Abstract
AIMS: To determine whether inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is associated with pathogenic or enteroadherent Escherichia coli. METHODS: A least two stool specimens and one rectal biopsy were taken from 30 patients with IBD and from 20 controls. A large number of E coli-like colonies cultured from each stool sample and biopsy was tested, using DNA probes, for the presence of genes encoding shiga-like toxins, invasiveness, attachment-effacement and the ability to adhere to HEp-2 cells. Similarity among isolates from stool samples and rectal biopsies was determined by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis. RESULTS: Enterohaemorrhagic and enteroinvasive E coli were not found in samples from either patients or controls. No significant difference in the detection rate of enteroadherent E coli between patients and controls was found. Rectal biopsies from 11 of 28 patients with IBD and 4 of 18 controls contained E coli, which hybridised with probes for detection of genes encoding diffuse adherence to HEp-2 cells, or encoding P-pili (p = 0.2). Enteroadherent E coli isolated from two or three stool specimens from the same patient or control appeared to be identical by RAPD analysis, and are considered to be residents in the colon. Probe positive isolates obtained from stool specimens and corresponding rectal biopsies were always identical on RAPD analysis. CONCLUSIONS: E coli strains possessing adherence factors reside in the large intestine and adhere to the rectal mucosa, irrespective of the presence of colitis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlerberth I., Hanson L. A., Svanborg C., Svennerholm A. M., Nordgren S., Wold A. E. Adhesins of Escherichia coli associated with extra-intestinal pathogenicity confer binding to colonic epithelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1995 Jun;18(6):373–385. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1995.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agace W., Hedges S., Andersson U., Andersson J., Ceska M., Svanborg C. Selective cytokine production by epithelial cells following exposure to Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):602–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.602-609.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry B., Maurelli A. T., Clerc P., Sadoff J. C., Sansonetti P. J. Localization of plasmid loci necessary for the entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells, and characterization of one locus encoding four immunogenic polypeptides. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3403–3413. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry B., Savarino S. J., Vial P., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M. A sensitive and specific DNA probe to identify enteroaggregative Escherichia coli, a recently discovered diarrheal pathogen. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1249–1251. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan M. K., Raj P., Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Bhandari N., Srivastava R., Kumar R., Sazawal S. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli associated with persistent diarrhea in a cohort of rural children in India. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jun;159(6):1061–1064. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.6.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilge S. S., Clausen C. R., Lau W., Moseley S. L. Molecular characterization of a fimbrial adhesin, F1845, mediating diffuse adherence of diarrhea-associated Escherichia coli to HEp-2 cells. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4281–4289. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4281-4289.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook M. G., Smith H. R., Bannister B. A., McConnell M., Chart H., Scotland S. M., Sawyer A., Smith M., Rowe B. Prospective study of verocytotoxin-producing, enteroaggregative and diffusely adherent Escherichia coli in different diarrhoeal states. Epidemiol Infect. 1994 Feb;112(1):63–67. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800057423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. A., Axon A. T. Adhesive Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease and infective diarrhoea. BMJ. 1988 Jul 9;297(6641):102–104. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6641.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. A., Axon A. T. Hydrophobic adhesin of E coli in ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1988 Jan;29(1):41–43. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cravioto A., Tello A., Navarro A., Ruiz J., Villafán H., Uribe F., Eslava C. Association of Escherichia coli HEp-2 adherence patterns with type and duration of diarrhoea. Lancet. 1991 Feb 2;337(8736):262–264. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90868-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):3953–3961. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.3953-3961.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Sartor R. B., Tennyson G. S., Riddell R. H. Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1995 Oct;109(4):1344–1367. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90599-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. I., Labigne A., Le Bouguenec C. Nucleotide sequence of the afimbrial-adhesin-encoding afa-3 gene cluster and its translocation via flanking IS1 insertion sequences. J Bacteriol. 1994 Dec;176(24):7601–7613. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.24.7601-7613.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaffer M. H., Holdsworth C. D., Duerden B. I. Virulence properties of Escherichia coli strains isolated from patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1992 May;33(5):646–650. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.5.646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley M. G., Hudson M. J., Swarbrick E. T., Gent A. E., Hellier M. D., Grace R. H. Adhesive and hydrophobic properties of Escherichia coli from the rectal mucosa of patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1993 Jan;34(1):63–67. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jallat C., Livrelli V., Darfeuille-Michaud A., Rich C., Joly B. Escherichia coli strains involved in diarrhea in France: high prevalence and heterogeneity of diffusely adhering strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):2031–2037. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.2031-2037.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Yu J., Tall B. D., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogfelt K. A. Bacterial adhesion: genetics, biogenesis, and role in pathogenesis of fimbrial adhesins of Escherichia coli. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jul-Aug;13(4):721–735. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.4.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouguenec C., Archambaud M., Labigne A. Rapid and specific detection of the pap, afa, and sfa adhesin-encoding operons in uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1189–1193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1189-1193.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungh A., Eriksson M., Eriksson O., Henter J. I., Wadström T. Shiga-like toxin production and connective tissue protein binding of Escherichia coli isolated from a patient with ulcerative colitis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1988;20(4):443–446. doi: 10.3109/00365548809032484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques L. R., Abe C. M., Griffin P. M., Gomes T. A. Association between alpha-hemolysin production and HeLa cell-detaching activity in fecal isolates of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Oct;33(10):2707–2709. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.10.2707-2709.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick B. A., Colgan S. P., Delp-Archer C., Miller S. I., Madara J. L. Salmonella typhimurium attachment to human intestinal epithelial monolayers: transcellular signalling to subepithelial neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):895–907. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki B., Labigne A., Moseley S., Hull R., Hull S., Moulds J. The Dr hemagglutinin, afimbrial adhesins AFA-I and AFA-III, and F1845 fimbriae of uropathogenic and diarrhea-associated Escherichia coli belong to a family of hemagglutinins with Dr receptor recognition. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):279–281. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.279-281.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki B., Truong L., Moulds J., Hull R. Presence of the Dr receptor in normal human tissues and its possible role in the pathogenesis of ascending urinary tract infection. Am J Pathol. 1988 Oct;133(1):1–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olusanya O., Steinrück H., Aleljung P., Ascencio F., Curman B., Järnerot G., Wadström T., Ljungh A. Surface properties, connective tissue protein binding and Shiga-like toxin production of Escherichia coli isolated from patients with ulcerative colitis. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1992 Jan;276(2):254–263. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savarino S. J. Diarrhoeal disease: current concepts and future challenges. Enteroadherent Escherichia coli: a heterogeneous group of E. coli implicated as diarrhoeal pathogens. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1993 Dec;87 (Suppl 3):49–53. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(93)90539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotland S. M., Smith H. R., Said B., Willshaw G. A., Cheasty T., Rowe B. Identification of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated in Britain as enteroaggregative or as members of a subclass of attaching-and-effacing E. coli not hybridising with the EPEC adherence-factor probe. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Nov;35(5):278–283. doi: 10.1099/00222615-35-5-278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen W., Steinrück H., Ljungh A. Expression of binding of plasminogen, thrombospondin, vitronectin, and fibrinogen, and adhesive properties by Escherichia coli strains isolated from patients with colonic diseases. Gut. 1995 Mar;36(3):401–406. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.3.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Kaper J. B., Mack D. R. Intestinal mucin inhibits adhesion of human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HEp-2 cells. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1995 Oct;21(3):269–276. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199510000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullus K., Kühn I., Orskov I., Orskov F., Möllby R. The importance of P and type 1 fimbriae for the persistence of Escherichia coli in the human gut. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Jun;108(3):415–421. doi: 10.1017/s095026880004992x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
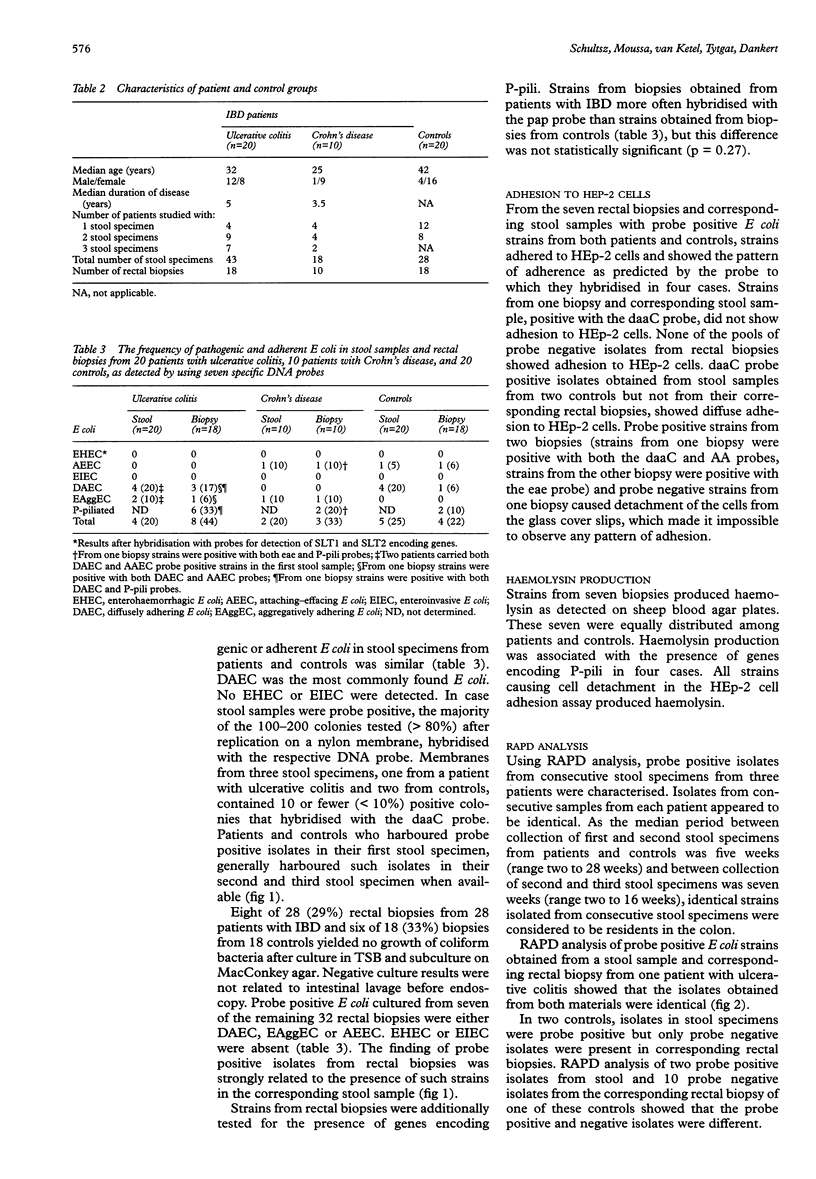
- Versalovic J., Koeuth T., Lupski J. R. Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6823–6831. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerlund B., Korhonen T. K. Bacterial proteins binding to the mammalian extracellular matrix. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(4):687–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., Scotland S. M., Field A. M., Rowe B. Heterogeneity of Escherichia coli phages encoding Vero cytotoxins: comparison of cloned sequences determining VT1 and VT2 and development of specific gene probes. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 May;133(5):1309–1317. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-5-1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold A. E., Caugant D. A., Lidin-Janson G., de Man P., Svanborg C. Resident colonic Escherichia coli strains frequently display uropathogenic characteristics. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;165(1):46–52. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold A. E., Thorssén M., Hull S., Edén C. S. Attachment of Escherichia coli via mannose- or Gal alpha 1----4Gal beta-containing receptors to human colonic epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2531–2537. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2531-2537.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wulffen H., Rüssmann H., Karch H., Meyer T., Bitzan M., Kohrt T. C., Aleksic S. Verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O2:H5 isolated from patients with ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1989 Jun 24;1(8652):1449–1450. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]