Abstract
The bidirectional interaction between the immune system and whole-body metabolism has been well recognized for many years. Via effects on adipocytes and hepatocytes, immune cells can modulate whole-body metabolism (in metabolic syndromes such as type 2 diabetes and obesity) and, reciprocally, host nutrition and commensal-microbiota-derived metabolites modulate immunological homeostasis. Studies demonstrating the metabolic similarities of proliferating immune cells and cancer cells have helped give birth to the new field of immunometabolism, which focuses on how the cell-intrinsic metabolic properties of lymphocytes and macrophages can themselves dictate the fate and function of the cells and eventually shape an immune response. We focus on this aspect here, particularly as it relates to regulatory T cells.
Resting T cells are relatively inert from a metabolic standpoint and require little energy generation or expenditure to ‘keep the engine idling’. Upon activation, their energy needs increase substantially and, as will be described below, various substrates, including glucose, amino acids (especially glutamine) and fatty acids, are used to meet this demand. Most of the initial studies of T cells focused on naive T cells and effector T cells (Teff cells)–memory T cells (Tmem cells), which have both shared metabolic features and distinct metabolic features. Subsequently, increasing attention has been focused on regulatory T cells (Treg cells), with the recognition that these cells have their own signaling and metabolic ‘preferences’ that can drive and dictate their function and stability.
The best-characterized subset of Treg cells is defined by expression of the co-receptor CD4, the cytokine receptor CD25 and the transcription factor Foxp3 (encoded by an X-linked gene). The importance of Treg cells is exemplified by patients with the immunodeficiency syndrome IPEX (‘immunodys regulation polyendocrinopathy enteropathy X-linked’) and mice of the scurfy strain, each of which lack functional Foxp3 and suffer from severe systemic autoimmunity. Treg cells can originate in the thymus, as well as extrathymically in the periphery as a consequence of the induction of Foxp3 expression following the activation of naive T cells1. In this Review, we will use ‘tTreg cells’ for thymus-derived Treg cells, ‘pTreg cells’ for peripherally induced Treg cells, and ‘iTreg cells’ for in-vitro-generated Treg cells2. Although tTreg cells and pTreg cells share many key features, such as their reliance on Foxp3 expression and dependence on interleukin 2 (IL-2) for their suppressive function and maintenance, they differ in the repertoires of their T cell antigen receptors (TCRs) and in the epigenetic marking of control elements in the Foxp3 locus3–7. Most importantly, of course, they differ in whether Foxp3 is expressed constitutively (tTreg cells) or whether its expression is induced following antigen-mediated activation (pTreg cells). Given these distinctions, it is likely that tTreg cells and pTreg cells will not be found to be metabolically identical, and these differences might arise from specific developmental programming and/or context-dependent external cues.
In this Review we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the metabolic properties of both subsets of Treg cells (i.e., thymus derived and extra-thymically induced) and how these can modulate and be reciprocally influenced by the immune response.
T cell bioenergetics and features of Treg cell metabolism
Upon being activated, resting naive T cells that differentiate toward the Teff cell lineage shift from catabolic energy metabolism to an anabolic state. This is driven predominantly by the glycolytic-lipogenic pathway and is associated with glutamine oxidation that fuels mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation through the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. This use of aerobic glycolysis, similar to the metabolism in many cancer cells, is called the ‘Warburg effect’ and is orchestrated via the mTOR-dependent nutrient-sensing pathway activated downstream of signaling via the kinases PI(3)K and Akt8–10. As an immune response resolves, cells that persist and/or transit into the memory pool (as demonstrated by CD8+ T cells) revert to a catabolic state and rely mainly on lipid oxidation regulated by signaling via the AMP-activated kinase AMPK and promoted by increased mitochondrial biogenesis, both of which are associated with cellular longevity and the ability of T cells to rapidly respond to reinfection10–12.
Glycolysis-driven de novo fatty-acid synthesis is a critical determinant of the fate of the TH1, TH2 and TH17 subsets of helper T cells13–15. Consistent with that, Teff cell differentiation can be inhibited by various means, including inhibition of HIF-1α (‘hypoxia-inducible factor 1α’), the transcription factor required for glycolysis; blockade of PDHK (‘pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase’), the TCA enzyme that indirectly promotes glycolysis by blocking pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH); or blockade of ACC1 (‘acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1’), the key enzyme that drives fatty-acid synthesis. This has been demonstrated not only genetically but also pharmacologically, via treatment with 2-deoxy-glucose (2-DG), dicholoroacetate or soraphen, which block each of those three processes, respectively (Table 1). Notably, this not only inhibits Teff cell differentiation but also promotes iTreg cell induction14,16,17.
Table 1.
