Abstract
Objective
So-called cold physical plasmas for biomedical applications generate reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and the latter can trigger DNA damage at high concentrations. Therefore, the mutagenic risks of a certified atmospheric pressure argon plasma jet (kINPen MED) and its predecessor model (kINPen 09) were assessed.
Methods
Inner egg membranes of fertilized chicken eggs received a single treatment with either the kINPen 09 (1.5, 2.0, or 2.5 min) or the kINPen MED (3, 4, 5, or 10 min). After three days of incubation, blood smears (panoptic May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain) were performed, and 1000 erythrocytes per egg were evaluated for the presence of polychromatic and normochromic nuclear staining as well as nuclear aberrations and binucleated cells (hen’s egg test for micronuclei induction, HET-MN). At the same time, the embryo mortality was documented. For each experiment, positive controls (cyclophosphamide and methotrexate) and negative controls (NaCl-solution, argon gas) were included. Additionally, the antioxidant potential of the blood plasma was assessed by ascorbic acid oxidation assay after treatment.
Results
For both plasma sources, there was no evidence of genotoxicity, although at the longest plasma exposure time of 10 min the mortality of the embryos exceeded 40%. The antioxidant potential in the egg’s blood plasma was not significantly reduced immediately (p = 0.32) or 1 h (p = 0.19) post exposure to cold plasma.
Conclusion
The longest plasma treatment time with the kINPen MED was 5–10 fold above the recommended limit for treatment of chronic wounds in clinics. We did not find mutagenic effects for any plasma treatment time using the either kINPen 09 or kINPen MED. The data provided with the current study seem to confirm the lack of a genotoxic potential suggesting that a veterinary or clinical application of these argon plasma jets does not pose mutagenic risks.
Introduction
Transportable cold physical plasma sources, operating in the range of the body temperature (so-called cold plasma), pose new therapeutic options in medicine. For example, high potential is seen in the treatment of chronic wounds [1–3]. The kINPen cold plasma source used in this study has been shown to generate reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) in the gas phase [4–6] that diffuse into and react with liquids [7–9] and cells [10–12]. Thus, the oxidation of proteins and lipids is considered to be the plasma’s main route of action[13]. At low concentrations, these species contribute to cell signaling [14]. At high concentrations, they are cytotoxic, effectively inducing apoptosis [15–17]. Importantly, permanent and/or excessive oxidative stress, such as smoking or extensive exposure to UV-light, is known to be mutagenic [18]. It is therefore important to understand the genotoxic risks of plasma-derived ROS/RNS before plasma can be offered as standard therapy in clinics.
The high reactivity of oxygen radicals has two reasons. Thermodynamically, they are oxidizing agents. Kinetically, oxygen radicals and many other charged gas radicals undergo one-electron reactions which are much faster than more complex redox reactions [19]. As such, highly reactive species, for example hydroxyl radicals, even oxidize seemingly inert materials such as elemental gold [20]. However, vertebrate systems are equipped with an arsenal of options for ROS/RNS detoxification [21]. Yet, this defense system can be overcome by high concentrations of reactive molecules and some in vitro studies suggested DNA damage to be present following exposure to cold plasmas [22–29]. Yet, final conclusions of these studies using non-OECD tests are somewhat limited. First, they were carried out only in cell culture models. Second, they utilized read-out system such as cytochrome C release, Comet-assay, or the ATM/ATR system that are not exclusively linked only to DNA-damage but also to general oxidative stress and apoptosis [30–32]. By contrast, mutagenicity studies carried out and according to OECD guidelines concluded a lack of permanent DNA damage following exposure to cold plasma [33, 34], also for the plasma jet used in this study [35]. Nonetheless, all studies mentioned were in vitro work, and such test models do not allow for biologically relevant conclusions in vertebrate organisms.
We utilized fertilized chicken eggs and well-described mutagenic assays of blood cells to investigate the genotoxic hazard in these eggs following exposure to two atmospheric pressure argon plasma jets. The kINPen MED was approved as a class IIa medical device. Its use is indicated for the treatment of chronic or infected wounds as well as pathogen-related diseases of the skin. Its predecessor, the kINPen 09, has previously been used for veterinary purposes and differs in terms of energy output. Using the highly-sensitive chorioallantoic membrane of fertilized chicken eggs both jets have been shown to be tolerated well, suggesting the plasma’s compatibility with tissues [36]. Studies using porcine and human tissues underlined this notion [37, 38] which was a prerequisite for first observational studies in humans [2]. To complement the risks assessment made with the kINPen MED and kINPen 09, we here investigated their genotoxic potential.
