Abstract
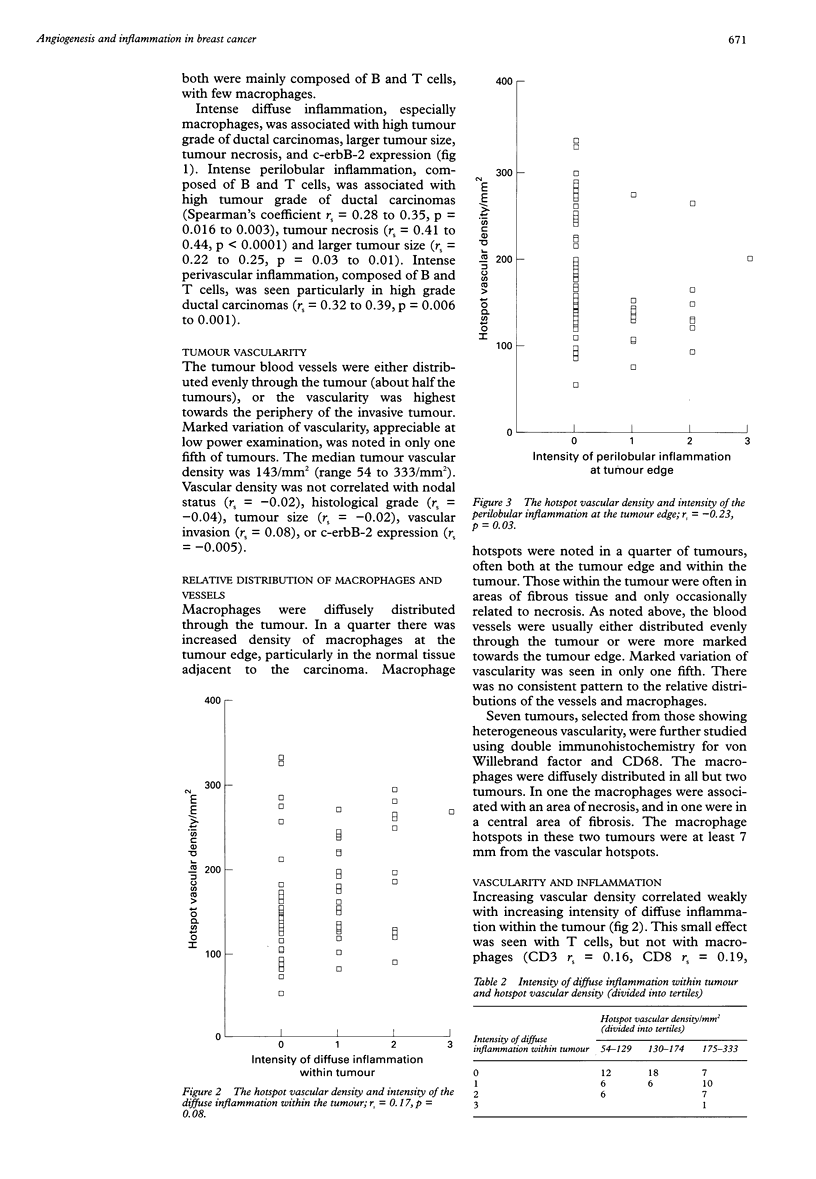
AIM: To investigate the relation between angiogenesis and inflammation in invasive carcinoma of the breast. METHODS: Sections from 75 invasive carcinomas of the breast were stained using immunohistochemistry for von Willebrand factor, CD3, CD8, CD45RO, CD45RA, CD20, CD68, and c-erbB-2. Tumour vascularity was assessed by counting vessels in the three most vascular areas, and calculating the average (x 400 magnification, field 0.168 mm2). Each pattern of inflammation was scored semiquantitatively. RESULTS: The main pattern of inflammation was a diffuse infiltrate of macrophages, and to a lesser extent T cells. Perivascular and perilobular clusters of B and T cells were noted at the edge of the carcinomas, but were less prominent than the diffuse inflammation. Diffuse inflammation, particularly macrophages, was associated with high tumour grade, tumour necrosis, large tumour size, and c-erbB-2 expression. Perivascular and perilobular inflammation also increased with tumour grade. Tumour vascularity increased slightly with intensity of diffuse inflammation (Spearman's rank correlation coefficient rs = 0.17, p = 0.08), and was inversely related to perilobular inflammation (rs = -0.23, p = 0.03). CONCLUSIONS: The correlations between inflammation and vascularity were weak in this study (r2 about 0.04) and thus there was no evidence of an important relation. Discrepancies between this and other studies may be resolved by studying expression of angiogenic cytokines and proteolytic enzymes by tumour infiltrating inflammatory cells, and their relation to tumour vascularity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaltomaa S., Lipponen P., Eskelinen M., Kosma V. M., Marin S., Alhava E., Syrjänen K. Lymphocyte infiltrates as a prognostic variable in female breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1992;28A(4-5):859–864. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(92)90134-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderson M. R., Hamlin I., Staunton M. D. The relative significance of prognostic factors in breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1971 Dec;25(4):646–656. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1971.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch C. M., Riley L. B., Bae Y. J., Salmeron M. A., Platsoucas C. D., von Eschenbach A., Itoh K. Patterns of human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in 120 human cancers. Arch Surg. 1990 Feb;125(2):200–205. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1990.01410140078012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan A. K., DesMarais C. L. Immunohistologic characterization of major histocompatibility antigens and inflammatory cellular infiltrate in human breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Sep;71(3):507–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston C. W., Ellis I. O. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 1991 Nov;19(5):403–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston C. W., Gresham G. A., Rao G. S., Zebro T., Haybittle J. L., Houghton J., Kearney G. The cancer research campaign (King's/Cambridge trial for early breast cancer: clinico-pathological aspects. Br J Cancer. 1982 May;45(5):655–669. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S. B., Westwood M., Moghaddam A., Comley M., Turley H., Whitehouse R. M., Bicknell R., Gatter K. C., Harris A. L. The angiogenic factor platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase is up-regulated in breast cancer epithelium and endothelium. Br J Cancer. 1996 Feb;73(3):275–280. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlinger H. G., Rieber P., Gokel J. M., Lohe K. J., Riethmüller G. Infiltrating mononuclear cells in human breast carcinoma: predominance of T4+ monocytic cells in the tumor stroma. Int J Cancer. 1985 Feb 15;35(2):199–205. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildenbrand R., Dilger I., Hörlin A., Stutte H. J. Urokinase and macrophages in tumour angiogenesis. Br J Cancer. 1995 Oct;72(4):818–823. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak E. R., Leek R., Klenk N., LeJeune S., Smith K., Stuart N., Greenall M., Stepniewska K., Harris A. L. Angiogenesis, assessed by platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule antibodies, as indicator of node metastases and survival in breast cancer. Lancet. 1992 Nov 7;340(8828):1120–1124. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93150-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. M., Davison R. S., Bliss E., McGee J. O. Macrophages in human breast disease: a quantitative immunohistochemical study. Br J Cancer. 1988 Feb;57(2):174–177. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Polverini P. J., Leibovich S. J. Induction of neovascularization by activated human monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 Feb;39(2):233–238. doi: 10.1002/jlb.39.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. H., Happerfield L. C., Bobrow L. G., Millis R. R. Angiogenesis and inflammation in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. J Pathol. 1997 Feb;181(2):200–206. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199702)181:2<200::AID-PATH726>3.0.CO;2-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. H., Happerfield L. C., Millis R. R., Bobrow L. G. Inflammatory infiltrate in invasive lobular and ductal carcinoma of the breast. Br J Cancer. 1996 Sep;74(5):796–801. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leek R. D., Lewis C. E., Whitehouse R., Greenall M., Clarke J., Harris A. L. Association of macrophage infiltration with angiogenesis and prognosis in invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1996 Oct 15;56(20):4625–4629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miescher S., Whiteside T. L., Carrel S., von Fliedner V. Functional properties of tumor-infiltrating and blood lymphocytes in patients with solid tumors: effects of tumor cells and their supernatants on proliferative responses of lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1899–1907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Laughlin S., Braverman M., Smith-Jefferies M., Buckley P. Macrophages (histiocytes) in various reactive and inflammatory conditions express different antigenic phenotypes. Hum Pathol. 1992 Dec;23(12):1410–1418. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90062-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parl F. F., Dupont W. D. A retrospective cohort study of Histologic risk factors in breast cancer patients. Cancer. 1982 Dec 1;50(11):2410–2416. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19821201)50:11<2410::aid-cncr2820501128>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilke F., Colnaghi M. I., Cascinelli N., Andreola S., Baldini M. T., Bufalino R., Della Porta G., Ménard S., Pierotti M. A., Testori A. Prognostic significance of HER-2/neu expression in breast cancer and its relationship to other prognostic factors. Int J Cancer. 1991 Aug 19;49(1):44–49. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910490109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roses D. F., Bell D. A., Flotte T. J., Taylor R., Ratech H., Dubin N. Pathologic predictors of recurrence in stage 1 (TINOMO) breast cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Dec;78(6):817–820. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/78.6.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunderkötter C., Steinbrink K., Goebeler M., Bhardwaj R., Sorg C. Macrophages and angiogenesis. J Leukoc Biol. 1994 Mar;55(3):410–422. doi: 10.1002/jlb.55.3.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toi M., Hoshina S., Taniguchi T., Yamamoto Y., Ishitsuka H., Tominaga T. Expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1995 Apr 21;64(2):79–82. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910640202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toi M., Inada K., Suzuki H., Tominaga T. Tumor angiogenesis in breast cancer: its importance as a prognostic indicator and the association with vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995;36(2):193–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00666040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visscher D. W., DeMattia F., Ottosen S., Sarkar F. H., Crissman J. D. Biologic and clinical significance of basic fibroblast growth factor immunostaining in breast carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 1995 Aug;8(6):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visscher D. W., Tabaczka P., Long D., Crissman J. D. Clinicopathologic analysis of macrophage infiltrates in breast carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 1995 Nov;191(11):1133–1139. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)80658-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Folkman J., Pozza F., Bevilacqua P., Allred E. N., Moore D. H., Meli S., Gasparini G. Tumor angiogenesis: a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Dec 16;84(24):1875–1887. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.24.1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuk J. A., Walker R. A. Immunohistochemical analysis of HLA antigens and mononuclear infiltrates of benign and malignant breast. J Pathol. 1987 Aug;152(4):275–285. doi: 10.1002/path.1711520406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


