Abstract
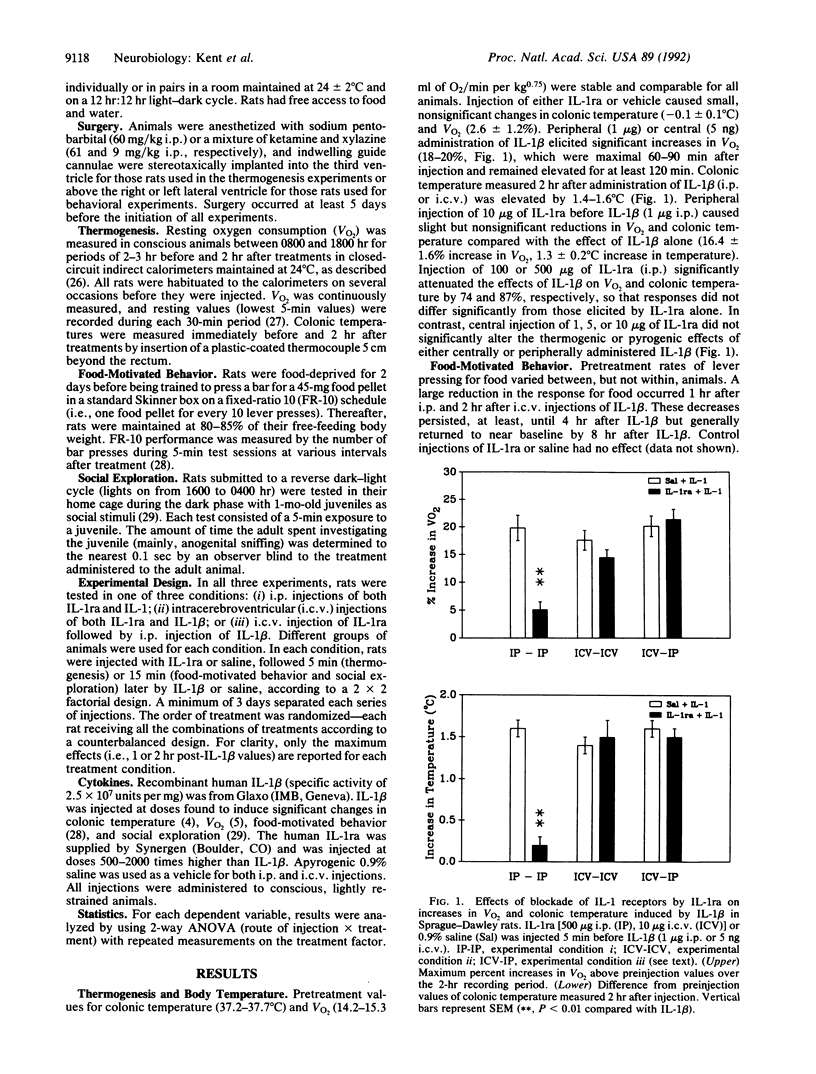
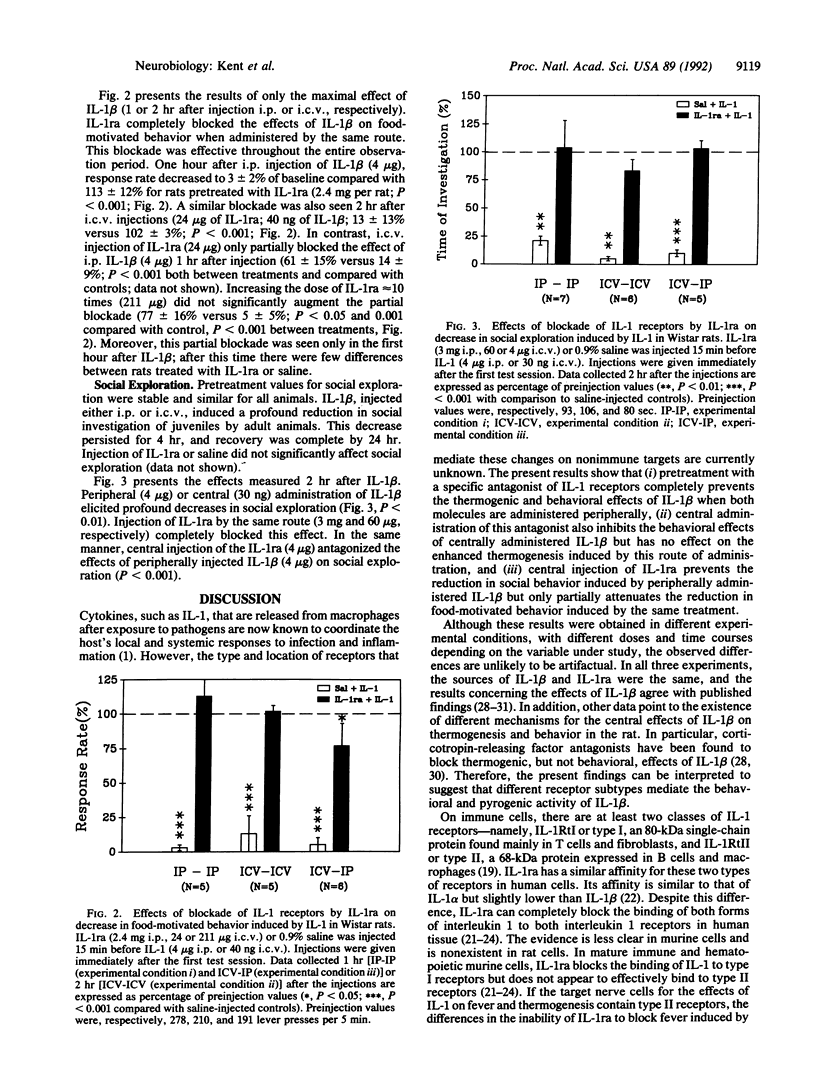
Interleukin 1 (IL-1) is a cytokine released during immune activation that mediates the host's response to infection and inflammation. Peripheral and central injections of IL-1 induce fever and sickness behavior, including decreased food motivation and reduced interest in social activities. To determine the receptor mechanisms responsible for these effects, rats were injected with IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra), an endogenous cytokine that acts as a pure antagonist of IL-1 receptors. IL-1ra blocked the increased body temperature and oxygen consumption induced by injection of recombinant human IL-1 only when both cytokines were administered i.p. In contrast, i.p. or intracerebroventricular administration of IL-1ra blocked the depressive effect of IL-1 beta on food-motivated behavior and social exploration when this cytokine was administered by the same route as the antagonist. In addition, intracerebroventricular IL-1ra blocked the reduction in social exploration produced by i.p. IL-1 beta but had only partial antagonist effects on the decrease in food-motivated behavior induced by i.p. IL-1 beta. In each case, the dose of IL-1ra was 100- to 1000-fold in excess of the biologically active dose of IL-1. These results suggest that the receptor mechanisms that mediate the behavioral and pyrogenic effects of IL-1 are heterogeneous.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Welgus H. G., Thompson R. C., Eisenberg S. P. Biological properties of recombinant human monocyte-derived interleukin 1 receptor antagonist. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1694–1697. doi: 10.1172/JCI114622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandtlow C. E., Meyer M., Lindholm D., Spranger M., Heumann R., Thoenen H. Regional and cellular codistribution of interleukin 1 beta and nerve growth factor mRNA in the adult rat brain: possible relationship to the regulation of nerve growth factor synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1701–1711. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkenbosch F., van Oers J., del Rey A., Tilders F., Besedovsky H. Corticotropin-releasing factor-producing neurons in the rat activated by interleukin-1. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):524–526. doi: 10.1126/science.2443979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatteis C. M., Bealer S. L., Hunter W. S., Llanos-Q J., Ahokas R. A., Mashburn T. A., Jr Suppression of fever after lesions of the anteroventral third ventricle in guinea pigs. Brain Res Bull. 1983 Nov;11(5):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(83)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breder C. D., Dinarello C. A., Saper C. B. Interleukin-1 immunoreactive innervation of the human hypothalamus. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):321–324. doi: 10.1126/science.3258444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chizzonite R., Truitt T., Kilian P. L., Stern A. S., Nunes P., Parker K. P., Kaffka K. L., Chua A. O., Lugg D. K., Gubler U. Two high-affinity interleukin 1 receptors represent separate gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8029–8033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Lees J., Dinarello C. A. Occurrence of interleukin-1 in cerebrospinal fluid of the conscious cat. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 19;446(2):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90883-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzer R., Bluthe R. M., Kelley K. W. Androgen-dependent vasopressinergic neurotransmission attenuates interleukin-1-induced sickness behavior. Brain Res. 1991 Aug 23;557(1-2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90123-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzer R., Kelley K. W. Stress and immunity: an integrated view of relationships between the brain and the immune system. Life Sci. 1989;44(26):1995–2008. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dripps D. J., Verderber E., Ng R. K., Thompson R. C., Eisenberg S. P. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist binds to the type II interleukin-1 receptor on B cells and neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20311–20315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Evans R. J., Arend W. P., Verderber E., Brewer M. T., Hannum C. H., Thompson R. C. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of a human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):341–346. doi: 10.1038/343341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Weber E., Dayer J. M. Synthesis of interleukin 1/endogenous pyrogen in the brain of endotoxin-treated mice: a step in fever induction? J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1696–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannum C. H., Wilcox C. J., Arend W. P., Joslin F. G., Dripps D. J., Heimdal P. L., Armes L. G., Sommer A., Eisenberg S. P., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity of a human interleukin-1 inhibitor. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):336–340. doi: 10.1038/343336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B. L. Biological basis of the behavior of sick animals. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1988 Summer;12(2):123–137. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(88)80004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerstein M. K., Meydani S. N., Meydani M., Wu K., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1-induced anorexia in the rat. Influence of prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):228–235. doi: 10.1172/JCI114145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Nagata S., Ago Y., Takahashi K., Karibe M. The central inhibitory effect of interleukin-1 on gastric acid secretion. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Oct 30;119(1):114–117. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90769-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuura G., Arimura A., Koves K., Gottschall P. E. Involvement of organum vasculosum of lamina terminalis and preoptic area in interleukin 1 beta-induced ACTH release. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):E163–E171. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.1.E163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent S., Bluthé R. M., Kelley K. W., Dantzer R. Sickness behavior as a new target for drug development. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jan;13(1):24–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90012-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluger M. J. Fever: role of pyrogens and cryogens. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jan;71(1):93–127. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. M., Walter J., Dinarello C. A., Wolff S. M., Chedid L. Sleep-promoting effects of endogenous pyrogen (interleukin-1). Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):R994–R999. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.6.R994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechan R. M., Toni R., Clark B. D., Cannon J. G., Shaw A. R., Dinarello C. A., Reichlin S. Immunoreactive interleukin-1 beta localization in the rat forebrain. Brain Res. 1990 Apr 23;514(1):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90445-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. O., Kluger M. J., Vander A. J. Effect of centrally administered interleukin-1 and endotoxin on food intake of fasted rats. Physiol Behav. 