Abstract
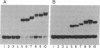
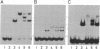
The replication of plasmid pSC101 requires the plasmid-encoded protein RepA. This protein has a double role: it binds to three directly repeated sequences in the pSC101 origin and promotes replication of the plasmid; it binds to two inversely repeated sequences in its promoter region and regulates its own transcription. A series of RepA protein derivatives carrying deletions of the C-terminal region were assayed for specific binding. We found that the last third of the protein is not needed for binding to the various specific sites. Truncated proteins that still bind can also form heterodimers with a wild-type protein. Analysis of band retardation assays conducted with wild-type and truncated proteins indicates that RepA binds to directly repeated sequences as a monomer and to inversely repeated sequences as a dimer.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arini A., Tuscan M., Churchward G. Replication origin mutations affecting binding of pSC101 plasmid-encoded Rep initiator protein. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):456–463. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.456-463.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong K. A., Acosta R., Ledner E., Machida Y., Pancotto M., McCormick M., Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. A 37 X 10(3) molecular weight plasmid-encoded protein is required for replication and copy number control in the plasmid pSC101 and its temperature-sensitive derivative pHS1. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):331–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90352-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biek D. P., Cohen S. N. Involvement of integration host factor (IHF) in maintenance of plasmid pSC101 in Escherichia coli: characterization of pSC101 mutants that replicate in the absence of IHF. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2056–2065. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2056-2065.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bétermier M., Lefrère V., Koch C., Alazard R., Chandler M. The Escherichia coli protein, Fis: specific binding to the ends of phage Mu DNA and modulation of phage growth. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):459–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoraj D. K., Mason R. J., Wickner S. H. Mini-P1 plasmid replication: the autoregulation-sequestration paradox. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):551–557. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90468-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchward G., Linder P., Caro L. The nucleotide sequence of replication and maintenance functions encoded by plasmid pSC101. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5645–5659. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Chandler M., Caro L. The effects of an Escherichia coli dnaAts mutation on the replication of the plasmids colE1 pSC101, R100.1 and RTF-TC. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jul 13;174(2):117–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00268349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamas P., Burger A. C., Churchward G., Caro L., Galas D., Chandler M. Replication of pSC101: effects of mutations in the E. coli DNA binding protein IHF. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jul;204(1):85–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00330192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasunuma K., Sekiguchi M. Replication of plasmid pSC101 in Escherichia coli K12: requirement for dnaA function. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Sep 9;154(3):225–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00571277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4 protein, synthesized in vitro, binds HIS3 regulatory sequences: implications for general control of amino acid biosynthetic genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4, a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, binds as a dimer to target DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2781–2784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Churchward G., Caro L. Plasmid pSC101 replication mutants generated by insertion of the transposon Tn1000. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):287–303. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Churchward G., Xia G. X., Yu Y. Y., Caro L. An essential replication gene, repA, of plasmid pSC101 is autoregulated. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 5;181(3):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90227-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manen D., Caro L. The replication of plasmid pSC101. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):233–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manen D., Izaurralde E., Churchward G., Caro L. Transcription events in the origin of replication of plasmid pSC101. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6482–6492. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6482-6492.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEachern M. J., Bott M. A., Tooker P. A., Helinski D. R. Negative control of plasmid R6K replication: possible role of intermolecular coupling of replication origins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7942–7946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meacock P. A., Cohen S. N. Partitioning of bacterial plasmids during cell division: a cis-acting locus that accomplishes stable plasmid inheritance. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):529–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90639-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel T. T., MacAllister T., Bastia D. Cooperativity at a distance promoted by the combined action of two replication initiator proteins and a DNA bending protein at the replication origin of pSC101. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1453–1463. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel T. T., Patel P., Bastia D. The integration host factor of Escherichia coli binds to bent DNA at the origin of replication of the plasmid pSC101. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura S., Tanaka M., Masamune Y., Yamaguchi K. DNA binding properties of purified replication initiator protein (Rep) encoded by plasmid pSC101. J Biochem. 1990 Mar;107(3):369–376. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vocke C., Bastia D. DNA-protein interaction at the origin of DNA replication of the plasmid pSC101. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):495–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vocke C., Bastia D. Primary structure of the essential replicon of the plasmid pSC101. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6557–6561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vocke C., Bastia D. The replication initiator protein of plasmid pSC101 is a transcriptional repressor of its own cistron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2252–2256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner S., Hoskins J., McKenney K. Monomerization of RepA dimers by heat shock proteins activates binding to DNA replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):7903–7907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.7903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia G. X., Manen D., Goebel T., Linder P., Churchward G., Caro L. A copy-number mutant of plasmid pSC101. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):631–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Masamune Y. Autogenous regulation of synthesis of the replication protein in plasmid pSC101. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(3):362–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00425718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Yamaguchi M. The replication origin of pSC101: the nucleotide sequence and replication functions of the ori region. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]