Materials and Methods
The HET-MN model
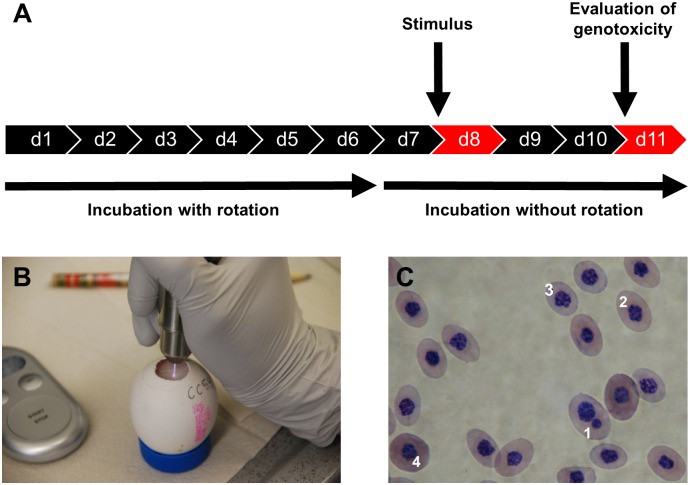
Due to lack of pain perception until day 11 of incubation [39], the hen’s egg test for micronucleus induction (HET-MN) is not classified as an animal experiment [40]. Fertilized, pathogen-free eggs were taken from Leghorn chickens (Lohmann Tierzucht, Germany). Eggs with intact shells were selected, weighted, and disinfected with 70% ethanol. Subsequently, eggs were incubated at 37.5 ± 1.0°C with a relative humidity of 62.0 ± 7.5% in a thermal incubator (J. Hemel Brutgeräte, Germany). From day one to day six, eggs were rotated automatically in a three-hour interval (Fig 1A). On day seven, they were placed in a vertical position with the blunt pole on top and further incubated without rotation. Following recent suggestions [41], the application of the test substances was carried out on day eight while blood was collected on day 11. On day eight, eggs were screened with a Powerlux-Lamp (Schier-lamp, J. Hemel Brutgeräte, Germany) for presence of blood vessels, and unfertilized eggs were sorted out. Immediately before opening the egg shell, the eggs were disinfected on the blunt pole to prevent penetration of microorganisms during preparation of the egg [42] because infection has been linked to increase embryo mortality [43]. Using the Schier-lamp, the boundaries of the air chamber were marked with a pen to prevent any violation of the inner shell membrane during the preparation process. The egg shell was carefully removed under aseptic conditions to uncover the inner egg membrane which was chosen for cold plasma application because it is considered to be very sensitive [32]. After exposure to the test agents, the egg opening was covered with a bacteria-impermeable, sterile, transparent Tegaderm dressing (3M, Germany), and incubated for three days before blood was collected to determine genotoxic effects. At the same time, embryo mortality was assessed.
Fig 1. Cold plasma treatment of the HET-MN.
(A) The experimental chronology is shown. (B) Treatment of the inner egg membrane with the kINPen MED. (C) A representative blood smear and Giemsa staining is shown. Labeling refers to micronucleated (1), normochromic (2), late polychromatic (3), and primitive (4) erythrocytes.
Cold plasma jets
Two atmospheric pressure argon plasma jets, the kINPen 09 and the kINPen MED (both neoplas, Germany), were tested. These sources were operated at a feed gas flow rate of 5 standard liters of argon per minute. In contrast to the pulsed (on:off cycle = 1:1) operation of the kINPen MED, the kINPen 09 generates its plasma in a continuous mode, resulting in higher energy densities. Operation details and parameters were previously described [44]. The gas temperatures at the typical working distance (8 mm effluent length) were 45°C for the kINPen 09 [45] and 37°C for the kINPen MED [46], respectively. Treatment was carried out manually. To ensure that during exposure the distance of either of the jets was not lower than 8 mm, an autoclavable spacer was used.