Potential therapeutic strategies for regulating Treg cell metabolism for immunomodulation
| Molecule | Metabolic pathway affected | Mode of drug action and proposed effect | Implications and disease models | Refs. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface receptors | CTLA-4 and PD-1 | CTLA-4 blocks glycolysis without augmenting FAO; PD-1 blocks glycolysis and enhances FAO in Teff cells by activating ATGL | Checkpoint blockade to enhance Teff cells while potentially inhibiting Treg cells that are reliant on FAO | Cancer therapy | 48 |
| P2X7 | Activation of P2X7 via ART by extracellular NAD+ released during inflammation and cellular damage | Systemic administration of NAD+ depletes 75–80% of Treg cells in mice; an NAD+ inhibitor (the single-domain anti-body ART2.2) protects Treg cells from NICD | Cancer therapy; autoimmunity | 71 | |
| CD39-CD73 and A2AR | Catabolism of ATP to adenosine by Treg cells that in turn inhibits Teff cell responses via A2AR | CD39-CD73 blockade; CD39-CD73 activator; A2AR antagonists in next-generation checkpoint blockade | Cancer therapy; autoimmunity; transplantation | 75–77 | |
| Intracellular kinases and phosphatases | PTEN | Inhibits PI(3)K-Akt signaling and glycolysis in Treg cells | A PTEN inhibitor causes Treg cell destabilization and tumor regression | Cancer therapy; autoimmunity | 45,47,78 |
| Leptin-mTOR signaling axis | mTOR promotes glycolysis via HIF-1α and inhibits iTreg cells | Rapamycin blocks mTOR and enhances Treg cell proliferation | EAE | 17,34 | |
| AMPK | Activates FAO and enhances iTreg cell generation | Metformin activates AMPK signaling and increases lipid oxidation | Allergic asthma | 13 | |
| Metabolic enzymes | HK | Catalyzes the first rate-limiting reaction in glycolysis | 2-DG blocks HK activity and glycolytic pathway | Prolongs allograft survival and diminishes EAE | 17,20 |
| GLS | Converts glutamine to glutamate, the first step in gluatmine oxidation | DON blocks glutamine transport and glutaminase enzymes | DON, along with other metabolic inhibitors (2-DG and metformin), prolongs allograft survival | 20 | |
| PDHK1 | Inhibits PDH (which catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA) and indirectly enhances glycolysis | DCA blocks PDHK and increases the entry of pyruvate into the TCA cycle | Diminishes colitis, EAE and collagen-II-induced arthritis | 16,79 | |
| ACC | Carboxylates acteyl-coA to malonyl-CoA, which is essential for lipid synthesis | SorA blocks ACC and inhibits TH17 development and favors Treg cells | ACC blockade attenuates EAE | 14 | |
| HMGCR | Rate-limiting enzyme involved in the synthesis of cholesterol and isoprenoid lipids that are required for coordinating Treg cell proliferation and optimal induction of CTLA-4 and ICOS in an mTORC1-dependent manner | 25-hydroxycholesterol (general lipid-synthesis inhibitor) and drugs such as simvastatin, atorvastatin and lovastatin inhibit HMGCR and impair the suppressive activity of Treg cells | Cancer therapy | 18 | |
| IDO | Tryptophan-catabolizing enzyme expressed by dendritic cells that suppresses T cell responses by upregulating PD-1 on Treg cells via amino-acid-sensitive GCN2, which blocks mTOR | IDO-inhibitor drugs can increase Akt phosphorylation in Treg cells; interferon-γ and CTLA-4–Ig can enhance IDO expression in dendritic cells; the small molecule halofuginone activates GCN2 (AAR) and inhibits TH17 differentiation | Cancer therapy; allogenic bone-marrow transplantation; EAE | 47,80,81 | |
| SIRT1 | Activated by an increase in the NAD+/NADH ratio and can directly deacetylate Foxp3, which leads to its proteosomal degradation | Inhibitors EX527 and splitomycin block SIRT1 activity; resveratrol supports mitochondrial biogenesis in a SIRT1-dependent manner | Prolongation of allograft survival | 82–84 | |
| Mitochondrial ATPase | Crucial for mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation | Small-molecule inhibitor (Bz-423) that inhibits mitochondrial F1F0 ATPase in alloreactive T cells that depends on FAO in a GVHD model | Bone-marrow transplantation | 85,86 | |
| Metabolic intermediates | PEP | One of the products of glycolysis (enhanced by PCK1) that sustains Ca2+ mobilization and NFAT signaling by inhibiting SERCA activity | Enhances Teff responses, effect on Treg cell TBD | Anti-tumor immunity | 19 |
| α-KG | Glutamine-derived TCA cycle metabolite | The α-KG analog DMK enhances T-bet expression and TH1 responses, while a decrease in α-KG can enhance Treg cells | Glutamine deprivation enhances the suppressive activity of Treg cells in an autoimmune colitis model | 22 | |
| Mevalonate | A metabolite in the lipid-synthesis pathway downstream of HMGCR | Mevalonate completely reverses the effects of statins (described above) and is involved in maintaining Treg cell functional fitness in an mTORC1-dependent manner | Autoimmunity | 18 | |
| Chromatin modifiers | EZH2 | Associates with Foxp3 to create repressive chromatin but is also crucial for establishing polyfunctionality in Teff cells | Glucose deprivation inhibits EZH2 by microRNAs and Teff cell function; net effect of EZH2 inhibitors on Treg cells is TBD | Cancer; autoimmunity | 63,64 |
HK, hexokinase; GLS, glutaminase; EAE, experimental autoimmune encephalitis; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; HMGCR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutryl-CoA reductase; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; DMK, dimethyl α-ketoglutarate; ICOS, effector molecule; NICD, NAD+-induced T cell death; DCA, dichloroacetate; SorA, soraphen; Ig, immunoglobulin; AAR, amino-acid–starvation response; F1F0 ATPase, F-type ATPase (ATP synthase); GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; PCK1, kinase; TBD, to be determined.
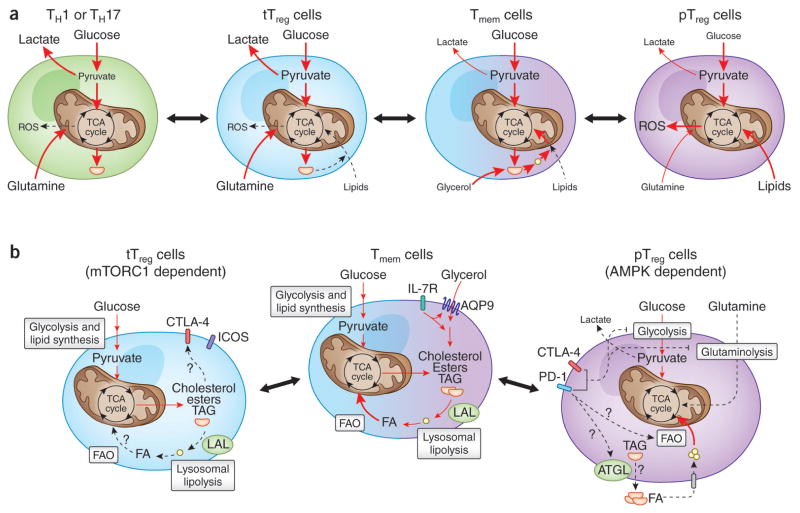
Treg cells that develop in vivo (tTreg cells) resemble Teff cells in that they depend on glycolysis-driven lipogenesis for their proliferation and functional fitness, with the mevalonate pathway demonstrated to be particularly important in this subset18. Interestingly, studies of mouse B16 melanoma tumor models have shown that intratumoral and splenic Treg cells exhibit more glucose uptake than do non-Treg cells19. Moreover, in vivo blockade of glycolysis and glutaminolysis and enhancement of fatty-acid oxidation (FAO) diminishes the proliferation of Treg cells (although to a lesser degree than the effect on Teff cells) in a model of infection with vaccinia virus and adoptive transfer of T cells20. Although such studies have suggested a clear metabolic distinction between tTreg cells and iTreg cells (the latter being probably indicative of pTreg cells as well), these differences are probably context dependent (Fig. 1a). Subsequent to those studies, it was reported that human Treg cells isolated ex vivo are highly glycolytic and engage in both glycolysis and FAO when cultured in vitro21. Furthermore, in a model in which human Treg cells were induced in vitro by suboptimal TCR stimulation without use of the cytokines TGF-β or IL-10, glycolysis was shown to be required for optimal induction of Foxp3 expression and Treg cell function (discussed in more detail below).
