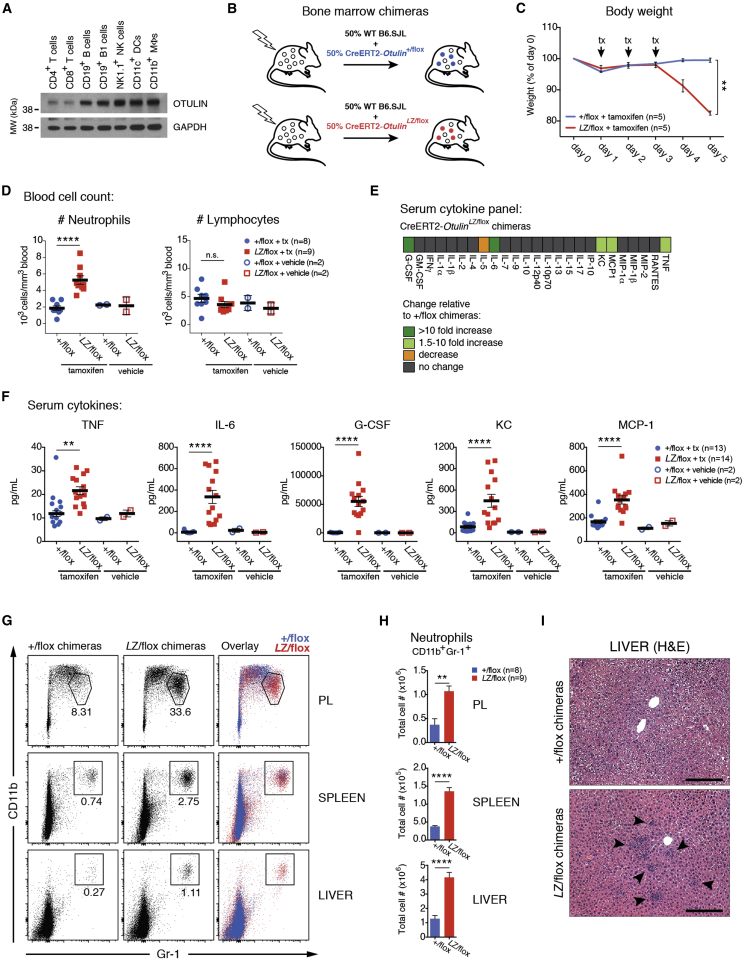
Figure 2.
Deletion of Otulin in Immune Cells Causes Acute Systemic Inflammation in Mice
(A) OTULIN immunoblot on immune cells from wild-type mice. NK cell, natural killer cell; DC, dendritic cell; MΦ, macrophage.
(B) Schematic representation of mixed bone marrow chimera generation. Wild-type (WT) B6.SJL cells are CD45.1+, and CreERT2-Otulinflox cells are CD45.2+.
(C) Body weight following i.p. administration of tamoxifen (tx; arrows) to CreERT2-Otulinflox chimeric mice.
(D) Neutrophil and lymphocyte counts from blood of CreERT2-Otulinflox chimeras and vehicle-treated controls at day 5 following tamoxifen administration.
(E and F) Luminex multiplex analysis of serum cytokines and chemokines from terminal bleeds on day 5 presented as (E) a heatmap of relative changes in concentration of all analytes between CreERT2-Otulin+/flox and CreERT2-OtulinLacZ/flox chimeras and (F) serum concentrations of cytokines and chemokines increased in CreERT2-OtulinLacZ/flox chimeras. Data were pooled from two independent experiments.
(G and H) Flow cytometry analysis of CD11b+Gr-1+ neutrophils in total cellular infiltrate (CD45.1+ and CD45.2+) in peritoneal lavage (PL), spleen, and liver from CreERT2-Otulinflox chimeras presented as (G) representative dot plots with percentage of cells in gate indicated and (H) total cell number.
(I) Micrographs of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained sections reveal inflammatory foci (arrowheads) in liver parenchyma. Micrographs are representative of 13 CreERT2-Otulin+/flox and 14 CreERT2-OtulinLacZ/flox chimeras from two independent experiments. Scale bars, 200 μm.
(C, D, F, and H) Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and n represents number of mice.