Abstract
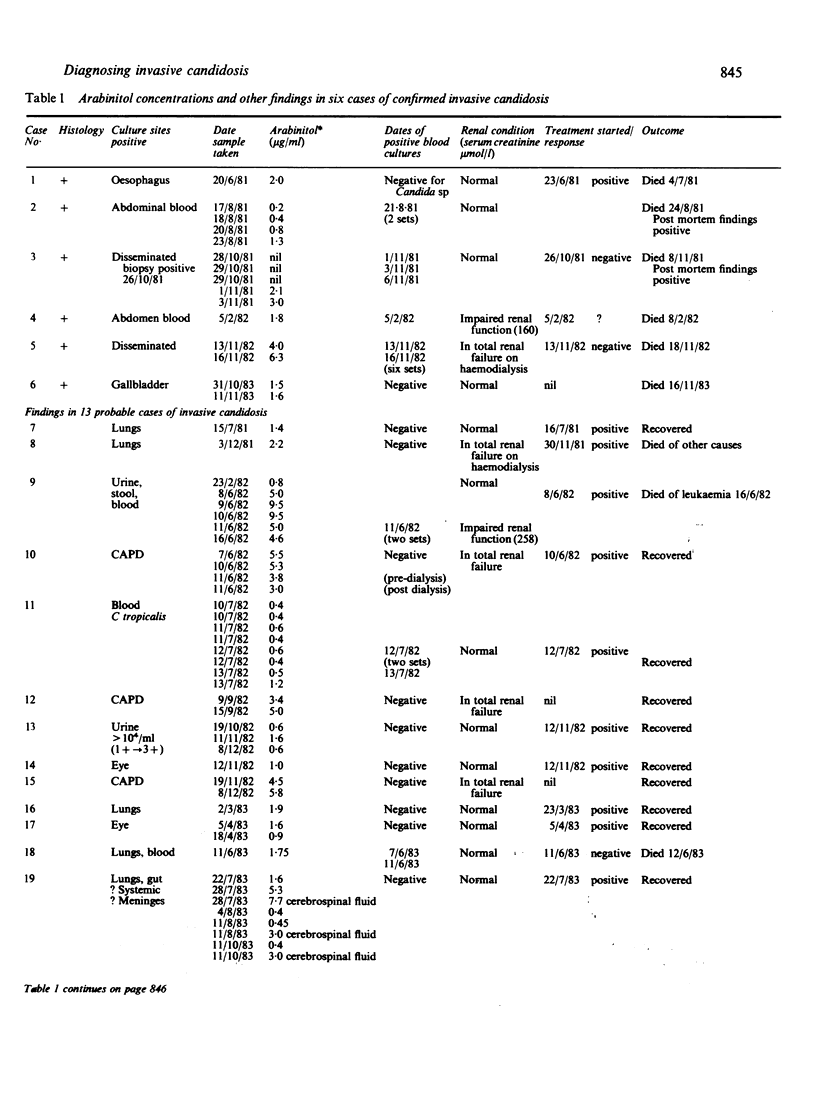
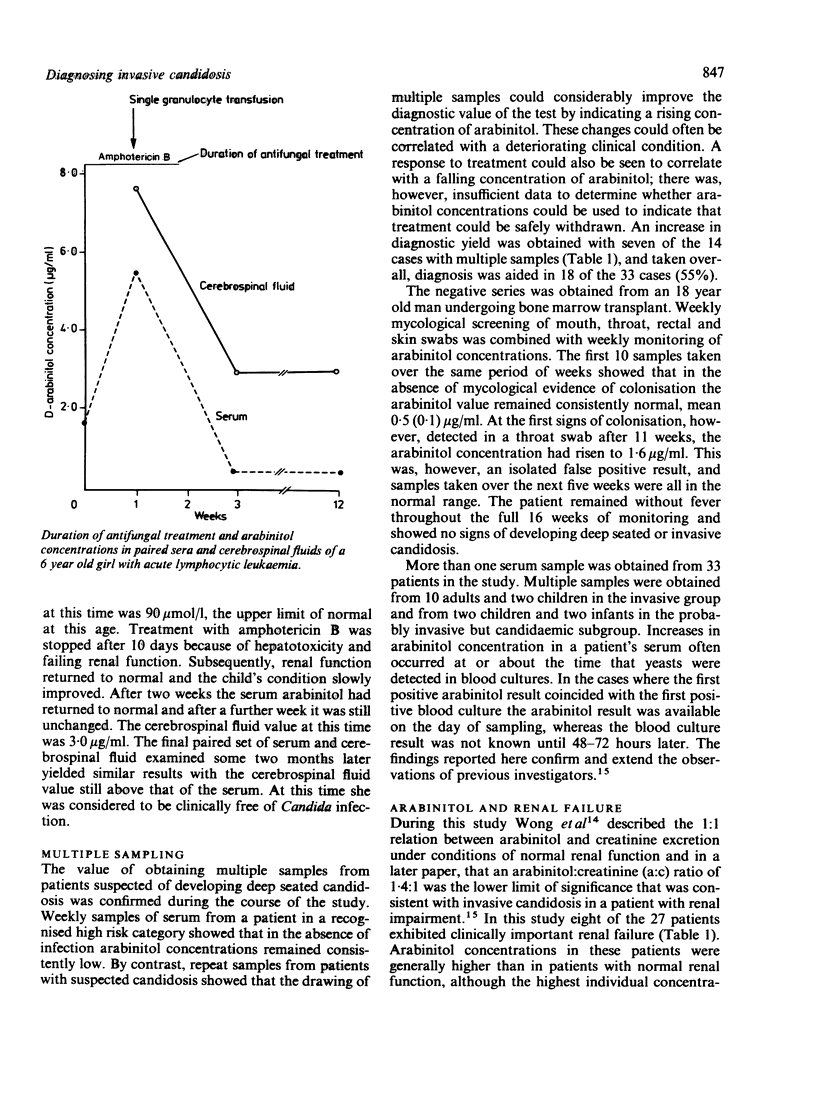
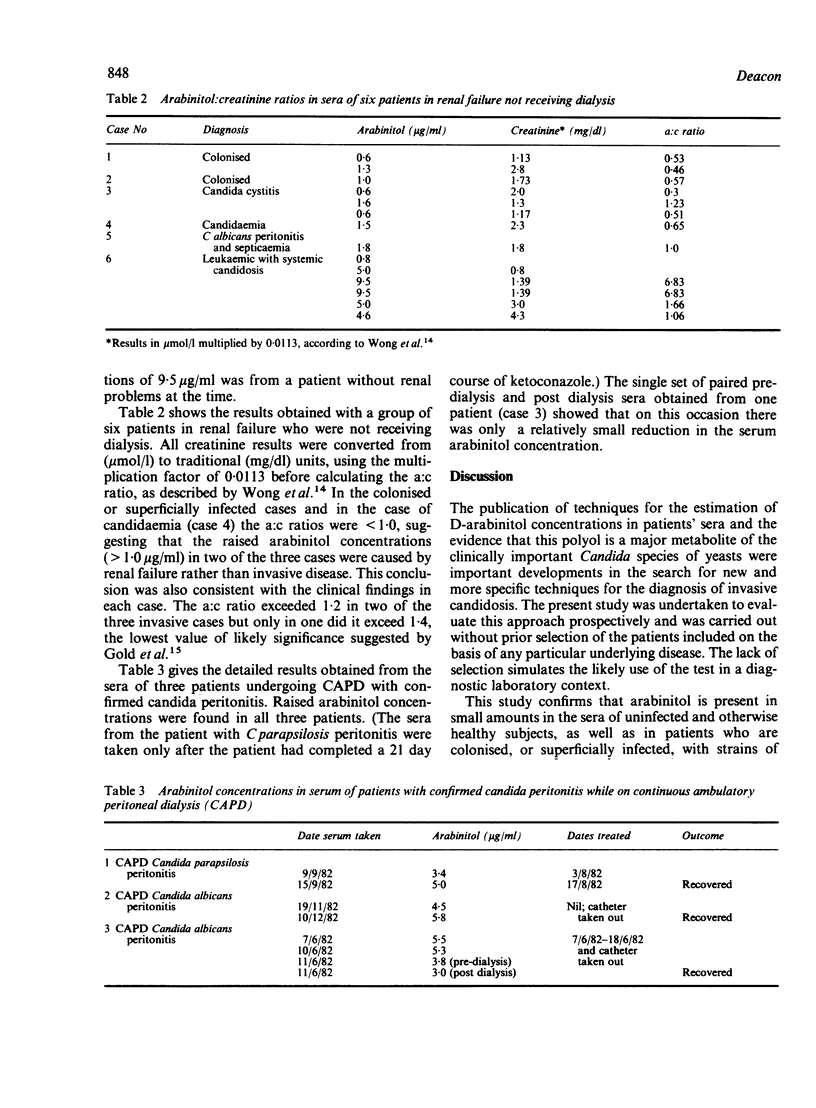
Arabinitol concentrations were determined in 157 serum samples from 95 patients with suspected invasive candidosis and in 10 serum samples from healthy laboratory workers. Fifty eight of the 95 patients, subsequently diagnosed as not having invasive candidosis had concentrations of arabinitol below 1.2 micrograms/ml (mean 0.59 (SD) 0.26). Sera from the healthy laboratory workers gave similar results (mean 0.55 (0.05]. Concentrations above the normal range were found in 18 of the 19 cases of confirmed or probable invasive candidosis and in seven of eight patients with infected intravenous lines or cannulas and clinical evidence of systemic infection. Raised concentrations were also seen in 10 other patients, including nine with renal failure who did not have invasive infections. Multiple serum samples obtained from 33 patients showed that sequential estimations were of value for diagnosing a developing infection. Despite some difficulties of interpretation the technique is rapid and specific and is suitable for use in the diagnostic laboratory of a larger general hospital.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer A. S., Blumenkrantz M. J., Montgomerie J. Z., Galpin J. E., Coburn J. W., Guze L. B. Candida peritonitis. Report of 22 cases and review of the English literature. Am J Med. 1976 Dec;61(6):832–840. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90407-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. E. Diagnosis and management of candidiasis in the immunosuppressed host. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(16):83–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard E. M., Christiansen K. J., Tsang S. F., Kiehn T. E., Armstrong D. Rate of arabinitol production by pathogenic yeast species. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):189–194. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.189-194.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb S. J., Parratt D. Determination of antibody levels to Candida albicans in healthy and hospitalised adults using a radioimmunoassay. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Dec;31(12):1161–1166. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.12.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Chmel H., Buse M. Serum levels of arabinitol in the detection of invasive candidiasis in animals and humans. J Infect Dis. 1981 May;143(5):677–683. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.5.