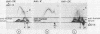Abstract
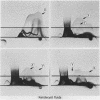
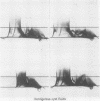
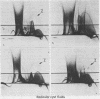
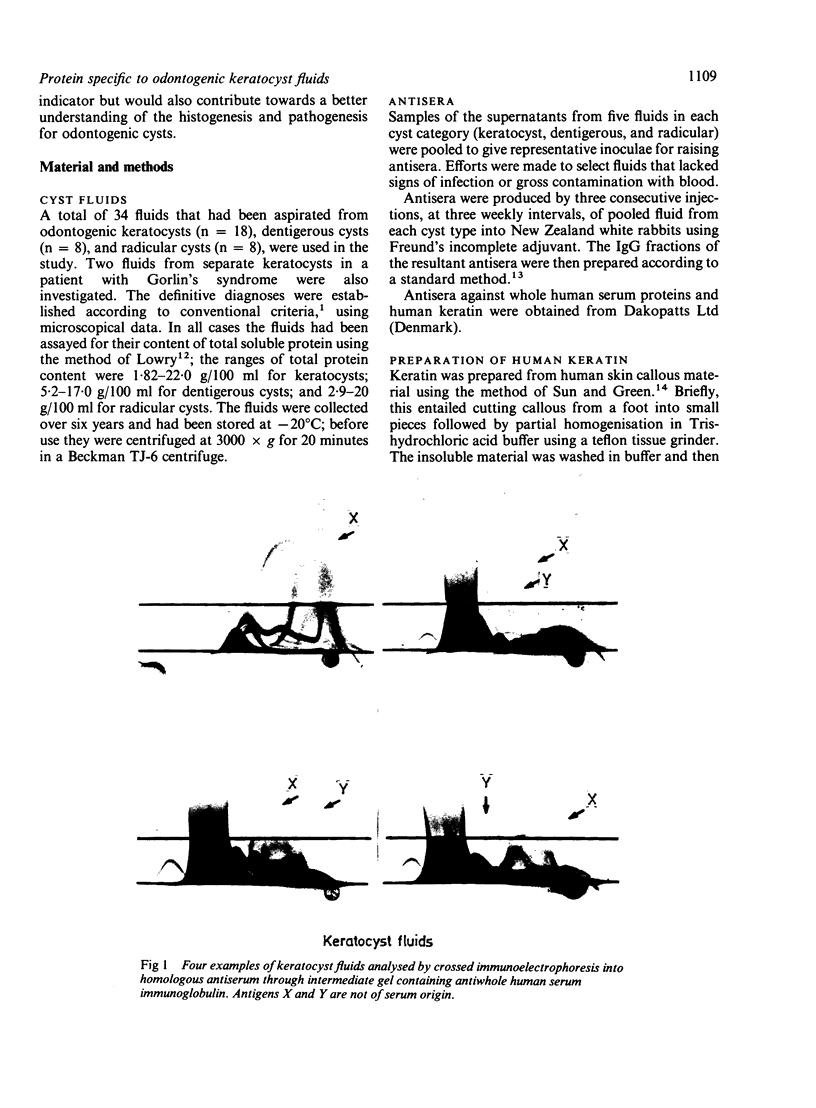
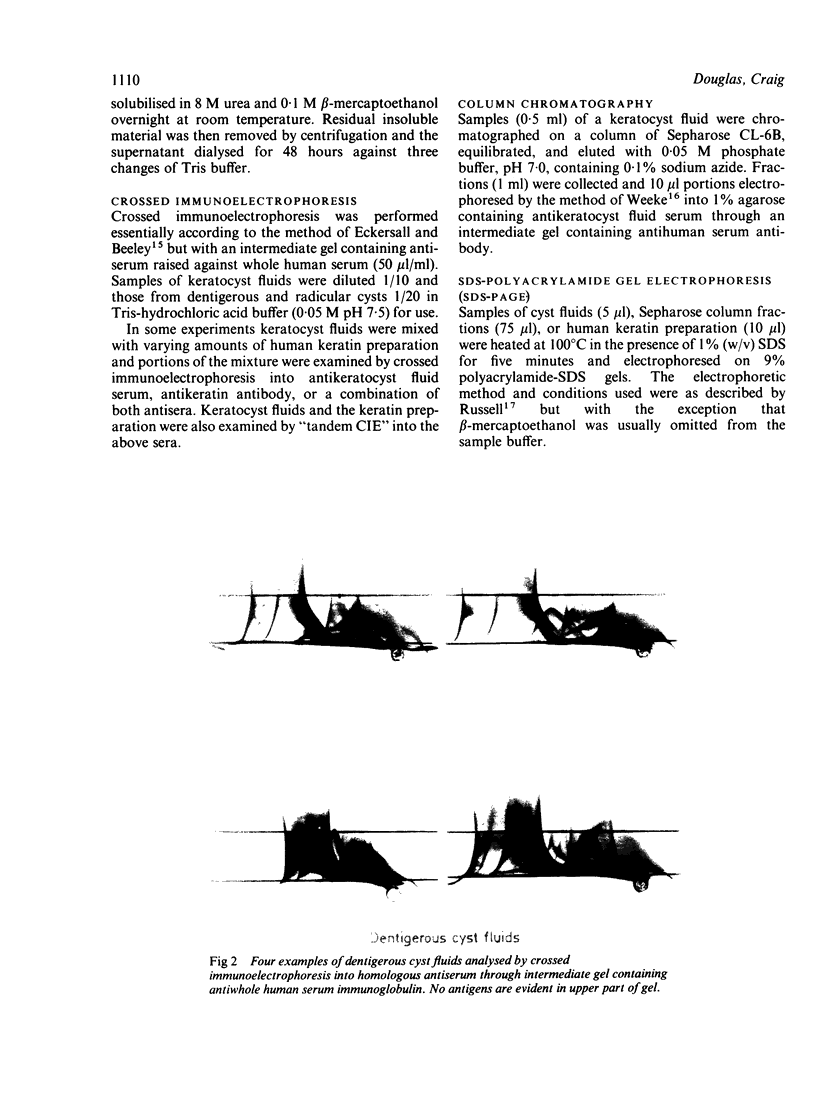
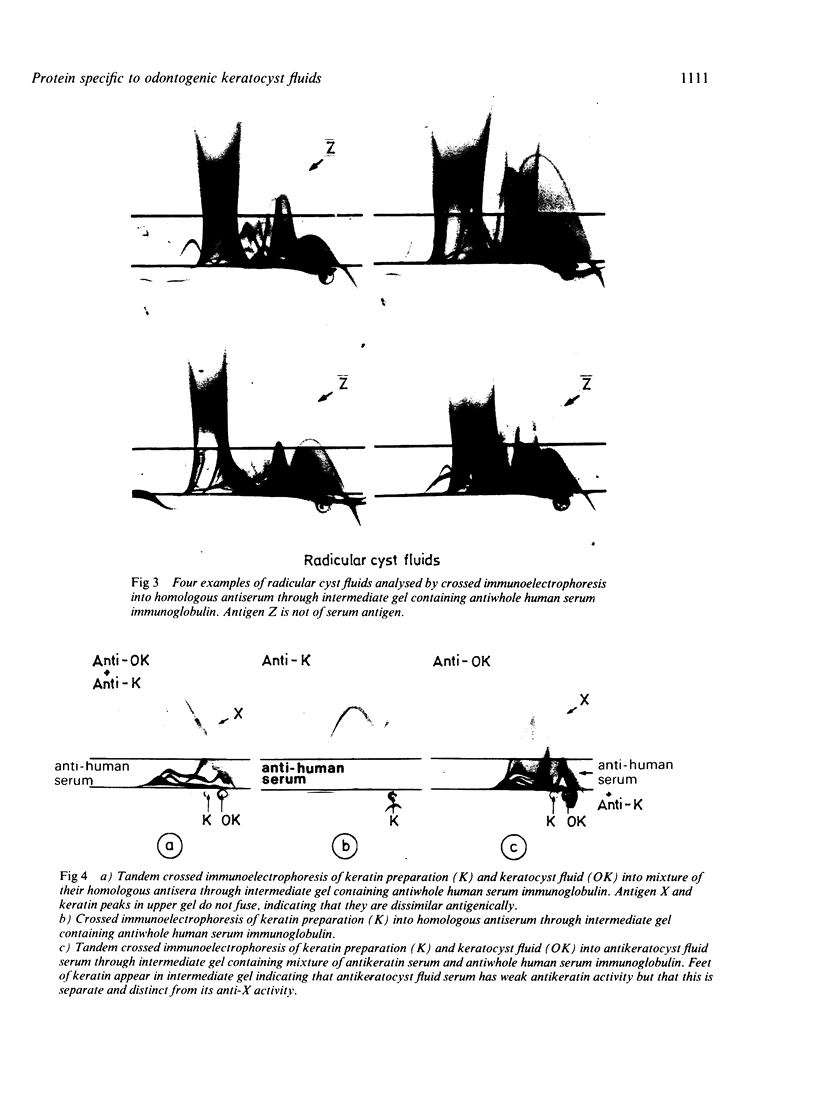
Separate antisera were raised against keratocyst, dentigerous cyst, and radicular cyst fluids and used to analyse a range of fluids from cysts of known type. Samples were subjected to crossed immunoelectrophoresis into homologous antiserum through an intermediate gel containing antibody to whole human serum to screen out serum derived components. A major antigen, designated X, which seems to be of epithelial origin but is not a keratin, was identified in keratocyst fluids. X resolves as two bands on sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) with molecular weights of 81 K and 89 K and its major antigenic epitope is associated with disulphide bonds. Of the cysts studied to date, antigen X has been found consistently and exclusively in fluids from keratocysts; its presence and detection is independent of total soluble protein concentration and thus offers real potential as a reliable marker for preoperative diagnosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlfors E., Larsson A., Sjögren S. The odontogenic keratocyst: a benign cystic tumor? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1984 Jan;42(1):10–19. doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(84)90390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne R. M. The odontogenic keratocyst. Clinical aspects. Br Dent J. 1970 Mar 3;128(5):225–231. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.4802449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. W., Russell R. R. The adsorption of human salivary components to strains of the bacterium Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1984;29(10):751–757. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(84)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskimies A. I., Ylipaavalniemi P., Tuompo H. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of proteins in fluids from jaw cysts. Proc Finn Dent Soc. 1975;71(1):6–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer I. R., Toller P. A. The use of exfoliative cytology and protein estimations in preoperative diagnosis of odontogenic keratocysts. Int J Oral Surg. 1973;2(4):143–151. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9785(73)80031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINDBORG J. J., HANSEN J. STUDIES ON ODONTOGENIC CYST EPITHELIUM. 2. CLINICAL AND ROENTGENOLOGIC ASPECTS OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;58:283–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Glucan-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans serotype c. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 May;112(1):197–201. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Keratin filaments of cultured human epidermal cells. Formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds during terminal differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):2053–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toller P. Origin and growth of cysts of the jaws. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1967 May;40(5):306–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:37–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yli-Paavalniemi P., Tuompo H., Calonius P. E. Proteins and inflammation in jaw cysts. Proc Finn Dent Soc. 1976 Dec;72(6):191–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylipaavalniemi P., Tuompo H. Effect of proteolytic digestion on jaw cyst fluids. Proc Finn Dent Soc. 1977 Aug;73(4):179–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylipaavalniemi P., Tuompo H., Koskimies A. I. Immunoelectrophoresis of proteins in fluids from jaw cysts. Proc Finn Dent Soc. 1976 Feb;72(1):7–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]