Abstract
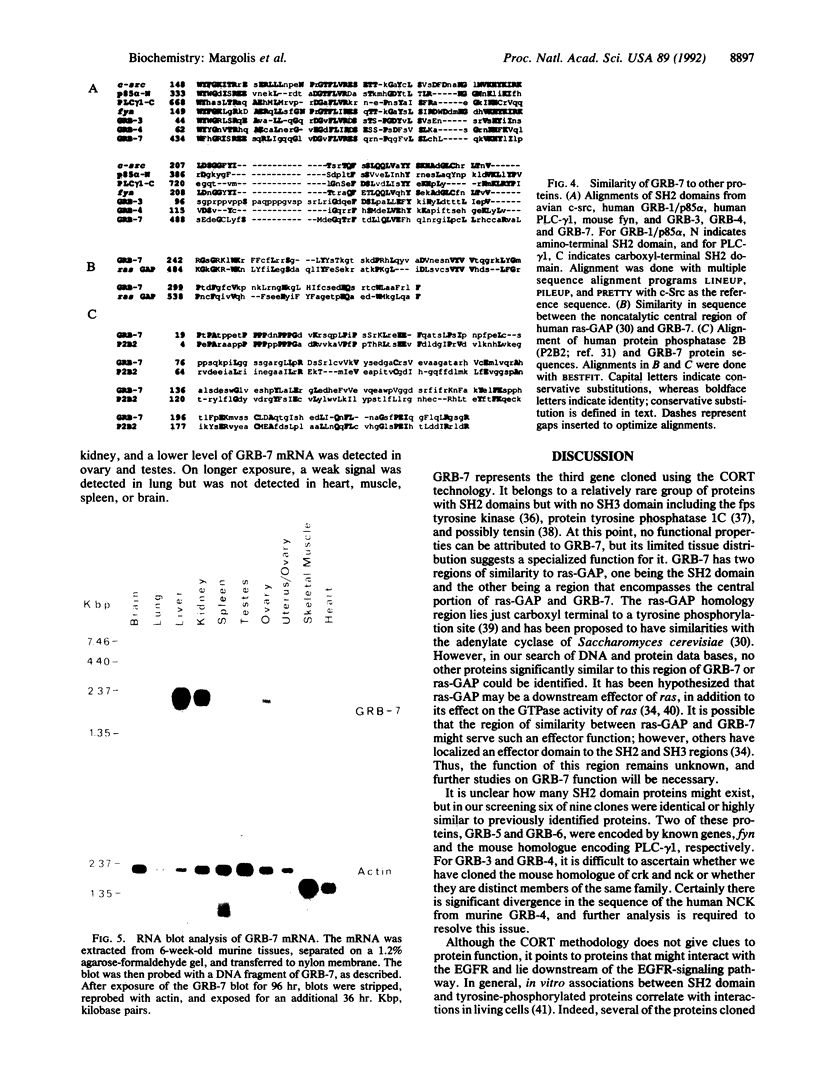
Src homology 2 domains bind to tyrosine-phosphorylated growth factor receptors and are found in proteins that serve as substrates for tyrosine kinases, such as phospholipase C-gamma 1 and ras GTPase-activating protein. We have previously described the cloning of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase-associated p85 from expression libraries with the tyrosine-phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor as a probe. We have now modified this technique by using T7 polymerase-based expression libraries, which significantly improves sensitivity of the method. In one screening of such a library, we identified five different murine Src homology 2 domain-containing proteins, which we call GRBs (growth factor receptor-bound proteins). Two of these proteins represented the tyrosine kinase fyn and the mouse homologue of phospholipase C-gamma 1, whereas two genes encoded proteins similar to v-crk and NCK. We also isolated the gene for GRB-7, which encodes a protein of 535 amino acids. In addition to a Src homology 2 domain, GRB-7 also has a region of similarity to the noncatalytic domain of ras GTPase-activating protein and is highly expressed in liver and kidney. Use of this expression/cloning system should increase our ability to identify downstream modulators of growth factor action.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aroian R. V., Koga M., Mendel J. E., Ohshima Y., Sternberg P. W. The let-23 gene necessary for Caenorhabditis elegans vulval induction encodes a tyrosine kinase of the EGF receptor subfamily. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):693–699. doi: 10.1038/348693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge R. B., Fajardo J. E., Mayer B. J., Hanafusa H. Tyrosine-phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor and cellular p130 provide high affinity binding substrates to analyze Crk-phosphotyrosine-dependent interactions in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10588–10595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Dionne C. A., Kaplow J., Mudd R., Friesel R., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J., Jaye M. Characterization and cDNA cloning of phospholipase C-gamma, a major substrate for heparin-binding growth factor 1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor)-activated tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4770–4777. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. G., Stern M. J., Horvitz H. R. C. elegans cell-signalling gene sem-5 encodes a protein with SH2 and SH3 domains. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):340–344. doi: 10.1038/356340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatases come of age. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21435–21438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Perlmutter R. M. Expression of a novel form of the fyn proto-oncogene in hematopoietic cells. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):66–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Lu M. L., Lo S. H., Lin S., Butler J. A., Druker B. J., Roberts T. M., An Q., Chen L. B. Presence of an SH2 domain in the actin-binding protein tensin. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):712–715. doi: 10.1126/science.1708917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Burgess R. R. Sigma factors from E. coli, B. subtilis, phage SP01, and phage T4 are homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6745–6763. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerini D., Klee C. B. Cloning of human calcineurin A: evidence for two isozymes and identification of a polyproline structural domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9183–9187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H. SH2 domains: elements that control protein interactions during signal transduction. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):450–452. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90175-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Interaction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-associated p85 with epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):981–990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. M., Riethmüller G., Johnson J. P. Nck, a melanoma cDNA encoding a cytoplasmic protein consisting of the src homology units SH2 and SH3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1048–1048. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. Q., Pawson T. The epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylates GTPase-activating protein (GAP) at Tyr-460, adjacent to the GAP SH2 domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2511–2516. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein E. J., Daly R. J., Batzer A. G., Li W., Margolis B., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Skolnik E. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Schlessinger J. The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90167-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Li N., Koch A., Mohammadi M., Hurwitz D. R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Pawson T., Schlessinger J. The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4375–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B. Proteins with SH2 domains: transducers in the tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Jan;3(1):73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. A., Yatani A., Clark R., Conroy L., Polakis P., Brown A. M., McCormick F. GAP domains responsible for ras p21-dependent inhibition of muscarinic atrial K+ channel currents. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1553544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlade C. J., Ellis C., Reedijk M., Anderson D., Mbamalu G., Reith A. D., Panayotou G., End P., Bernstein A., Kazlauskas A. SH2 domains of the p85 alpha subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulate binding to growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):991–997. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palazzolo M. J., Hamilton B. A., Ding D. L., Martin C. H., Mead D. A., Mierendorf R. C., Raghavan K. V., Meyerowitz E. M., Lipshitz H. D. Phage lambda cDNA cloning vectors for subtractive hybridization, fusion-protein synthesis and Cre-loxP automatic plasmid subcloning. Gene. 1990 Mar 30;88(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90056-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichman C. T., Mayer B. J., Keshav S., Hanafusa H. The product of the cellular crk gene consists primarily of SH2 and SH3 regions. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Jul;3(7):451–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Honegger A. M., Margolis B. L., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Presence of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1 enhances substrate phosphorylation by increasing the affinity toward the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9678–9683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Stone J. C., Pawson T. A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., D'Eustachio P., Givol D., Schlessinger J. Cloning and expression of a widely expressed receptor tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6112–6116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweighoffer F., Barlat I., Chevallier-Multon M. C., Tocque B. Implication of GAP in Ras-dependent transactivation of a polyoma enhancer sequence. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):825–827. doi: 10.1126/science.1317056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Bastien L., Posner B. I., Chrétien P. A protein-tyrosine phosphatase with sequence similarity to the SH2 domain of the protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):736–739. doi: 10.1038/352736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C: complete cDNA and protein sequences and sequence homology to tyrosine kinase-related oncogene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5419–5423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., Wong G., Halenbeck R., Rubinfeld B., Martin G. A., Ladner M., Long C. M., Crosier W. J., Watt K., Koths K. Molecular cloning of two types of GAP complementary DNA from human placenta. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1697–1700. doi: 10.1126/science.3201259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]