Abstract
Beet western yellows luteovirus, like other luteoviruses, cannot be transmitted to host plants by mechanical inoculation but requires an aphid vector, a feature that has heretofore presented a serious obstacle to the study of such viruses. In this paper we describe use of agroinfection to infect hosts with beet western yellows virus without recourse to aphids. Agroinfection is a procedure for introducing a plant virus into a host via Agrobacterium tumefaciens harboring a Ti plasmid, which can efficiently transfer a portion of the plasmid (T-DNA) to plant cells near a wound. The viral genome must be inserted into the T-DNA in such a way that it can escape and begin autonomous replication, a requirement that has, so far, limited agroinfection to pathogens with a circular genome. We have cloned cDNA corresponding to the complete beet western yellows virus RNA genome between the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter and the nopaline synthase transcription termination signal. In one construct, a self-cleaving (ribozyme) sequence was included so as to produce a transcript in planta with a 3' extremity almost identical to natural viral RNA. When inoculated mechanically to host plants, the naked plasmid DNA was not infectious but, when introduced into T-DNA and agroinfected to plants, both the construct with and without the ribozyme produced an infection. This approach should be applicable to virtually any plant virus with a linear plus-strand RNA genome.
Full text
PDF


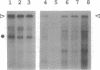
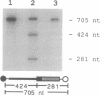
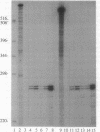
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benfey P. N., Ren L., Chua N. H. The CaMV 35S enhancer contains at least two domains which can confer different developmental and tissue-specific expression patterns. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2195–2202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M., Barnes W. M., Chilton M. D. Structure and transcription of the nopaline synthase gene region of T-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):369–385. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. Binary Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8711–8721. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commandeur U., Jarausch W., Li Y., Koenig R., Burgermeister W. cDNAs of beet necrotic yellow vein virus RNAs 3 and 4 are rendered biologically active in a plasmid containing the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):493–495. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90806-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson W. O., Beck D. L., Knorr D. A., Grantham G. L. cDNA cloning of the complete genome of tobacco mosaic virus and production of infectious transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1832–1836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derrick K. S. Quantitative assay for plant viruses using serologically specific electron microscopy. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):652–653. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzianott A. M., Bujarski J. J. Derivation of an infectious viral RNA by autolytic cleavage of in vitro transcribed viral cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4823–4827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of plus and minus RNAs of a virusoid and a structural model for the active sites. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90562-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimsley N., Hohn B., Hohn T., Walden R. "Agroinfection," an alternative route for viral infection of plants by using the Ti plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3282–3286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimsley N., Hohn T., Hohn B. Recombination in a plant virus: template-switching in cauliflower mosaic virus. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):641–646. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseloff J., Gerlach W. L. Simple RNA enzymes with new and highly specific endoribonuclease activities. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):585–591. doi: 10.1038/334585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiss E., Timpe U., Brisske-Rode A., Lesemann D. E., Casper R. Infectious in vivo transcripts of a plum pox potyvirus full-length cDNA clone containing the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S RNA promoter. J Gen Virol. 1992 Mar;73(Pt 3):709–713. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-3-709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo M. A., Robinson D. J., Jolly C. A., Hyman L. Nucleotide sequence of potato leafroll luteovirus RNA. J Gen Virol. 1989 May;70(Pt 5):1037–1051. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-5-1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. A., Waterhouse P. M., Gerlach W. L. Sequence and organization of barley yellow dwarf virus genomic RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6097–6111. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Mise K., Kobayashi K., Okuno T., Furusawa I. Infectivity of plasmids containing brome mosaic virus cDNA linked to the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S RNA promoter. J Gen Virol. 1991 Feb;72(Pt 2):243–246. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozo T., Hooykaas P. J. Electroporation of megaplasmids into Agrobacterium. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 May;16(5):917–918. doi: 10.1007/BF00015085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of RNA in the replication of small pathogens of plants and animals. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Nov;14(11):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Töpfer R., Matzeit V., Gronenborn B., Schell J., Steinbiss H. H. A set of plant expression vectors for transcriptional and translational fusions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5890–5890. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veidt I., Bouzoubaa S. E., Leiser R. M., Ziegler-Graff V., Guilley H., Richards K., Jonard G. Synthesis of full-length transcripts of beet western yellows virus RNA: messenger properties and biological activity in protoplasts. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):192–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veidt I., Lot H., Leiser M., Scheidecker D., Guilley H., Richards K., Jonard G. Nucleotide sequence of beet western yellows virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9917–9932. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaya J., Yoshioka M., Meshi T., Okada Y., Ohno T. Expression of tobacco mosaic virus RNA in transgenic plants. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Mar;211(3):520–525. doi: 10.1007/BF00425710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. J., Kelly L., Larkin P. J., Waterhouse P. M., Gerlach W. L. Infectious in vitro transcripts from a cloned cDNA of barley yellow dwarf virus. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):372–379. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90042-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Wilk F., Huisman M. J., Cornelissen B. J., Huttinga H., Goldbach R. Nucleotide sequence and organization of potato leafroll virus genomic RNA. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]