Figure 1.
Proposed model for the metabolic signatures of various Treg cell subsets. (a) Activated CD4+ T cells that differentiate into the Teff cell lineage (green) (TH1 or TH17 cells) are dependent mainly on carbon substrates such as glucose and glutamine for their anabolic metabolism. In contrast to that, pTreg cells that potentially mirror activated T cells that have differentiated into the iTreg cell lineage in vitro (purple) can rely on exogenous lipids and glucose-derived pyruvate that they can oxidize in the TCA cycle. Owing to their substantial dependence on FAO, iTreg cells generate increased amounts of ROS but are resistant to ROS-mediated damage, as they might be armed with antioxidant molecules to maintain their integrity. However, the metabolic properties of tTreg cells (blue) seem to resemble those of activated Teff cells to a greater degree than those of their pTreg cell counterparts in that they might be more dependent on glucose and glutamine than on fatty acids. (b) Tmem cells depend on glycolysis-driven lipogenesis and IL-7 receptor (IL-7R)-mediated expression of AQP9 for uptake of glycerol to generate cholesterol esters and triacylglycerols that can be hydrolyzed by LAL to mobilize free fatty acids (FA) to fuel FAO. Both tTreg cells and pTreg cells mirror certain metabolic properties of Tmem cells, in that they seem to rely on glucose-derived lipogenesis and FAO, respectively. Furthermore, the activation of co-inhibitory receptors such as CTLA-4 and PD-1 (which inhibit glycolysis while promoting FAO in activated T cells) might potentially have a role in influencing FAO in pTreg cells. In particular, activation of PD-1 has been shown to upregulate the enzyme ATGL (‘adipose triglyceride lipase’) that hydrolyzes intracellular triacylglycerol (TAG) into glycerol-3-phosphate and fatty acids for their utilization in FAO in activated T cells. Thus, although like Tmem cells, pTreg cells can depend on FAO, the means by which they obtain fatty acids might be different. Whether tTreg cells depend on FAO is yet to be determined.
Amino acids, particularly glutamine and leucine, have an essential role in Teff cell differentiation. However, iTreg cells seem to be less dependent on amino acids for their energy needs. For example, depriving CD4+ T cells of glutamine leads to their differentiation toward a Treg cell phenotype22. Conversely, the glutamine-derived TCA-cycle intermediate α-ketoglutarate enhances TH1 differentiation by promoting expression of the transcription factor T-bet22. In addition, genetic deficiency in neutral-amino-acid transporters such as Slc7a5 and Slc1a5 diminishes glutamine uptake and glucose metabolism and decreases Teff cell differentiation without effects on the generation of iTreg cells23,24 (Fig. 1).
Interestingly, the metabolic byproducts of tryptophan catabolism, such as kynurenine, promote the generation of iTreg cells by binding to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor25–27. Depleting cells of tryptophan can also lead to activation of the amino-acid-starvation response via the kinase GCN2, with resultant inhibition of TH17 differentiation27,28. Furthermore, Treg cells have been shown to increase their expression of amino-acid-catabolizing enzymes such as ARG1 (‘arginase 1’), HDC (‘histidine decarboxylase’), TDH (‘threonine dehydrogenase’) and IL4I1 (‘interleukin-4 induced 1’; similar to l-amino-acid oxidase) in skin grafts and bone-marrow-derived dendritic cells, which suggests that Treg cells can modulate the concentration of certain amino acids and their catabolic products in the local milieu, an effect that can itself ‘preferentially’ enhance suppression mediated by Treg cells27.
To meet their energetic demands, Tmem cells depend on FAO, a process that is dependent upon Cpt1a (‘carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A’), the rate-limiting enzyme for mitochondrial lipid uptake11. To support this pathway, Tmem cells depend upon both exogenous glycerol and endogenous lipids (Fig. 1b). They import exogenous glycerol via IL-7-induced expression of the pore-forming membrane protein AQP9 (‘glycerol channel aquaporin 9’) and also generate lipids de novo from glucose29. Furthermore, Tmem cells express the enzyme LAL (‘lysosomal acid lipase’), which hydrolyzes glucose-derived endogenous cholesterol esters and triacylglyerols to fuel FAO30. Both tTreg cells and pTreg cells seem to exhibit some metabolic features that resemble those of Tmem cells, in that pTreg cells can depend upon FAO (mirroring iTreg cells), while tTreg cells utilize a glycolytic-lipogenic cholesterol-biosynthetic pathway for both survival and optimal suppressive function, as described in the previous section13,14,18,31 (Fig. 1b). Whether tTreg cells can import exogenous fatty acids and/or use their endogenous stores of triacylglycerides to feed FAO is not yet known (Fig. 1b).
Some features of Treg cell metabolism are also closely tied to anatomical location. For example, the dependence of Treg cells on lipid metabolism in vivo is particularly evident in tissue-resident Treg cells that localize in non-lymphoid tissues such as visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and intestinal mucosa32,33. VAT Treg cells express PPARγ (‘peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ’), a master regulator of adipocyte differentiation and function, and have high expression of CD36, a scavenger receptor that facilitates the import of exogenous fatty acids31,33. Like other Treg cells, VAT Treg cells also express leptin receptors32,34,35. Moreover, adipocytes in the VAT of obese mice have high expression of leptin, which results in overactivation of mTOR in Treg cells and a decrease in the number of Treg cells35. Conversely, the VAT of lean aged male mice or mice deficient in leptin or its receptor shows enrichment for Treg cells31,36. As an example from another anatomical site, the colon provides an environment rich in short-chain fatty acids, such as butyrate, acetate and propionate, that are generated from the bacterial fermentation of dietary fiber, and this has been closely linked to promoting the generation of Treg cells32,33,37–39. One mechanism by which butyrate induces Treg cells in the gut is through inhibition of histone deacetylases, which enhances the acetylation of histone H3 at Lys27 at the Foxp3 locus and thereby increases Foxp3 expression37–39. Tissue-resident Treg cells are therefore attuned to local metabolic cues that can be exploited for their phenotypic and functional specialization, as well as for ‘preferential’ survival in the tissue microenvironment.
