Abstract
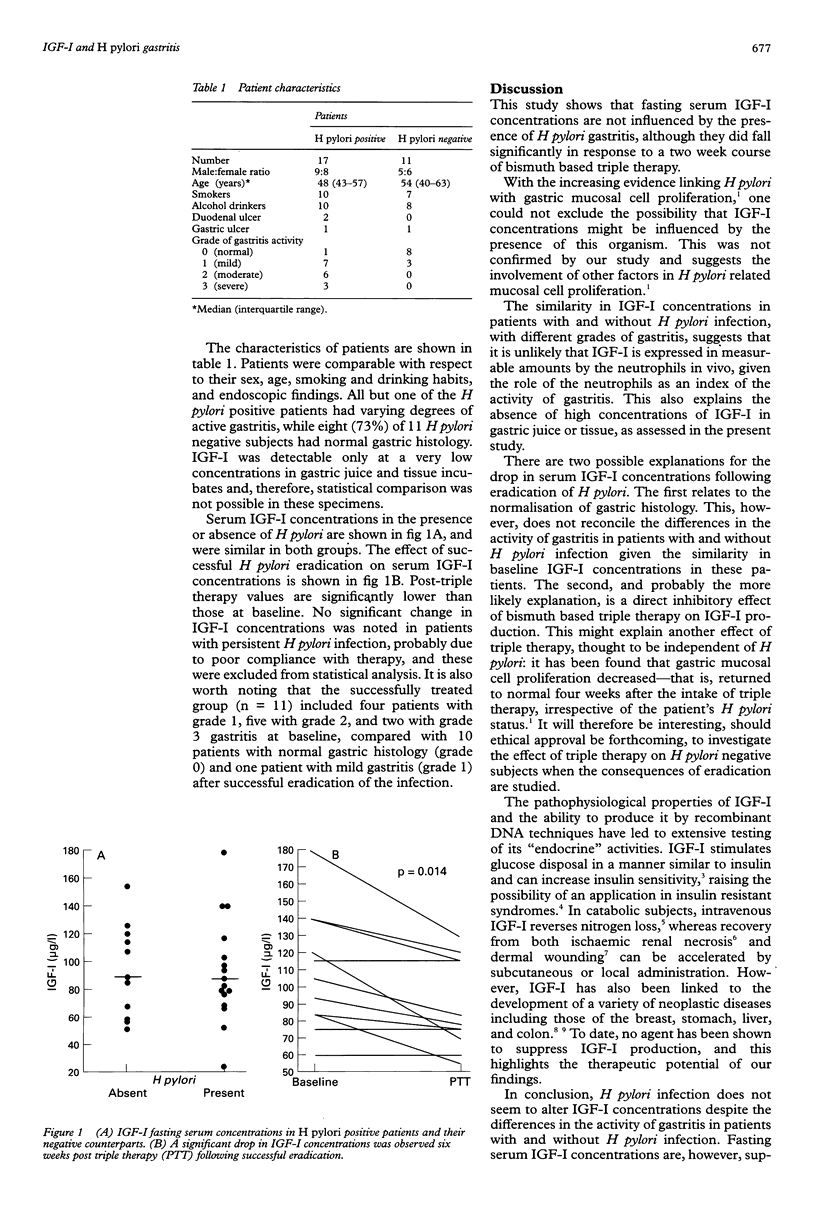
AIMS: To measure insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) concentrations in the presence and absence of Helicobacter pylori infection and in response to eradication of the organism. METHODS: An enzyme linked immunosorbent assay was used to measure gastric and fasting serum concentrations of IGF-I in 17 patients with and 11 without H pylori infection. Repeat assessments were performed in the infected patients six weeks after they received a two week course of bismuth chelate, metronidazole, and amoxycillin. RESULTS: IGF-I was detected at very low concentrations in gastric juice and in mucosal incubates. The median serum IGF-I concentration was 88 micrograms/l in the patients infected with H pylori compared with 90 micrograms/l in the non-infected controls; IGF-I concentrations dropped to 77 micrograms/l following eradication therapy (p = 0.014). CONCLUSION: The similarity in baseline IGF-I concentrations in the presence and absence of H pylori suggests that their subsequent drop after treatment is more likely to be due to the treatment.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clemmons D. R., Smith-Banks A., Underwood L. E. Reversal of diet-induced catabolism by infusion of recombinant insulin-like growth factor-I in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jul;75(1):234–238. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.1.1619015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Y. S., Beauchamp R. D., Jin G. F., Townsend C. M., Jr, Thompson J. C. Insulinlike growth factor-binding protein modulates the growth response to insulinlike growth factor 1 by human gastric cancer cells. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jun;104(6):1595–1604. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90634-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoith D., Clemmons D., Nissley P., Rechler M. M. NIH conference. Insulin-like growth factors in health and disease. Ann Intern Med. 1992 May 15;116(10):854–862. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-10-854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. A., Mapstone N. P., Clarke A. M., Sobala G. M., Jackson P., Morrison L., Dixon M. F., Quirke P., Axon A. T. Cell proliferation in Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis and the effect of eradication therapy. Gut. 1995 Mar;36(3):346–350. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.3.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. B., Martin D. R., Kissane J., Hammerman M. R. Insulin-like growth factor I accelerates recovery from ischemic acute tubular necrosis in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11876–11880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P., Rubin N. Insulinlike growth factors and binding proteins in colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 1993 Oct;105(4):1218–1237. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90971-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh D. Y., Hunt T. K., Spencer E. M. Insulin-like growth factor-I reverses the impairment of wound healing induced by corticosteroids in rats. Endocrinology. 1992 Nov;131(5):2399–2403. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.5.1425438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala A. L., Madigan T., Burguera B., Sinha M. K., Caro J. F., Cunningham P., Powell J. G., Butler P. C. Brief report: treatment of insulin-resistant diabetic ketoacidosis with insulin-like growth factor I in an adolescent with insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1992 Sep 17;327(12):853–857. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199209173271205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenobi P. D., Graf S., Ursprung H., Froesch E. R. Effects of insulin-like growth factor-I on glucose tolerance, insulin levels, and insulin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):1908–1913. doi: 10.1172/JCI115796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