Exposure of the inner shell membrane to cold plasma or test agents
The eggs were exposed on day eight. A 72 h contact time was allowed for all substances because it yields an high MNE II-rate, a low toxicity, and a high xenobiotic metabolisms [41, 47, 48]. Moreover, we wanted to investigate the long-term effects of plasma by identifying possible mutagenic effects of a single plasma exposure regimen which exceeded the recommended application time by far [1, 46, 49]. Prior to plasma exposure (Fig 1B) and to reduce dehydration, 100 μl of 0.9% NaCl solution was applied. To account for any effect of the NaCl application alone, the solution was added to the inner membrane also immediately after (instead of before) exposure to plasma for one treatment condition (5 min, kINPen MED). Exposure times for the kINPen 09 (30 s per spot) were 1.5 min (3 spots), 2.0 min (4 spots), or 2.5 min (5 spots), and for the kINPen MED (60 s per spot) 3 min (3 spots), 4 min (4 spots), 5 min (5 spots) or 10 min (10 spots). Spots were treated manually by holding the jet steady above each spot for 30 s (kINPen 09) or 60 s (kINPen MED) without any movement and with the visible tip of the effluent touching the egg’s surface (about 10 mm for the kINPen MED and 11 mm for the kINPen 09 but not less than 8 mm which was achieved by using an autoclavable spacer). Spots were treated one after the other with the spots being 5-10 mm apart from each other with the total treatment area being about 2 cm2. Several spots were treated to prevent perforation of the sensitive egg membrane, and different treatment times per spots (30 s for the kINPen 09 and 60 s for the kINPen MED) were chosen according to the plasma’s intensity (continuous mode in the kINPen 09 vs. pulsed operation in the kINPen MED). Only the visible plasma effluent was in contact with the inner egg’s membrane (Fig 1B). Positive controls were exposed to 100 μl PBS containing either 50 μg/egg of CYP450-activated, pro-mutagenic cyclophosphamide (CAS 50-18-0; Baxter Oncology, Germany) [50], or 5μg/egg of CYP450-independent, pro-mutagenic methotrexate (CAS 59-05-2; TEVA, Germany) [51]. Negative controls were exposed to either 100 μl 0.9% NaCl alone or non-ionized argon gas (flow rate of 5 standard liters per minute). After exposure, eggs were continued to be incubated for 3 days without rotation. Eleven independent experiments were conducted with three eggs per treatment group and experiment (1.5, 2.0, 2.5 min with the kINPen 09; 3, 4, and 5 min with the kINPen MED; NaCl negative control; 5 min of argon gas alone; and cyclophosphamide positive control). Within these eleven experiments, eight experiments also included 10 min (with NaCl addition before treatment) and 5 min (with NaCl addition after treatment) of kINPen MED plasma exposure with three eggs per group and experiment. Three experiments included 10 min treatment of argon gas, and seven experiments included treatment with methotrexate, both with three eggs per group and experiment. The total number of eggs among all experimental groups is given in Table 1 with differences to the planed number of eggs being attributed to sorting out eggs that were either unfertilized or damaged during the preparation procedure.
Table 1. Frequencies of nuclear aberrations, binucleated cells, and micronucleated definite erythrocytes.