Metabolic control of Treg cells by mTOR
The mTOR-dependent nutrient-sensing pathway is composed of two distinct complexes: mTORC1 and mTORC2. In T cells, mTORC1 activity is elicited by signaling through the TCR and the co-receptor CD28 (ref. 40), as well as through the expression and activity of nutrient transporters23,24,41. For example, the glutamine transporter ASCT2 and the system-L transporter Slc7a5 (which ‘preferentially’ mediates the uptake of leucine) are both critical for sustained mTORC1-dependent expression of the transcription factor c-Myc and optimal TH1 and TH17 differentiation of naive T cells. Notably, either transporter is dispensable for the induction of iTreg cells. Consistent with that, leucine transport is required for the expression of other nutrient transporters, such as Glut1 and CD71, and Glut1 expression itself has emerged as a critical factor in driving glycolysis in Teff cells, whereas Treg cells generated either in vitro or in vivo develop and function independently of Glut1 (ref. 41). These examples illustrate how amino acids control metabolism in an mTOR-dependent manner, affecting mainly Teff cells and sparing Treg cells. Moreover, one mechanism by which Treg cells achieve suppression relies on the induction, in antigen-presenting cells, of the expression of amino-acid-consuming enzymes such as IDO (upregulated through Treg cell–specific ligation of the costimulatory molecules CD80 or CD86 via the inhibitory receptor CTLA-4) and ARG1 (upregulated by inflammation), which block the proliferation of Teff cells and promote the induction of Treg cells via inhibition of mTOR signaling42.
The main negative regulator of PI(3)K activity in T cells is the lipid phosphatase PTEN43,44. Treg cell–specific deletion of PTEN enhances a glycolytic program in association with compromised function and lineage instability45. Moreover, PTEN has been shown to be critical in limiting Akt activity and, consequently, maintaining the transcription-factor activity of Foxo3a in intratumoral Treg cells through the semaphorin Sema4a and neuropilin Nrp1, which suggests that this pathway might be a potential therapeutic target for the potentiation of anti-tumor responses and limiting of Treg cell–mediated tolerance to tumors46. It has also been reported that IDO-induced activation and function of Treg cells requires activation of PTEN via the checkpoint receptor PD-1 and that PTEN-deficient Treg cells are compromised in their ability to create a suppressive tumor microenvironment47. In activated T cells, PD-1 inhibits the transport and utilization of both glucose and glutamine and alters the metabolic program from glycolysis to FAO, which suggests that PD-1 might affect metabolism through PTEN-mediated control of PI(3)K signaling48.
Although strong PI(3)K signals clearly have a negative effect on the differentiation, function and stability of Treg cells, this does not indicate that Treg cells are completely PI(3)K independent45,47,49. Indeed, an oscillatory nature of mTOR signaling in Treg cells in response to leptin and nutrients has been described34. Furthermore, PI(3)K signaling via the TCR and IL-2 maintains functional fitness and suppressive activity via mTORC1-mediated induction of cholesterol and lipid metabolism and upregulation of CTLA-4 expression18 (Figs. 1b and 2). Interestingly, mTORC1 has a role in inhibiting the mTORC2 pathway in Treg cells, and mTORC2 activity is required for Akt-mediated inhibition of Foxo transcription factors. Given the importance of these transcription factors in the development, maintenance and function of Treg cells, it is possible that the ability of mTORC1 to inhibit mTORC2 contributes to the control of metabolism via maintenance of the activity of Foxo transcription factors in the nucleus50–52. This is consistent with the finding that Foxo1 inhibits glycolytic and oxidative metabolism through antagonizing c-Myc function. Of note, Foxo1 also has a role in the memory formation and function of CD8+ T cells53,54. CD8+ Tmem cells are perhaps the population most similar to Treg cells in their metabolic profile, and we are tempted to speculate that their metabolic properties and reliance on Foxo1 signaling are interrelated.
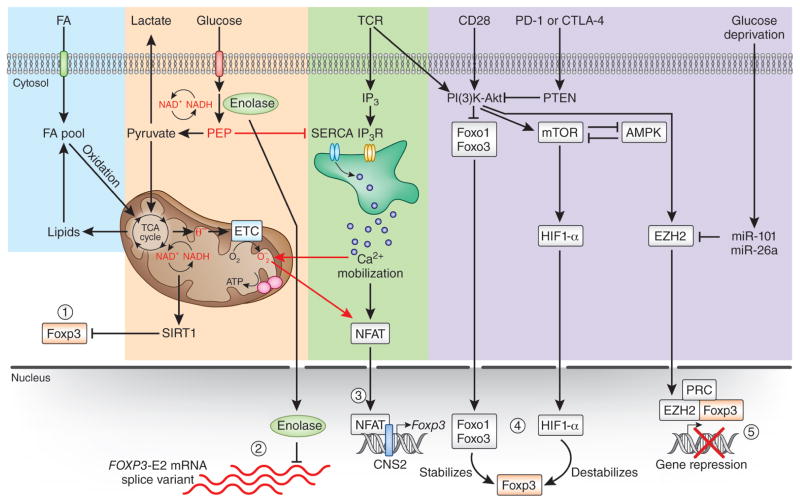
Figure 2.
Effects of metabolism on Foxp3 expression and the generation of Treg cells. There are various scenarios in which Treg cell signaling and metabolic pathways might integrate and potentially affect Foxp3 expression. One of the downstream effects of an enhancement in glycolytic metabolism is the production of metabolic intermediates that can also function as signaling molecules (1). For example, NAD+ and NADH might control Foxp3 stability via the activation of histone deacetylases such as SIRT proteins, which directly deacetylate Foxp3 in the nucleus and lead to its proteosomal degradation in the cytoplasm. Furthermore, the glycolytic enzyme enolase-1 can repress the FOXP3 splice variant containing exon 2 (E2) in human Treg cells, and its engagement in glycolysis serves as a mechanism by which glycolysis can control Foxp3 expression (2). Signaling molecules from glycolysis and mitochondrial metabolism (PEP and ROS) activate NFAT via Ca2+ mobilization during T cell activation, a process that could potentially affect Foxp3 expression in Treg cells as well (3). Activation of Foxo transcription factors and HIF-1α downstream of the PI(3)K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway can reciprocally affect Foxp3 expression (4). Finally, the chromatin-modifying enzyme EZH2 that is crucial for the establishment of a repressive Treg cell gene program can be inhibited by specific microRNAs (such as miR-101 and miR-26a) under circumstances of glucose deprivation, which leads to Treg cell instability (5). ETC, electron-transport chain; PRC, polycomb repressive complex; IP3 and IP3R, inositol-1,3,4-trisphosphate and its receptor.
