Abstract
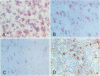
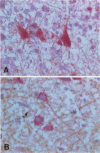
AIMS: To determine the distribution and cellular origin of endogenous tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) in the cellular components of human gliomas. METHODS: Frozen sections of 26 gliomas (four astrocytomas (As); two oligoastrocytomas (OA); one ansplastic astrocytoma (AA); one anaplastic oligoastrocytoma (AOA); 18 glioblastomas (GB)) were examined immunohistochemically using antihuman TNF alpha and anti-Leu-M5 (CD11c) antibodies. Additional studies with double immunohistocchemical procedures were performed with anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein and anti-neurofilament antibodies. RESULTS: Eighty per cent of the AA, AOA, and GB (16 of 20) had a positive reaction for TNF alpha, but only 17% of As and OA (one of six) were positive. Positive cells were seen in both the tumour tissue and adjacent brain tissues. TNF alpha protein was detected not only in the tumour cells but also in the endothelium of tumour vessels as well as reactive astrocytes and neurons. CONCLUSIONS: Endogenous TNF alpha is present in cells of various origins in glial tumours including tumour vessels; however, the role of TNF alpha may be different in different types of cells or altered microenvironment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste E. N., Sparacio S. M., Bethea J. R. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha enhances interferon-gamma-mediated class II antigen expression on astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Dec;25(2-3):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90139-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin (tumor necrosis factor): a macrophage hormone governing cellular metabolism and inflammatory response. Endocr Rev. 1988 Feb;9(1):57–66. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett J., Gerlach H., Nawroth P., Steinberg S., Godman G., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin increases permeability of endothelial cell monolayers by a mechanism involving regulatory G proteins. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1977–1991. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockhaus M., Schoenfeld H. J., Schlaeger E. J., Hunziker W., Lesslauer W., Loetscher H. Identification of two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3127–3131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung I. Y., Benveniste E. N. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by astrocytes. Induction by lipopolysaccharide, IFN-gamma, and IL-1 beta. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2999–3007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Kristensen F., Dubs R., Gemsa D., Weber E. Production of prostaglandin E and an interleukin-1 like factor by cultured astrocytes and C6 glioma cells. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei K., Bodmer S., Schwerdel C., Fontana A. Astrocytes of the brain synthesize interleukin 3-like factors. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4044–4047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Baker T. J., Shih L. C., Lachman L. B. Interleukin 1 of the central nervous system is produced by ameboid microglia. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):594–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Baemayr J., Weil M., Merrill J. E. Lymphokines and immunoregulatory molecules in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Mar;58(3):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90124-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R. Cytokine interactions in the central nervous system. Reg Immunol. 1990;3(5):268–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Johnson K., Merrill J. E. Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):607–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaka T., Yoshimine T., Maruno M., Hayakawa T. Morphological effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on the blood vessels in rat experimental brain tumors. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1996 Jul;36(7):423–427. doi: 10.2176/nmc.36.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleihues P., Burger P. C., Scheithauer B. W. The new WHO classification of brain tumours. Brain Pathol. 1993 Jul;3(3):255–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1993.tb00752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman L. B., Brown D. C., Dinarello C. A. Growth-promoting effect of recombinant interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor for a human astrocytoma cell line. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2913–2916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi E., Suzumura A., Murasko D. M., Murray E. M., Silberberg D. H., Weiss S. R. Tumor necrosis factor induces expression of MHC class I antigens on mouse astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Jun;18(3):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90102-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruno M., Yoshimine T., Isaka T., Ghulam Muhammad A., Nishioka K., Hayakawa T. Cellular targets of exogenous tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) in human gliomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1996;138(12):1437–1441. doi: 10.1007/BF01411123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Stern D. M. Modulation of endothelial cell hemostatic properties by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):740–745. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. S., Shirazi Y., Drysdale B. E., Lieberman A., Shin H. S., Shin M. L. Production of cytotoxic factor for oligodendrocytes by stimulated astrocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2593–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roessler K., Suchanek G., Breitschopf H., Kitz K., Matula C., Lassmann H., Koos W. T. Detection of tumor necrosis factor-alpha protein and messenger RNA in human glial brain tumors: comparison of immunohistochemistry with in situ hybridization using molecular probes. J Neurosurg. 1995 Aug;83(2):291–297. doi: 10.3171/jns.1995.83.2.0291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada M., Kondo N., Suzumura A., Marunouchi T. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by microglia and astrocytes in culture. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 10;491(2):394–397. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmaj K. W., Farooq M., Norton W. T., Raine C. S., Brosnan C. F. Proliferation of astrocytes in vitro in response to cytokines. A primary role for tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief M. K., McLean B., Thompson E. J. Elevated serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1993 Jun;33(6):591–596. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedeschi B., Barrett J. N., Keane R. W. Astrocytes produce interferon that enhances the expression of H-2 antigens on a subpopulation of brain cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2244–2253. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meir E., Sawamura Y., Diserens A. C., Hamou M. F., de Tribolet N. Human glioblastoma cells release interleukin 6 in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 15;50(20):6683–6688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D., Dorovini-Zis K. Upregulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression in primary cultures of human brain microvessel endothelial cells by cytokines and lipopolysaccharide. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Jul;39(1-2):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90170-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]