| Test Agent | kINPen Plasma (min) | Eggs (n) | Nuclear aberrations (‰) | Binucleated cells (‰) | micronucleated erythrocytes (‰): | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| polychromatic | normochromic | sum | |||||
| kINPen 09 | 1.5 | 30 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.30 + 0.79 | 0.03 + 0.18 | 0.13 + 0.35 | 0.17 + 0.38 |
| 2.0 | 30 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.29 ± 0.66 | 0.11 ± 0.31 | 0.18 ± 0.39 | 0.29 ± 0.46 | |
| 2.5 | 30 | 0.11 ± 0.31 | 0.29 ± 0.53 | 0.04 ± 0.19 | 0.21 ± 0.50 | 0.25 ± 0.52 | |
| kINPen MED (NaCl before treatment) | 3 | 29 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.61 ± 1.77 | 0.11 ± 0.31 | 0.29 ± 0.53 | 0.39 ± 0.63 |
| 4 | 29 | 0.07 ± 0.26 | 0.46 ± 1.04 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.14 ± 0.36 | 0.14 ± 0.36 | |
| 5 | 29 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.17 ± 0.38 | 0.08 ± 0.28 | 0.17 ± 0.38 | 0.25 ± 0.44 | |
| 10 | 19 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.36 ± 1.21 | 0.09 ± 0.30 | 0.18 ± 0.40 | 0.27 ± 0.47 | |
| kINPen MED (NaCl after treatment) | 5 | 19 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.24 ± 0.56 | 0.12 ± 0.33 | 0.24 ± 0.44 | 0.35 ± 0.49 |
| NaCl | - | 30 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.17 ± 0.38 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.30 ± 0.70 | 0.30 ± 0.70 |
| Argon gas only | 5 | 31 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.26 ± 0.68 | 0.03 ± 0.18 | 0.16 ± 0.73 | 0.19 ± 0.75 |
| 10 | 9 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.44 ± 1.01 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.22 ± 0.44 | 0.22 ± 0.44 | |
| Cyclophosphamide | - | 30 | 1.21 ± 1.37 | 4.31 ± 5.24 | 2.79 ± 3.27 | 9.66 ± 4.07 | 12.21 ± 6.16 |
| Methotrexate | - | 18 | 1.12 ± 1.17 | 3.29 ± 3.22 | 7.59 ± 5.09 | 1.76 ± 1.60 | 9.35 ± 5.23 |
Mean ± S.D were given for all parameters (nuclear aberrations, binucleated cells, and micronucleated erythrocytes), statistically significant differences compared to NaCl controls were only given for cyclophosphamide (p<0.001) and methotrexate (p<0.001) but not any other treatment regimen (p>0.05) as evaluated using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett post-testing.
Micronuclei test
On day 11, blood from the umbilical artery was collected using a micro-hematocrit capillary (Brand, Germany). Subsequently, blood smears and panoptic May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining were carried out [52]. For each blood smear, 1000 erythrocytes were investigated for the presence of micronuclei, nuclear aberrations, and/or binucleation using an H 500 microscope with 100x oil immersion objective (Helmut Hund, Germany). Erythrocyte staging (Fig 1C) was carried out as previously described [40, 53, 54]. The sum of micronucleated polychromatic and normochromatic definite erythrocytes was obtained and used as an index for genomic toxicity. According to Müller and Streffer [55], a micronucleus is a small nucleus present in addition to the main nucleus. Micronuclei are similar to the morphology of cell nuclei and display a round to oval form with clear borders and their size being up to one third of the diameter of the cell nucleus. Additionally, cells with nuclear aberrations and binucleated cells were counted, as they can be alert parameters for genotoxicity Cells were counted as binucleated if they showed two uniform main nuclei, whereas non-uniform multiple nuclei without a main nucleus were counted as nuclear aberrations, if not fulfilling the criteria for micronuclei [31].
The antioxidant potential (AOP) in the extra-embryonic compartment
On day 11 and immediately after exposure to control agents or 10 min of plasma treatment (kINPen MED), the inner egg’s membrane was removed and blood was collected into heparinized capillaries (Radiometer Medical, Denmark). Alternatively, collection took place 1 h after plasma treatment to account for a possible delay in oxidative processes. Day 11 was chosen because it is technically challenging to draw blood from the CAM capillaries at earlier time points whereas from day 12 on the embroy’s nervous system develops, making this approach an in vivo animal model. The early sampling time point (immediately after treatment and due to experimental handling about 10 min after exposure) was chosen because reactive species quickly react with antioxidants, making a reduced AOP in blood plasma likely. The second blood sampling time point (60 min after exposure) was chosen to investigate late alteration or even recovery of the blood’s AOP after plasma treatment. Drawing blood from the same egg multiple times is not possibility as the veins are very fragile [51]. As positive control, UV-A radiation was generated using a Spectroline EA-160/FE at 50 Hz and 0.17 A (Spectronics Corporation, USA) resulting in a final power of 6 W longwave UV-A at 365 nm (distance: 2 cm). As negative control 0.9% NaCl was applied. Capillaries were gently mixed, centrifuged at 1000 x g for 10 minutes, and the blood plasma was stored at -70°C until analysis. The water-soluble antioxidant potential was determined by measuring the blood plasma’s capability to oxidize exogenously added ascorbic acid using a PHOTOCHEM device (Analytik Jena, Germany) as previously described [56]. The eggs used for this study were not the eggs that were used to assess genotoxicity but were bred independently for this assay.
