Abstract
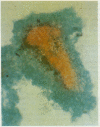
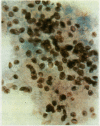
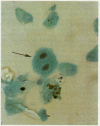
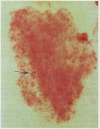
Sixty episodes of pneumonia occurring in 53 immunosuppressed patients were investigated by bronchoalveolar lavage. Pneumocystis carinii was diagnosed on 15 (25%) occasions. In all cases the Papanicolaou stained lavage fluid presented a distinctive appearance and contained abundant, often biphasic, staining, "honeycomb" debris, and few alveolar macrophages. The Grocott methenamine silver technique confirmed the presence of characteristic cystic organisms in the debris in all 15 instances. Cysts containing internal sporozoites were identified in Gram stained material only with difficulty. Neither May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain nor fluorescence microscopy under ultraviolet light were effective for routine investigation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballardie F. W., Winearls C. G., Cohen J., Carr D. H., Rees A. J., Williams G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in renal transplant recipients--clinical and radiographic features, diagnosis and complications of treatment. Q J Med. 1985 Nov;57(223):729–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellino R. A., Blank N. Etiologic diagnosis of focal pulmonary infection in immunocompromised patients by fluoroscopically guided percutaneous needle aspiration. Radiology. 1979 Sep;132(3):563–567. doi: 10.1148/132.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutz W. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Pathol Annu. 1970;5:309–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAJDUSEK D. C. Pneumocystis carinii; etiologic agent of interstitial plasma cell pneumonia of premature and young infants. Pediatrics. 1957 Apr;19(4 Pt 1):543–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghali V. S., Garcia R. L., Skolom J. Fluorescence of Pneumocystis carinii in Papanicolaou smears. Hum Pathol. 1984 Oct;15(10):907–909. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordin F. M., Simon G. L., Wofsy C. B., Mills J. Adverse reactions to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Apr;100(4):495–499. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-4-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Schroff R., Schanker H. M., Weisman J. D., Fan P. T., Wolf R. A., Saxon A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and mucosal candidiasis in previously healthy homosexual men: evidence of a new acquired cellular immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1425–1431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasleton P. S., Curry A. Pneumocystis carinii: the continuing enigma. Thorax. 1982 Jul;37(7):481–485. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.7.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkin J. M., Turney J. H., Young J. A., Adu D., Michael J. Rapid diagnosis of obscure pneumonia in immunosuppressed renal patients by cytology of alveolar lavage fluid. Lancet. 1983 Aug 6;2(8345):299–301. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T. Five-year absence of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in a pediatric oncology center. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):305–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.305-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye S. B. Pneumocystis pneumonia. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Feb 12;286(6364):499–500. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6364.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan D., Massry S. G., Romoff M. S., Campese V. M. Autonomic nervous system dysfunction in patients with acute renal failure. Am J Nephrol. 1982;2(4):213–220. doi: 10.1159/000166649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane J. T., Finch R. G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Thorax. 1985 Aug;40(8):561–570. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.8.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher A. M., Shelhamer J., MacLowry J., Parker M., Masur H. Pneumocystis carinii identified by gram stain of lung imprints. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):484–485. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahan C. T., Sale G. E. Rapid methenamine silver stain for Pneumocystis and fungi. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978 Jul;102(7):351–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchevsky A., Rosen M. J., Chrystal G., Kleinerman J. Pulmonary complications of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: a clinicopathologic study of 70 cases. Hum Pathol. 1985 Jul;16(7):659–670. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthay R. A., Moritz E. D. Invasive procedures for diagnosing pulmonary infection. A critical review. Clin Chest Med. 1981 Jan;2(1):3–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. F., Felton C. P., Garay S. M., Gottlieb M. S., Hopewell P. C., Stover D. E., Teirstein A. S. Pulmonary complications of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Report of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute workshop. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 21;310(25):1682–1688. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406213102529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J. Investigation of tissue organelles by a combination of analytical subcellular fractionation and enzymic microanalysis: a new approach to pathology. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jan;34(1):1–12. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puksa S., Hutcheon M. A., Hyland R. H. Usefulness of transbronchial biopsy in immunosuppressed patients with pulmonary infiltrates. Thorax. 1983 Feb;38(2):146–150. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.2.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey P. G., Rubin R. H., Tolkoff-Rubin N. E., Cosimi A. B., Russell P. S., Greene R. The renal transplant patient with fever and pulmonary infiltrates: etiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Medicine (Baltimore) 1980 May;59(3):206–222. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198005000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen M. J., Tow T. W., Teirstein A. S., Chuang M. T., Marchevsky A., Bottone E. J. Diagnosis of pulmonary complications of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Thorax. 1985 Aug;40(8):571–575. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.8.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangenthal S., Beer D. J., Snydman D. R., Findlay S. R., Rocklin R. E., Fanburg B. L. Pneumocystis carinii and cytomegalovirus pneumonia in a previously healthy adult. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 May;125(5):601–603. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.5.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover D. E., Zaman M. B., Hajdu S. I., Lange M., Gold J., Armstrong D. Bronchoalveolar lavage in the diagnosis of diffuse pulmonary infiltrates in the immunosuppressed host. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jul;101(1):1–7. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strumpf I. J., Feld M. K., Cornelius M. J., Keogh B. A., Crystal R. G. Safety of fiberoptic bronchoalveolar lavage in evaluation of interstitial lung disease. Chest. 1981 Sep;80(3):268–271. doi: 10.1378/chest.80.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinburn C. R., Pozniak A. L., Sutherland S., Banks R. A., Teall A. J., Johnson N. M. Early experience and difficulties with bronchoalveolar lavage and transbronchial biopsy in the diagnosis of AIDS associated pneumonia in Britain. Thorax. 1985 Mar;40(3):166–170. doi: 10.1136/thx.40.3.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Perl D. P., Krogstad D. J., Rawson P. G., Schultz M. G. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the United States. Epidemiologic, diagnostic, and clinical features. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):83–93. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. A., Hopkin J. M., Cuthbertson W. P. Pulmonary infiltrates in immunocompromised patients: diagnosis by cytological examination of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Apr;37(4):390–397. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.4.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the treatment of adults with pneumonia due to Pneumocystis carinii. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):608–613. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]