1986;36(4):745–749. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(86)90363-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre K. W., Stepan G. J., Kolinsky K. D., Benjamin W. R., Plocinski J. M., Kaffka K. L., Campen C. A., Chizzonite R. A., Kilian P. L. Inhibition of interleukin 1 (IL-1) binding and bioactivity in vitro and modulation of acute inflammation in vivo by IL-1 receptor antagonist and anti-IL-1 receptor monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):931–939. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan C. J., Slack J. L., Mosley B., Cosman D., Lupton S. D., Brunton L. L., Grubin C. E., Wignall J. M., Jenkins N. A., Brannan C. I. A novel IL-1 receptor, cloned from B cells by mammalian expression, is expressed in many cell types. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2821–2832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07831.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Björk P., Bergenfeldt M., Hageman R., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist reduces mortality from endotoxin shock. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):550–552. doi: 10.1038/348550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opp M. R., Krueger J. M. Interleukin 1-receptor antagonist blocks interleukin 1-induced sleep and fever. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 2):R453–R457. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1991.260.2.R453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A., Olafsson A. S., Lancaster C., Zhang W. R. Interleukin-1 is cytoprotective, antisecretory, stimulates PGE2 synthesis by the stomach, and retards gastric emptying. Life Sci. 1991;48(2):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90405-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J. CRF is involved in the pyrogenic and thermogenic effects of interleukin 1 beta in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):E111–E115. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.1.E111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J. Mechanisms of the pyrogenic actions of cytokines. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1990 Oct-Nov;1(4):211–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky R., Rivier C., Yamamoto G., Plotsky P., Vale W. Interleukin-1 stimulates the secretion of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.2821621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Klein-Nulend J., Alander C., Thompson R. C., Dayer J. M., Raisz L. G. Natural and recombinant human IL-1 receptor antagonists block the effects of IL-1 on bone resorption and prostaglandin production. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4181–4184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt J. T. Prostaglandin E as the neural mediator of the febrile response. Yale J Biol Med. 1986 Mar-Apr;59(2):137–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock M. J. An automatic, closed-circuit oxygen consumption apparatus for small animals. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Nov;39(5):849–850. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.5.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Tracey D. E., Mitchell W. M., De Souza E. B. Interleukin-1 receptors in mouse brain: characterization and neuronal localization. Endocrinology. 1990 Dec;127(6):3070–3078. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-6-3070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara A., Ishikawa Y., Okumura T., Okamura K., Sekiya C., Takasugi Y., Namiki M. Indomethacin blocks the anorexic action of interleukin-1. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 7;170(3):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90546-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