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. O., Wilkinson I. D., Lea A. S., Price M. F. Latex agglutination test for detection of Candida antigen in patients with disseminated disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):122–128. doi: 10.1007/BF02001577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold J. W., Wong B., Bernard E. M., Kiehn T. E., Armstrong D. Serum arabinitol concentrations and arabinitol/creatinine ratios in invasive candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):504–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Russell E., Jr, Remington J. S. The compromised host and infection. II. Deep fungal infection. J Infect Dis. 1969 Aug;120(2):169–191. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karam G. H., Elliott A. M., Polt S., Cobbs C. G. Elevated serum D-arabinitol levels in patients with sarcoidosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):26–29. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.26-29.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn T. E., Bernard E. M., Gold J. W., Armstrong D. Candidiasis: detection by gas-liquid chromatography of D-arabinitol, a fungal metabolite, in human serum. Science. 1979 Nov 2;206(4418):577–580. doi: 10.1126/science.493963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostiala A. A., Kostiala I. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for IgM, IgG and IgA class antibodies against Candida albicans antigens: development and comparison with other methods. Sabouraudia. 1981 Jun;19(2):123–134. doi: 10.1080/00362178185380191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. G., Witwer M. W., Braude A. I., Davis C. E. Rapid identification of Candida albicans septicemia in man by gas-liquid chromatography. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1235–1240. doi: 10.1172/JCI107867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. D., Washington J. A., 2nd Detection of fungi in blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):309–310. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.309-310.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roboz J., Suzuki R., Holland J. F. Quantification of arabinitol in serum by selected ion monitoring as a diagnostic technique in invasive candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Oct;12(4):594–601. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.4.594-601.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOUSTER O., HARWELL S. O. The isolation of L-arabitol from pentosuric urine. J Biol Chem. 1958 Feb;230(2):1031–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. C., Bartlett A., Bidwell D. E., Richardson M. D., Voller A., White L. O. Diagnosis of invasive candidosis by enzyme immunoassay of serum antigen. Br Med J. 1977 May 7;1(6070):1183–1185. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6070.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells C. L., Sirany M. S., Blazevic D. J. Evaluation of serum arabinitol as a diagnostic test for candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):353–357. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.353-357.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B., Bernard E. M., Armstrong D., Roboz J., Suzuki R., Holland J. F. Evaluation of the aldononitrile peracetate method for measuring arabinitol in serum. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):478–479. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.478-479.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B., Bernard E. M., Gold J. W., Fong D., Armstrong D. The arabinitol appearance rate in laboratory animals and humans: estimation from the arabinitol/creatine ratio and relevance to the diagnosis of candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep;146(3):353–359. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.3.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B., Bernard E. M., Gold J. W., Fong D., Silber A., Armstrong D. Increased arabinitol levels in experimental candidiasis in rats: arabinitol appearance rates, arabinitol/creatinine ratios, and severity of infection. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep;146(3):346–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.3.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Repentigny L., Kuykendall R. J., Chandler F. W., Broderson J. R., Reiss E. Comparison of serum mannan, arabinitol, and mannose in experimental disseminated candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):804–812. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.804-812.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Repentigny L., Marr L. D., Keller J. W., Carter A. W., Kuykendall R. J., Kaufman L., Reiss E. Comparison of enzyme immunoassay and gas-liquid chromatography for the rapid diagnosis of invasive candidiasis in cancer patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):972–979. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.972-979.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Repentigny L., Reiss E. Current trends in immunodiagnosis of candidiasis and aspergillosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6(3):301–312. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