An alternative to mTOR-driven metabolism is the AMPK-dependent pathway, which promotes mitochondrial oxidative metabolism and suppresses mTOR signaling and glycolysis55. A crucial role for AMPK in Teff cells under conditions of limited nutrient availability has been demonstrated56. Activated T cells with less access to glucose undergo a metabolic checkpoint marked by decreased mTORC1 activity that limits cell growth, cytokine production and proliferation but maintains cellular ATP levels, cell viability and the ability to resume cytokine production following the re-introduction of glucose. In the absence of AMPK during periods of glucose starvation, T cells are deficient in their ability to suppress mTORC1 activation, undergo metabolic reprogramming, and utilize glutamine to generate TCA-cycle intermediates for the support of oxidative phosphorylation.
Treg cells maintain high levels of AMPK activation, which mimics the metabolism of nutrient-deprived Teff cells, although important differences remain, in particular the reliance of Treg cells on lipid oxidation13. This aspect of the metabolic profile of Treg cells is particularly evident in the context of deficiency in the receptor ERRα, which leads to a block in glucose oxidation and glucose-dependent lipid synthesis. In this case, lipids restore the differentiation of Treg cells, but pyruvate does not, and neither is able to restore TH1, TH2 or TH17 cells57. Interestingly, in the absence of glutamine, the activation of naive T cells (even under TH1-skewing conditions) results in loss of mTORC1 activity and differentiation into Treg cells22. This is dependent on a decrease in intracellular levels of the glutamine-derived metabolite α-ketoglutarate, which identifies a role for intracellular metabolite production in the direct control of cell fate in the context of nutrient availability.
Metabolic control of Foxp3 and Treg cell lineage stability
Instability of the Treg cell lineage is associated with inflammatory conditions and is closely linked to alterations in metabolism45,46,58,59. Treg cell–specific deletion of Atg7 or Atg5, which encode two factors essential to autophagy, also leads to compromised stability of the Treg cell lineage due to unchecked control of mTORC1-dependent c-Myc expression and glycolysis58. While unrestrained glycolytic activity in Treg cells can contribute to their dysfunction, it is likely that glycolysis also has an important role in supporting this population. In human iTreg cells generated by sub-optimal TCR stimulation, the glycolytic activity of enolase-1 can promote the induction of FOXP3 splice variants containing exon 2 to confer suppressive activity60 (Fig. 2). After pharmacological blockade of glycolysis with 2-DG during the generation of iTreg cells, non-glycolytic activity of enolase-1 represses FOXP3 expression, while silencing of enolase-1 under these same conditions restores FOXP3 transcripts and expression of the exon-2-containing FOXP3 splice variants. This bi-functionality of a metabolic enzyme, whereby enolase-1 has distinct functions depending on whether or not Treg cells are engaged in glycolysis, has a parallel in Teff cells, in which GAPDH inhibits the production of interferon-γ when disengaged from glycolysis as a result of cellular reliance on oxidative metabolism15. Given the highly proliferative nature of Treg cells, it might not be surprising that they engage glycolysis under certain contexts. This has been directly characterized through analysis of mouse iTreg cell metabolism and in human Treg cells assessed ex vivo immediately after isolation or cultured in vitro16,21. Whether there is a greater reliance on glycolysis in human Treg cells than in mouse Treg cells, under physiological and pathological conditions, and whether this contributes to or diminishes suppressive capacity, remain to be determined.
Under certain contexts, the glycolytic ability of Treg cells might be indispensable. In activated T cells, this shift toward glycolysis is driven by c-Myc9. TH17 cells, however, rely on a HIF-1α-driven glycolytic program17. Interestingly, TH17 cells and iTreg cells demonstrate a reciprocal relationship in which the expression of HIF-1α represents a metabolic ‘tipping point’ between these two populations. This is true both under hypoxic conditions and normoxic conditions and relies in part on targeting of Foxp3 for degradation through direct binding of HIF-1α61 (Fig. 2). Surprisingly, the HIF-1α pathway has been revealed to induce Foxp3 expression under hypoxic conditions, which constitutes a negative feedback loop for controlling Teff cell responses elicited under inflammatory hypoxic conditions62. This again illustrates (as does the role of enolase-1 in Treg cells) that in certain contexts, a glycolytic program might be required for Treg cells to actively engage in suppressive activity.
The regulation of chromatin by the CD28-dependent histone methyl-transferase EZH2 is critical in maintaining a Foxp3-dependent gene program in Treg cells, particularly in non-lymphoid tissues and in settings of induced inflammation63. However EZH2 also regulates non-Treg cells. Glycolysis-driven EZH2 expression in CD4+ or CD8+ T cells is required for cytokine production in the context of anti-tumor responses64. Through glucose restriction imposed by the tumor microenvironment, T cells maintain expression of a set of microRNAs that target EZH2 expression, which results in loss of T cell polyfunctionality and cytokine production. Such studies suggest that glycolytic reprogramming occurs in coordination with chromatin modifications. As Treg cell stability has now been shown to be dependent on EZH2 expression, it remains to be determined if this occurs in a glycolysis-dependent manner (Fig. 2).
Interestingly, metabolism might also influence Treg cell stability through direct modulation of Foxp3 expression. Translocation of the transcription factor NFAT into the nucleus downstream of TCR stimulation is crucial for its association with the conserved noncoding sequence CNS2 region and Foxp3 promoter region65. In activated T cells, optimal NFAT activity has been shown to be dependent on reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced by Ca2+ mobilization and mitochondrial metabolism66 (Fig. 2). Additionally, glycolytic metabolites such as phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP) can also augment Ca2+ mobilization by blocking the ATPase SERCA (‘sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase’)19 (Fig. 2). Given the varying dependence of Treg cells on glycolysis and mitochondrial oxidation and increased levels of mitochondrial ROS in Treg cells16, it is plausible that glycolytic metabolites such as PEP and mitochondrial ROS might affect Foxp3 expression via the modulation of proximal TCR signaling and NFAT activity in Treg cells.
