Abstract
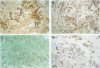
AIMS: To evaluate the performance of an immunoperoxidase stain using the monoclonal antibody EB-A1 to detect Aspergillus species in formalin fixed, paraffin wax embedded tissue. METHODS: The monoclonal antibody EB-A1 directed against galactomannan was used to detect Aspergillus species in 23 patients with suspected or confirmed invasive aspergillosis. Immunostaining was performed on formalin fixed, paraffin wax embedded tissue using the streptavidin-biotin method and compared with conventional haematoxylin and eosin, periodic acid-Schiff, and Gomori-Grocott stains. Results of immunostaining were semiquantitatively analysed with regard to both intensity of staining and number of positively staining micro-organisms. Tissue sections from 16 patients with confirmed invasive mycoses due to Candida species, Apophysomyces elegans, Rhizopus oryzae, Pseudallescheria boydii and Histoplasma capsulatum were used as controls. RESULTS: In 19 (83%) of 23 cases invasive aspergillosis was confirmed by both histological examination and culture (18 Aspergillus fumigatus and one A flavus). Immunoperoxidase stains were positive in 17 (89%) of 19 cases including one case of disseminated infection due to A flavus. Furthermore, the immunoperoxidase stain was positive in a culture negative tissue section with histological evidence of mycelial development, indicating the presence of Aspergillus species. Some cross-reactivity was observed with the highly related fungus P boydii, although the number of mycelial elements that stained was low. CONCLUSIONS: Immunoperoxidase staining using the monoclonal antibody EB-A1 performs well on routinely processed tissue sections and permits detection and generic identification of Aspergillus species, although it was no better than conventional histopathology in identifying the presence of an infection. An additional advantage is that the immunostain may help to provide an aetiological diagnosis when cultures remain negative.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anaissie E. J., Bodey G. P., Rinaldi M. G. Emerging fungal pathogens. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;8(4):323–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01963467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrese Estrada J., Stynen D., Goris A., Piérard G. E. Identification immunohistochimique des Aspergillus par l'anticorps monoclonal EB-A1. Ann Pathol. 1990;10(3):198–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrese Estrada J., Stynen D., Van Cutsem J., Piérard-Franchimont C., Piérard G. E. Immunohistochemical identification of Penicillium marneffei by monoclonal antibody. Int J Dermatol. 1992 Jun;31(6):410–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1992.tb02670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Vartivarian S. Aspergillosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 May;8(5):413–437. doi: 10.1007/BF01964057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng Z. L., Connor D. H. Progressive disseminated penicilliosis caused by Penicillium marneffei. Report of eight cases and differentiation of the causative organism from Histoplasma capsulatum. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Sep;84(3):323–327. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/84.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulshof C. M., van Zanten R. A., Sluiters J. F., van der Ende M. E., Samson R. S., Zondervan P. E., Wagenvoort J. H. Penicillium marneffei infection in an AIDS patient. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 May;9(5):370–370. doi: 10.1007/BF01973751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L. Laboratory methods for the diagnosis and confirmation of systemic mycoses. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;14 (Suppl 1):S23–S29. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.supplement_1.s23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Hayama M., Hotchi M. The application of immunoperoxidase staining for the detection of causative fungi in tissue specimens of mycosis I. Mycopathologia. 1988 May;102(2):107–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00437447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meis J. F., Kullberg B. J., Pruszczynski M., Veth R. P. Severe osteomyelitis due to the zygomycete Apophysomyces elegans. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Dec;32(12):3078–3081. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.12.3078-3081.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers W. J., Verweij P. E., van den Hurk P., van Belkum A., De Pauw B. E., Hoogkamp-Korstanje J. A., Meis J. F. General primer-mediated PCR for detection of Aspergillus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Jul;32(7):1710–1717. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.7.1710-1717.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz L. B., Ganjei P., Ziegels-Weissman J., Cleary T. J., Penneys N. S., Nadji M. Immunohistologic identification of fungi in systemic and cutaneous mycoses. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 May;110(5):433–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Veeneman G. H., van Zuylen C. W., Hoogerhout P., van Boom J. H. (1----5)-linked beta-D-galactofuranosides are immunodominant in extracellular polysaccharides of Penicillium and Aspergillus species. Mol Immunol. 1988 Oct;25(10):975–979. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips P., Weiner M. H. Invasive aspergillosis diagnosed by immunohistochemistry with monoclonal and polyclonal reagents. Hum Pathol. 1987 Oct;18(10):1015–1024. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piehl M. R., Kaplan R. L., Haber M. H. Disseminated penicilliosis in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Dec;112(12):1262–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stynen D., Goris A., Sarfati J., Latgé J. P. A new sensitive sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect galactofuran in patients with invasive aspergillosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Feb;33(2):497–500. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.2.497-500.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij P. E., Latgé J. P., Rijs A. J., Melchers W. J., De Pauw B. E., Hoogkamp-Korstanje J. A., Meis J. F. Comparison of antigen detection and PCR assay using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosing invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients receiving treatment for hematological malignancies. J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Dec;33(12):3150–3153. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.12.3150-3153.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiest P. M., Wiese K., Jacobs M. R., Morrissey A. B., Abelson T. I., Witt W., Lederman M. M. Alternaria infection in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: case report and review of invasive alternaria infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jul-Aug;9(4):799–803. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.4.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]