Statistics
To statistically compare the results of each, the nuclear aberrations, the number of binucleated cells, the number of micronucleated erythrocytes, and the AOP-values, one-way analysis of variances was used with Dunnett post-testing correcting for multiple comparison with *, **, and *** indicating p-values of <0.05, <0.01, and <0.001, respectively. Analysis was carried out using prism 6.07 (Graphpad software, USA).
Results
Irritation of the CAM after exposure to different test agents
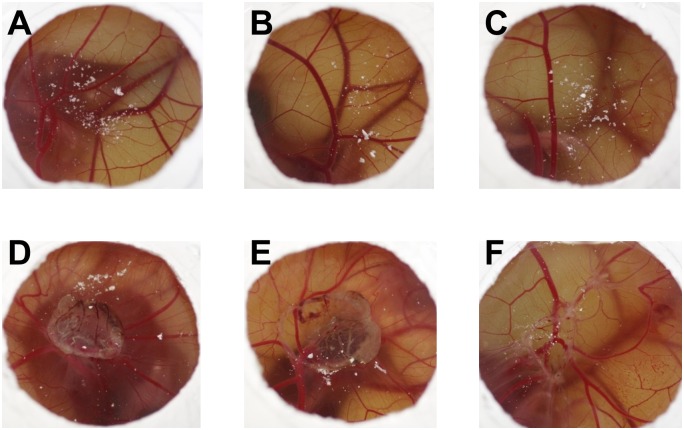
The irritation of the CAM gives a qualitative measure of disturbed tissue owing to exposure to the test agent in question (Fig 2). Three days after exposure, both the negative (0.9% NaCl solution) and the positive (cyclophosphamide and methotrexate) controls did not result in any irritation of the CAM (Fig 2A–2C). In contrast, the physical pressure of the argon gas flow alone caused disturbed tissue pattern on the CAM (Fig 2D). Plasma treatment with both the kINPen MED and kINPen 09 resulted in similar structures (Fig 2E and 2F).
Fig 2. CAM irritation of different test agents.
Given are representative images of the CAM three days after exposure to 0.9% NaCl solution (A), cyclophosphamide (B), methotrexate (C), argon gas treatment for 10 min (D), kINPen MED plasma treatment for 10 min (E), kINPen 09 plasma treatment for 2.5 min (F). D-F show hemorrhages, lysis/discoloration, coagulation (thrombus-intravascular and extravascular), and/or increased opacity.
Evaluation of the HET-MN test model
The HET-MN is a well-established system to test the genotoxicity [40]. The mutagenic agents cyclophosphamide and methotrexate have often been used as positive controls. The application of these substances yielded a mutagenic rate of micronucleated erythrocytes of 12.21 ‰ ± 6.16 ‰ and 9.35 ‰ ± 5.23 ‰, respectively (Table 1). Although thresholds and standard deviations are lab-specific, these results are about similar to what others have found [51, 57]. Nuclear aberrations and the number of binucleated cells in positive controls were significantly increased (p<0.001 for cyclophosphamide; p<0.001 for methotrexate) compared to both NaCl-treated controls and plasma-treated samples. Test validity was given as well for 0.9% NaCl solution (0.17 ‰ ± 0.38 ‰). The number of micronuclei in NaCl-treated samples (0.30 ‰ ± 0.70 ‰) was very low and comparable with that of double-distilled water in previous reports (1.00 ‰ ± 0.90 ‰) [57].