Foxp3 is also subject to multiple post-translational modifications, as well as post-translational regulation by microRNA. Acetylation of Foxp3, which is dependent on nuclear pools of acetyl-CoA, promotes Treg cell stability, whereby the deacetylase SIRT1 directly targets Foxp3 and subsequently increases the poly-ubiquitination of Foxp3 and its proteasomal degradation. This potentially links metabolic regulation of acetyl-CoA levels with Foxp3 expression and might be particularly relevant in balancing the induction of TH17 cells versus that of Treg cells, in which reliance on fatty-acid synthesis (TH17 cells) versus FAO (iTreg cells) can directly affect acetyl-CoA levels. Notably, inhibition of SIRT1 can increase the transcriptional activity of Foxp3 in human Treg cells67–69. The activity of SIRT1 is NAD+ dependent, and it is possible that SIRT1-dependent degradation of Foxp3 is linked to glycolytic flux, in which NAD+ is regenerated from the fermentation of pyruvate to lactate by metabolic enzymes, such as LDHA, that regulate the NAD+-NADH balance. The regulation of other intracellular metabolites, such as adenylates that influence AMPK activity, might influence the stability of Foxp3 as well. Whether Foxp3 expression itself can reinforce certain metabolic features that strengthen lineage stability remains to be demonstrated. It is interesting that the gene encoding phosphodiesterase PDE3B, which functions to hydrolyze cAMP and cGMP, has been shown to be one of the Foxp3 targets most downregulated in Treg cells70. Although the functional consequences of this are not entirely known, it has been suggested that repression of PDE3B is important for the proliferative fitness of Treg cells and their expression of a set of mitochondrial and biosynthetic proteins.
In addition to having a crucial intracellular role, bioenergetic intermediates such as NAD+ and ATP can also be released during cell damage and inflammation, in which they can activate the P2X7 (P2 purinergic) receptors that have high expression on Treg cells and thus compromise their function and survival71. Conversely, Treg cells, via the pathway of the ATP ectonucleotidase CD39 and the extracellular AMP nucleotidase CD73, are able to metabolize extracellular ATP to adenosine that can bind to adenosine receptors (such as A2AR) on responding conventional T cells and inhibit their function28. Together these findings suggest that both intracellular metabolic mediators and extracellular metabolic mediators can modulate the homeostasis and function of Treg cells (Table 1).
Modulating Treg cell function by manipulating metabolism
The field of immunometabolism is growing at an exponential rate, and delineation of the different utilization of metabolic pathways by distinct subsets of T cells, including Treg cells, suggests the exciting possibility that this might provide a means for subset-specific targeting (Table 1). In the context of transplantation, blocking glycolysis and glutamine metabolism with 2-DG and the glutamine analog DON, respectively, and promoting FAO with metformin prevents the rejection of skin and heart allografts, probably through ablation of all lymphocyte proliferation20. With the benefit of greater preservation of immunological function, drugs such as metformin and acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors have been shown to ‘preferentially’ enhance pTreg cell differentiation while blocking TH1 or TH17 differentiation in autoimmune mouse models of allergic asthma and experimental autoimmune encephalitis, respectively14. Along similar lines, blocking glycolysis via 2-DG or by inhibition of PDHK can selectively impair Teff cells and improve Treg cell function in experimental autoimmune encephalitis16,17 (Table 1).
In situations in which blocking Treg cell function is desirable, such as in the tumor microenvironment, much attention has been focused on the role of PI(3)K-Akt in Treg cells. A published study has suggested that Treg cells are induced in response to apoptotic tumor cells in an IDO-dependent manner and block Teff cell–mediated tumor elimination47. In this setting, pharmacological inhibition of either IDO or PTEN is associated with loss of Foxo3a (a target of Akt), Treg cell destabilization and rapid tumor regression47. Unexpectedly, expression of an Akt-insensitive mutant of Foxo1 that is constitutively retained in the nucleus has been shown to ‘preferentially’ ablate tumor-infiltrating and non–lymphoid-tissue activated Treg cells and thereby lead to enhanced anti-tumor responses by CD8+ T cells. This suggests that an alternative outcome might follow PI(3)K blockade under certain contexts in which retention of Foxo1 in the nucleus of Treg cells could potentially lead to their functional disruption72.
Concluding remarks
It is apparent from the literature reviewed above that while the understanding of Treg cell metabolism has progressed substantially in only a few years, much remains unknown. While genetic targeting of mice has yielded a great deal of new information, an obvious limitation is the extent to which mouse Treg cells and human Treg cells might differ from each other in their use of, and dependence on, distinct metabolic pathways. Additionally, the majority of studies so far have assessed Treg cell metabolism during differentiation or responses in vitro; it is certainly possible that metabolism in vivo differs from that in vitro due to various contextual features, such as cytokines, antigenic competition, tissue hypoxia and so on. Moreover, Treg cell metabolism in vivo varies by the site and type of immune response. Such plasticity of metabolism might be an important consideration in the design of approaches to target Treg cells or their subpopulations for immunomodulation. Finally, a limitation of many in vivo models is their frequent inability to distinguish between effects on tTreg cells and those on pTreg cells, which represents a key point, as data increasingly suggest that these two populations might act very differently from a metabolic standpoint. The use of pharmacological agents to manipulate metabolism in animals is an important step forward in the development of clinically relevant strategies, with the understanding, of course, that such drugs probably have effects on all lymphocyte populations, not just Treg cells.
Thus, the setting of ex vivo Treg cell population expansion and adoptive immunotherapy might be an ideal one in which to begin to apply immunomodulatory strategies. Such an approach has been used in an adoptive-transfer model of tumor-specific T cells in which limiting glycolysis during in vitro proliferation was shown to enhance in vivo persistence and anti-tumor efficacy73. The advent of genetic manipulation by CRISPR-based technologies presents an additional opportunity for the cell-specific manipulation of genes encoding products that control metabolic pathways as well, as might prove useful in enhancing the effectiveness of chimeric-antigen-receptor-based T cell therapies74. At present, this would need to be done in the adoptive-cell-therapy setting, but if in vivo cell-specific CRISPR targeting can be developed, then direct in situ approaches might prove possible one day.
Acknowledgments
We thank B. Blazar, J. Bluestone, H. Chi, J. Rathmell and members of the Turka laboratory for discussions. Supported by the US National Institutes of Health (P01-HL018646 to L.A.T. and B.P., and T32-AI007529 to R.N.).
