Abstract
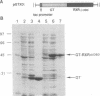
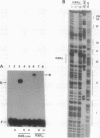
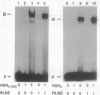
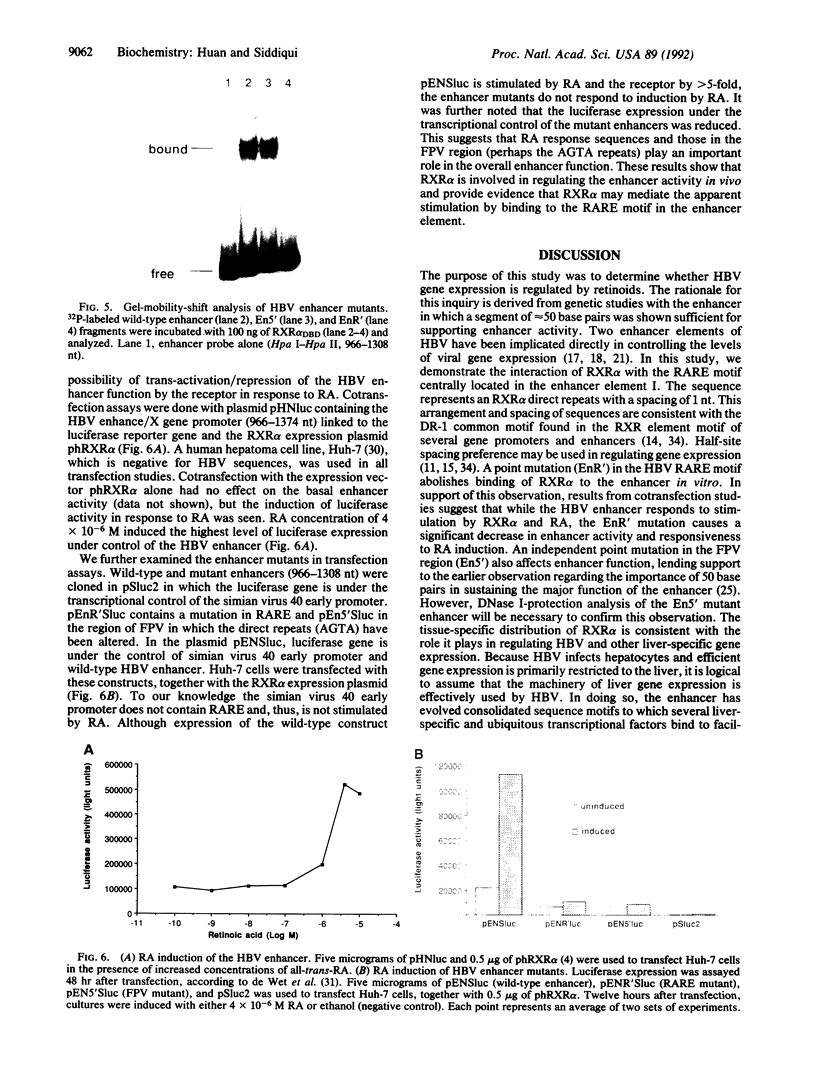
A retinoid X receptor (RXR) response element was located within the functionally defined hepatitis B virus (HBV) enhancer element. A short segment of the enhancer that contains this region has been shown with genetic analysis to play a key role in the regulation of enhancer function and to represent a major determinant of liver-specific activity. Both the full-length protein and the DNA-binding domain of the liver-specific receptor RXR alpha bound to the putative retinoic acid response element in the HBV enhancer. In vivo, an HBV enhancer-reporter gene construct responds to induction with retinoic acid when cotransfected with an RXR alpha expression vector. A single-base transition (G----A) in the HBV retinoic acid response element leads to a dramatic reduction both in the in vitro binding activity of RXR alpha and the in vivo activity of the HBV enhancer. Thus, retinoic acid and the RXR alpha are implicated as being significant determinants in the liver-specific regulation of HBV gene expression and the resultant disease pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Patel L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2118682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Levy R., Faktor O., Berger I., Shaul Y. Cellular factors that interact with the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1804–1809. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejean A., Bougueleret L., Grzeschik K. H., Tiollais P. Hepatitis B virus DNA integration in a sequence homologous to v-erb-A and steroid receptor genes in a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):70–72. doi: 10.1038/322070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duester G., Shean M. L., McBride M. S., Stewart M. J. Retinoic acid response element in the human alcohol dehydrogenase gene ADH3: implications for regulation of retinoic acid synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1638–1646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada K., Gleason S. L., Levi B. Z., Hirschfeld S., Appella E., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP, a member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that binds to both the regulatory element of major histocompatibility class I genes and the estrogen response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8289–8293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Stein R. B., Eichele G., Evans R. M., Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90479-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu K. Q., Siddiqui A. Regulation of the hepatitis B virus gene expression by the enhancer element I. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):721–726. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90906-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor-COUP-TF interactions modulate retinoic acid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1448–1452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Kuang A., Gifford A., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B protein purification from bovine spleen: nucleotide stimulation and binding site specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8825–8829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Umesono K., Kliewer S. A., Borgmeyer U., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. A direct repeat in the cellular retinol-binding protein type II gene confers differential regulation by RXR and RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Taketa K., Miyano K., Yamane T., Sato J. Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res. 1982 Sep;42(9):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K. Luciferase reporter gene vectors for analysis of promoters and enhancers. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostapchuk P., Scheirle G., Hearing P. Binding of nuclear factor EF-C to a functional domain of the hepatitis B virus enhancer region. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2787–2797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel N. U., Jameel S., Isom H., Siddiqui A. Interactions between nuclear factors and the hepatitis B virus enhancer. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5293–5301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5293-5301.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottman J. N., Widom R. L., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V., Karathanasis S. K. A retinoic acid-responsive element in the apolipoprotein AI gene distinguishes between two different retinoic acid response pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3814–3820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Rutter W. J., Laub O. A human hepatitis B viral enhancer element. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):427–430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerbell D., Maden M. Retinoic acid, a developmental signalling molecule. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Apr;13(4):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90006-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo M. A., Letovsky J., Maguire H. F., Lopez-Cabrera M., Siddiqui A. Functional analysis of a liver-specific enhancer of the hepatitis B virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3797–3801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang N., Schüle R., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Characterization of DNA binding and retinoic acid binding properties of retinoic acid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3559–3563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee J. K. A liver-specific enhancer in the core promoter region of human hepatitis B virus. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):658–661. doi: 10.1126/science.2554495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]