Evaluation of the mutagenicity of cold plasma generated by the kINPen
Reactive species are known to be mutagenic at very high concentrations. The plasma of the tested two types of plasma jets is ignited by using argon as feed gas. Accordingly, the argon gas was tested for its genotoxic effects (Table 1). Both treatment times (5 min and 10 min) did not induce an enhanced micronuclei formation (0.19 ± 0.75 ‰ and 0.22 ± 0.44 ‰, respectively). No nuclear aberrations were found in erythrocytes, and the frequency of binucleated cells (0.26 ± 0.68 ‰ and 0.44 ± 1.01 ‰, respectively) was significantly (p<0.001) different from positive controls. No exposure to the plasma of the kINPen 09 exceeded the micronuclei formation compared to the negative controls. Nuclear aberrations were only found for 2.5 min of treatment (0.11 ‰ ± 0.31 ‰) but were about 10 fold lower compared to the positive controls. The number of binucleated cells was similar to numbers determined in the cells of the hen’s egg receiving argon gas controls, indicating a negligible influence of the plasma itself. This was also the case for the nuclear aberrations found in erythrocytes following treatment with the kINPen MED. Similar to the kINPen 09, nuclear aberrations were not present, except in the 4 min group (0.07 ‰ ± 0.26 ‰) which was not differing significantly to the NaCl group (p = 0.16). Importantly, the number of cells with micronuclei was not significantly different from negative controls for any plasma treatment time (3–10 min). Within these samples, the highest micronuclei frequency was found to be 0.39 ± 0.63 ‰ for 3 min of plasma treatment. To reduce dehydration, NaCl solution (0.9%) was used as a negative control and for moistening purposes before or after the plasma treatment. While in the former regimen, evaporation of the water of the NaCl solution took place, positively regulating the exogenous osmotic pressure, the latter regimen was used to control for this effect. However, similar negative results between both regimes suggest such processes to be of minor importance. This was also true for CAM irritation (data not shown). Comparing the micronuclei frequencies of any plasma treatment mode to the NaCl negative control, no statistically significant difference could be found (p = 0.99). In order to eliminate possible negative effects of the kINPen plasma on erythrocytes maturation by potentially affecting the total number of micronuclei being formed, the ratio of polychromatic and normochromic erythrocytes was determined [31]. For the plasma treatment group (10 min), the ratio was calculated to be 0.79 which does not substantially differ from the accompanying negative control (0.74).
Chicken embryo viability
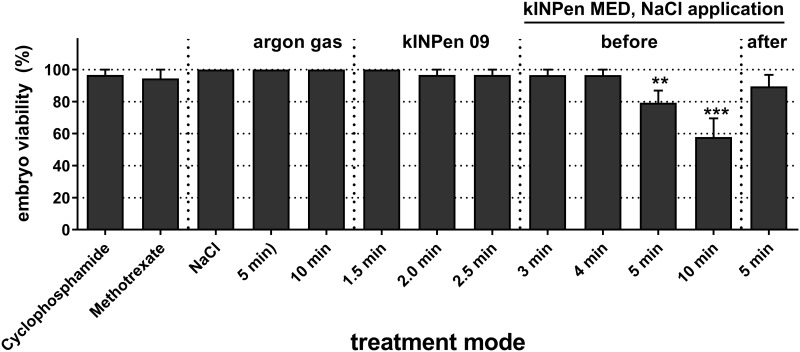
The chicken embryo viability was determined three days after application of the test agents (Fig 3). Cyclophosphamide and methotrexate showed a very modest toxicity (3–6%) whereas NaCl and argon gas treatment did not cause any chicken embryo mortality. Exposure to the plasma of kINPen 09 demonstrated a similar lethality compared to that of the positive controls. This was also true for HET-MN treatment with the kINPen MED for short exposure times (3 min and 4 min). However, longer exposure for up to 10 minutes caused acute toxicity with mortality rates of 10–42%. There was no strong difference between application of the NaCl solution before or after the plasma treatment.
Fig 3. Embryo viability following exposure to test agents.
Egg membranes were treated with different test agents. After three days, the embryo viability was determined for each group. Shown are mean values +S.E. of 11 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett post-testing.