Footnotes
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.Yadav M, Stephan S, Bluestone JA. Peripherally induced tregs—role in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Front Immunol. 2013;4:232. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Abbas AK, et al. Regulatory T cells: recommendations to simplify the nomenclature. Nat Immunol. 2013;14:307–308. doi: 10.1038/ni.2554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Curotto de Lafaille MA, Lafaille JJ. Natural and adaptive foxp3+ regulatory T cells: more of the same or a division of labor? Immunity. 2009;30:626–635. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ohkura N, et al. T cell receptor stimulation-induced epigenetic changes and Foxp3 expression are independent and complementary events required for Treg cell development. Immunity. 2012;37:785–799. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Maloy KJ, Powrie F. Fueling regulation: IL-2 keeps CD4+ Treg cells fit. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1071–1072. doi: 10.1038/ni1105-1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. A function for interleukin 2 in Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1142–1151. doi: 10.1038/ni1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.D’Cruz LM, Klein L. Development and function of agonist-induced CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the absence of interleukin 2 signaling. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1152–1159. doi: 10.1038/ni1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pollizzi KN, Powell JD. Integrating canonical and metabolic signalling programmes in the regulation of T cell responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14:435–446. doi: 10.1038/nri3701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang R, et al. The transcription factor Myc controls metabolic reprogramming upon T lymphocyte activation. Immunity. 2011;35:871–882. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.09.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pearce EL, Poffenberger MC, Chang CH, Jones RG. Fueling immunity: insights into metabolism and lymphocyte function. Science. 2013;342:1242454. doi: 10.1126/science.1242454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.van der Windt GJ, et al. Mitochondrial respiratory capacity is a critical regulator of CD8+ T cell memory development. Immunity. 2012;36:68–78. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.12.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pearce EL, et al. Enhancing CD8 T-cell memory by modulating fatty acid metabolism. Nature. 2009;460:103–107. doi: 10.1038/nature08097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Michalek RD, et al. Cutting edge: distinct glycolytic and lipid oxidative metabolic programs are essential for effector and regulatory CD4+ T cell subsets. J Immunol. 2011;186:3299–3303. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Berod L, et al. De novo fatty acid synthesis controls the fate between regulatory T and T helper 17 cells. Nat Med. 2014;20:1327–1333. doi: 10.1038/nm.3704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chang CH, et al. Posttranscriptional control of T cell effector function by aerobic glycolysis. Cell. 2013;153:1239–1251. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gerriets VA, et al. Metabolic programming and PDHK1 control CD4+ T cell subsets and inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:194–207. doi: 10.1172/JCI76012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shi LZ, et al. HIF1alpha-dependent glycolytic pathway orchestrates a metabolic checkpoint for the differentiation of TH17 and Treg cells. J Exp Med. 2011;208:1367–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.20110278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zeng H, et al. mTORC1 couples immune signals and metabolic programming to establish Treg-cell function. Nature. 2013;499:485–490. doi: 10.1038/nature12297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ho PC, et al. Phosphoenolpyruvate is a metabolic checkpoint of anti-tumor t cell responses. Cell. 2015;162:1217–1228. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lee CF, et al. Preventing allograft rejection by targeting immune metabolism. Cell Reports. 2015;13:760–770. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.09.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Procaccini C, et al. The proteomic landscape of human ex vivo regulatory and conventional T cells reveals specific metabolic requirements. Immunity. 2016;44:406–421. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.01.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Klysz D, et al. Glutamine-dependent α-ketoglutarate production regulates the balance between T helper 1 cell and regulatory T cell generation. Sci Signal. 2015;8:ra97. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aab2610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sinclair LV, et al. Control of amino-acid transport by antigen receptors coordinates the metabolic reprogramming essential for T cell differentiation. Nat Immunol. 2013;14:500–508. doi: 10.1038/ni.2556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nakaya M, et al. Inflammatory T cell responses rely on amino acid transporter ASCT2 facilitation of glutamine uptake and mTORC1 kinase activation. Immunity. 2014;40:692–705. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.04.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mezrich JD, et al. An interaction between kynurenine and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor can generate regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2010;185:3190–3198. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Opitz CA, et al. An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature. 2011;478:197–203. doi: 10.1038/nature10491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Buck MD, O’Sullivan D, Pearce EL. T cell metabolism drives immunity. J Exp Med. 2015;212:1345–1360. doi: 10.1084/jem.20151159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Priyadharshini B, Turka LA. T-cell energy metabolism as a controller of cell fate in transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2015;20:21–28. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cui G, et al. IL-7-induced glycerol transport and TAG synthesis promotes memory CD8+ T cell longevity. Cell. 2015;161:750–761. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.O’Sullivan D, et al. Memory CD8+ T cells use cell-intrinsic lipolysis to support the metabolic programming necessary for development. Immunity. 2014;41:75–88. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cipolletta D, et al. PPAR-γ is a major driver of the accumulation and phenotype of adipose tissue Treg cells. Nature. 2012;486:549–553. doi: 10.1038/nature11132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zeng H, Chi H. Metabolic control of regulatory T cell development and function. Trends Immunol. 2015;36:3–12. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2014.08.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Burzyn D, Benoist C, Mathis D. Regulatory T cells in nonlymphoid tissues. Nat Immunol. 2013;14:1007–1013. doi: 10.1038/ni.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Procaccini C, et al. An oscillatory switch in mTOR kinase activity sets regulatory T cell responsiveness. Immunity. 2010;33:929–941. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.11.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Procaccini C, Galgani M, De Rosa V, Matarese G. Intracellular metabolic pathways control immune tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2012;33:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Feuerer M, et al. Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters. Nat Med. 2009;15:930–939. doi: 10.1038/nm.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Arpaia N, et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature. 2013;504:451–455. doi: 10.1038/nature12726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Smith PM, et al. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science. 2013;341:569–573. doi: 10.1126/science.1241165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Furusawa Y, et al. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature. 2013;504:446–450. doi: 10.1038/nature12721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yang K, Neale G, Green DR, He W, Chi H. The tumor suppressor Tsc1 enforces quiescence of naive T cells to promote immune homeostasis and function. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:888–897. doi: 10.1038/ni.2068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Macintyre AN, et al. The glucose transporter Glut1 is selectively essential for CD4 T cell activation and effector function. Cell Metab. 2014;20:61–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cobbold SP, et al. Infectious tolerance via the consumption of essential amino acids and mTOR signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:12055–12060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903919106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Finlay DK, et al. Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 controls migration and malignant transformation but not cell growth and proliferation in PTEN-null lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 2009;206:2441–2454. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Newton RH, et al. Suppression of T-cell lymphomagenesis in mice requires PTEN phosphatase activity. Blood. 2015;125:852–855. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-571372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Huynh A, et al. Control of PI(3) kinase in Treg cells maintains homeostasis and lineage stability. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:188–196. doi: 10.1038/ni.3077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Delgoffe GM, et al. Stability and function of regulatory T cells is maintained by a neuropilin-1-semaphorin-4a axis. Nature. 2013;501:252–256. doi: 10.1038/nature12428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sharma MD, et al. The PTEN pathway in Tregs is a critical driver of the suppressive tumor microenvironment. Sci Adv. 2015;1:e1500845. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Patsoukis N, et al. PD-1 alters T-cell metabolic reprogramming by inhibiting glycolysis and promoting lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6692. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Haxhinasto S, Mathis D, Benoist C. The AKT-mTOR axis regulates de novo differentiation of CD4+Foxp3+ cells. J Exp Med. 2008;205:565–574. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kerdiles YM, et al. Foxo transcription factors control regulatory T cell development and function. Immunity. 2010;33:890–904. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ouyang W, et al. Foxo proteins cooperatively control the differentiation of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:618–627. doi: 10.1038/ni.1884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ouyang W, et al. Novel Foxo1-dependent transcriptional programs control Treg cell function. Nature. 2012;491:554–559. doi: 10.1038/nature11581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rao RR, Li Q, Gubbels Bupp MR, Shrikant PA. Transcription factor Foxo1 represses T-bet-mediated effector functions and promotes memory CD8+ T cell differentiation. Immunity. 2012;36:374–387. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.01.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tejera MM, Kim EH, Sullivan JA, Plisch EH, Suresh M. FoxO1 controls effector-to-memory transition and maintenance of functional CD8 T cell memory. J Immunol. 2013;191:187–199. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Shackelford DB, Shaw RJ. The LKB1-AMPK pathway: metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:563–575. doi: 10.1038/nrc2676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Blagih J, et al. The energy sensor AMPK regulates T cell metabolic adaptation and effector responses in vivo. Immunity. 2015;42:41–54. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.12.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Michalek RD, et al. Estrogen-related receptor-α is a metabolic regulator of effector T-cell activation and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:18348–18353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1108856108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wei J, et al. Autophagy enforces functional integrity of regulatory T cells by coupling environmental cues and metabolic homeostasis. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:277–285. doi: 10.1038/ni.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Feng Y, et al. Control of the inheritance of regulatory T cell identity by a cis element in the Foxp3 locus. Cell. 2014;158:749–763. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.De Rosa V, et al. Glycolysis controls the induction of human regulatory T cells by modulating the expression of FOXP3 exon 2 splicing variants. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:1174–1184. doi: 10.1038/ni.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Dang EV, et al. Control of TH17/Treg balance by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell. 2011;146:772–784. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Clambey ET, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 α-dependent induction of FoxP3 drives regulatory T-cell abundance and function during inflammatory hypoxia of the mucosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:E2784–E2793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1202366109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.DuPage M, et al. The chromatin-modifying enzyme Ezh2 is critical for the maintenance of regulatory T cell identity after activation. Immunity. 2015;42:227–238. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.01.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Zhao E, et al. Cancer mediates effector T cell dysfunction by targeting microRNAs and EZH2 via glycolysis restriction. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:95–103. doi: 10.1038/ni.3313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Li X, Liang Y, LeBlanc M, Benner C, Zheng Y. Function of a Foxp3 cis-element in protecting regulatory T cell identity. Cell. 2014;158:734–748. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Sena LA, et al. Mitochondria are required for antigen-specific T cell activation through reactive oxygen species signaling. Immunity. 2013;38:225–236. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.10.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.van Loosdregt J, et al. Regulation of Treg functionality by acetylation-mediated Foxp3 protein stabilization. Blood. 2010;115:965–974. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-207118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.van Loosdregt J, et al. Rapid temporal control of Foxp3 protein degradation by sirtuin-1. PLoS One. 2011;6:e19047. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Wellen KE, et al. ATP-citrate lyase links cellular metabolism to histone acetylation. Science. 2009;324:1076–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.1164097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Gavin MA, et al. Foxp3-dependent programme of regulatory T-cell differentiation. Nature. 2007;445:771–775. doi: 10.1038/nature05543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Hubert S, et al. Extracellular NAD+ shapes the Foxp3+ regulatory T cell compartment through the ART2-P2X7 pathway. J Exp Med. 2010;207:2561–2568. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Luo CT, Liao W, Dadi S, Toure A, Li MO. Graded Foxo1 activity in Treg cells differentiates tumour immunity from spontaneous autoimmunity. Nature. 2016;529:532–536. doi: 10.1038/nature16486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Sukumar M, et al. Inhibiting glycolytic metabolism enhances CD8+ T cell memory and antitumor function. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:4479–4488. doi: 10.1172/JCI69589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kawalekar OU, et al. Distinct signaling of coreceptors regulates specific metabolism pathways and impacts memory development in CAR T cells. Immunity. 2016;44:380–390. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Deaglio S, et al. Adenosine generation catalyzed by CD39 and CD73 expressed on regulatory T cells mediates immune suppression. J Exp Med. 2007;204:1257–1265. doi: 10.1084/jem.20062512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Borsellino G, et al. Expression of ectonucleotidase CD39 by Foxp3+ Treg cells: hydrolysis of extracellular ATP and immune suppression. Blood. 2007;110:1225–1232. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-12-064527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Leone RD, Lo YC, Powell JD. A2aR antagonists: Next generation checkpoint blockade for cancer immunotherapy. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2015;13:265–272. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2015.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Shrestha S, et al. Treg cells require the phosphatase PTEN to restrain TH1 and TFH cell responses. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:178–187. doi: 10.1038/ni.3076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Bian L, et al. Dichloroacetate alleviates development of collagen II-induced arthritis in female DBA/1 mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11:R132. doi: 10.1186/ar2799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Thebault P, et al. Role of IFNγ in allograft tolerance mediated by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by induction of IDO in endothelial cells. Am J Transplant. 2007;7:2472–2482. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.01960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Sundrud MS, et al. Halofuginone inhibits TH17 cell differentiation by activating the amino acid starvation response. Science. 2009;324:1334–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.1172638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Beier UH, et al. Sirtuin-1 targeting promotes Foxp3+ T-regulatory cell function and prolongs allograft survival. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31:1022–1029. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01206-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Tao R, et al. Deacetylase inhibition promotes the generation and function of regulatory T cells. Nat Med. 2007;13:1299–1307. doi: 10.1038/nm1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Price NL, et al. SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab. 2012;15:675–690. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Gatza E, et al. Manipulating the bioenergetics of alloreactive T cells causes their selective apoptosis and arrests graft-versus-host disease. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:67ra8. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Byersdorfer CA, et al. Effector T cells require fatty acid metabolism during murine graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2013;122:3230–3237. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-04-495515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]