Figure 6. Therapeutic effects by E. coli probiotics include the induction of a tumor-specific CTL-response sufficient for CT26 tumor clearance, while inadequate for RenCa control.
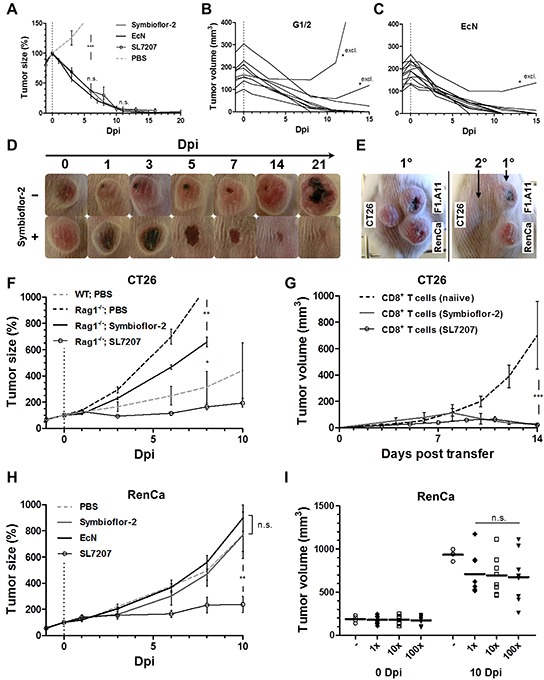
Therapeutic effects against CT26 and RenCa were evaluated upon single-dose systemic bacterial infection using E. coli probiotics. A. Kinetic of CT26 tumor regression in WT mice following systemic infection with Symbioflor-2, EcN or SL7207. B, C. CT26 tumor development profile for individual replicates infected with Symbioflor-2 representative G1/2 or EcN. Replicates marked “*excl.” were excluded from the mean in (A). D. Macroscopic profile of a regressing CT26 tumor. Representative time points and cropped images are displayed. E. Re-challenge (2°) with the same tumor cell line (CT26) upon successful CT26 tumor clearance in response to probiotic infection. A course of antibiotic treatment ensured infection resolution prior to re-challenge three months later. Concurrent primary inoculations (1°) of syngeneic tumor cell lines RenCa and F1. A11 served as controls. Day 14 post tumor inoculation is displayed. F. CT26 tumor development in Rag1−/− mice over the course of infection. G. CT26 tumor development in Rag1−/− mice reconstituted with CD8+ T cells at the time of CT26 inoculation. 3×106 CD8+ T cells were adoptively transferred from naiive or CT26 tumor bearing mice previously exposed to infection with Symbioflor-2 or SL7207, as indicated in the brackets. H. RenCa tumor development in WT mice over the course of infection with Symbioflor-2, EcN, and SL7207. I. Initial and end point tumor volume in WT mice deploying 1x, 10x, or 100x of the original infection dose of Symbioflor-2. N=6-8. Mean ± SEM.
