Abstract
Although echovirus 22 is presently classified as a member of the enterovirus group in the family of picornaviruses, it has been reported to have exceptional biological properties when compared with other representatives of the group. We have determined the complete nucleotide sequence of the echovirus 22 (Harris strain) genome, which appears to be significantly different from all the other studied picornaviruses. However, the organization of the genome [7339 nucleotides, excluding the poly(A) tract] is similar to that of previously sequenced picornaviruses. This genome includes a 5' untranslated region, relatively well-conserved when compared with aphtho- and cardioviruses, followed by an open reading frame coding for a 2180-amino acid-long polyprotein. The amino termini of capsid polypeptides VP1 and VP3 were determined by direct sequencing, and the other proteolytic cleavage sites in the polyprotein were predicted by comparison with other picornavirus proteins. The amino acid identities of echovirus 22 polypeptides with the corresponding proteins of other picornaviruses are in the 14-35% range, similar to those percentages seen when representatives of the five picornavirus groups (entero-, rhino-, cardio-, aphtho-, and hepatoviruses) are compared. Our results suggest that echovirus 22 belongs to an independent group of picornaviruses.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya R., Fry E., Stuart D., Fox G., Rowlands D., Brown F. The three-dimensional structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):709–716. doi: 10.1038/337709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
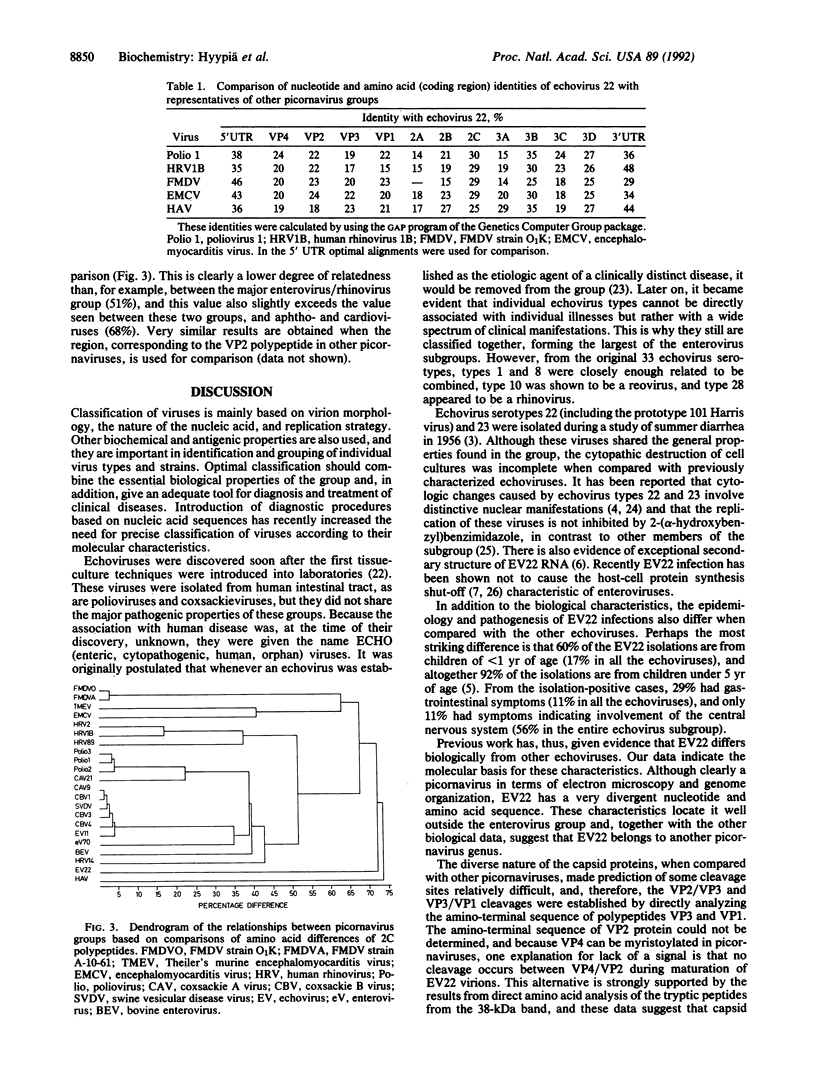
- Auvinen P., Hyypiä T. Echoviruses include genetically distinct serotypes. J Gen Virol. 1990 Sep;71(Pt 9):2133–2139. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-9-2133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auvinen P., Stanway G., Hyypiä T. Genetic diversity of enterovirus subgroups. Arch Virol. 1989;104(3-4):175–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01315541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. H., Auvinen P., Hyypiä T., Stanway G. The nucleotide sequence of coxsackievirus A9; implications for receptor binding and enterovirus classification. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3269–3280. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. H., Day C., Walker J., Hyypiä T., Stanway G. The nucleotide sequences of wild-type coxsackievirus A9 strains imply that an RGD motif in VP1 is functionally significant. J Gen Virol. 1992 Mar;73(Pt 3):621–626. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-3-621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Purcell R. H., Buckler-White A., Baroudy B. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of wild-type hepatitis A virus: comparison with different strains of hepatitis A virus and other picornaviruses. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):50–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.50-59.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. A., Chapman N. M., Beck M. A., Pallansch M. A., Gauntt C. J., Tracy S. M. Echovirus 22 is an atypical enterovirus. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2692–2701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2692-2701.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. G., Tracy S. M., Etchison D. Cap-binding complex protein p220 is not cleaved during echovirus 22 replication in HeLa cells. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3903–3905. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3903-3905.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGGERS H. J., TAMM I. Spectrum and characteristics of the virus inhibitory action of 2-(alpha-hydroxybenzyl)-benzimidazole. J Exp Med. 1961 Apr 1;113:657–682. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grist N. R., Bell E. J., Assaad F. Enteroviruses in human disease. Prog Med Virol. 1978;24:114–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huovilainen A., Kinnunen L., Ferguson M., Hovi T. Antigenic variation among 173 strains of type 3 poliovirus isolated in Finland during the 1984 to 1985 outbreak. J Gen Virol. 1988 Aug;69(Pt 8):1941–1948. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-8-1941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T., Auvinen P., Maaronen M. Polymerase chain reaction for human picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3261–3268. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. M. An electron microscopic study of the intracellular development of echovirus 22. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;44(3):184–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01240606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Kavanagh T. Speeding-up the sequencing of double-stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5198–5198. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roivainen M., Hyypiä T., Piirainen L., Kalkkinen N., Stanway G., Hovi T. RGD-dependent entry of coxsackievirus A9 into host cells and its bypass after cleavage of VP1 protein by intestinal proteases. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4735–4740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4735-4740.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal L. A., Jamison R. M. Evidence for secondary structure within the virion RNA of echovirus 22. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):641–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.641-644.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G. Structure, function and evolution of picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2483–2501. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIGAND R., SABIN A. B. Properties of ECHO types 22, 23 and 24 viruses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1961;11:224–247. doi: 10.1007/BF01241688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]