., Halnon N. J., Kawabe J., Homcy C. J. Isolation and characterization of a novel cardiac adenylylcyclase cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13553–13557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Broek D., Wigler M. DNA sequence and characterization of the S. cerevisiae gene encoding adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupinski J., Coussen F., Bakalyar H. A., Tang W. J., Feinstein P. G., Orth K., Slaughter C., Reed R. R., Gilman A. G. Adenylyl cyclase amino acid sequence: possible channel- or transporter-like structure. Science. 1989 Jun 30;244(4912):1558–1564. doi: 10.1126/science.2472670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J. M. Interactive molecular biology computing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1813–1820. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Iannuzzi M. C., Kerem B., Drumm M. L., Melmer G., Dean M., Rozmahel R., Cole J. L., Kennedy D., Hidaka N. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Krupinski J., Gilman A. G. Expression and characterization of calmodulin-activated (type I) adenylylcyclase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8595–8603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