Antioxidant potential
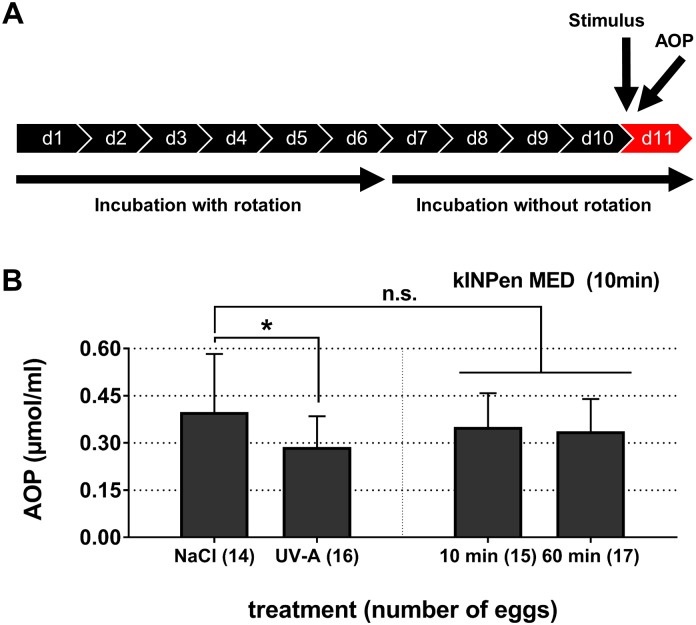
As a next step, we sought to determine whether the acute cytotoxic effect of the longer exposure times with the kINPen MED was due to excessive oxidation of the hen’s egg blood components via the plasma-derived reactive components. If such an oxidation effect would have been active systemically, we hypothesized that this should be reflected in the capacity of blood plasma to protect ascorbic acid from experimental oxidation (antioxidant potential, AOP). Irradiation of the inner shell membrane with UV-A significantly (p<0.05) decreased the AOP of blood plasma (Fig 4). By contrast, the AOP of plasma-treated embryos differed non-significantly immediately (p = 0.62) or 1 h (p = 0.40) after exposure when compared to NaCl-treated controls.
Fig 4. The antioxidant potential in blood plasma.
Chicken blood plasma was collected after cold plasma treatment, and the antioxidant potential (AOP) was measured by means of assessing the total ascorbic acid equivalents that have not been oxidized by the sample. (A) A experimental scheme is shown for investigating the blood plasma of chicken embryos that were treated with the kINPen MED. (B) AOP of blood plasma collected after treatment with 0.9% NaCl solution, UV-A, or kINPen plasma (10 min). UV-A treatment differed significantly (p<0.05) from NaCl controls whereas AOP in blood plasma 10 min (p = 0.62) or 60 min (p = 0.40) after exposure to the cold physical plasma of the kINPen MED did not (mean +S.D.).
Discussion
For the testing of cytotoxic and/or mutagenic agents, the HET-MN model takes an intermediate position between cell culture experiments and assessing effects in fully developed mammalian organisms, such as rodents. Unlike cell cultures, chicken embryos metabolically (phase I and phase II reactions) convert exogenously added substances [48], making this model more suitable to mimic systemic cytotoxic and/or genotoxic effects in complex organisms. At day eight of incubation, mainly definitive erythrocytes are present, which are formed by embryonic hematopoietic stem cells in the yolk sac [54, 58]. In the latter, biotransformation and erythropoiesis are parallel processes [48]. Up to day 13, the limited functionality of the embryonic spleen disallows a rapid phagocytosis of damaged erythrocytes or micronucleated erythrocytes [59] which makes this model suitable for genotoxic studies [60]. Further, a long exposure time of test agents is recommended to increase the sensitivity of the assay [41]. Thus, application at day eight and incubation to day 11 (72 h) was favored in the present study because it yields higher micronuclei rates, lower embryo toxicity, and higher xenobiotic metabolism [47, 48].
In contrast to red blood cells of mammalian organisms, avian erythrocytes are nucleated [61]. Accordingly, the HET-MN detects structural chromosome fragmentation and numerical aberrations. [57]. Furthermore, it should be noted that DNA repair mechanisms in avian erythrocytes are not as effective as in human cells [62, 63]. However, this can be neglected when interpreting the present results, because no genotoxic effects were evoked by cold plasma. Despite this finding, plasmas treatment adversely affected chicken embryo viability. This clinical impression was reflected by an increasing irritation of the CAM (coagulation, thrombus, and hemorrhage) and an enlarged irritation area as well as an increasing loss of viability. A slight but non-significant decrease of the AOP in the plasma group 10 min and 60 min after exposure underlined this view. In the embryo, lipid oxidation has been detected 9 h following lead injection [64] but this seems to be a rather secondary reaction whereas the plasma-derived ROS are short-lived and their effect on AOP should be apparent swiftly. Both the decrease in AOP and viability suggested that cold plasma components (atomic size: argon 0.21 nm; oxygen 0.12 nm; bond length of O, OH, 1O2, and NO ~0.1 nm; H2O2 ~0.34 nm; O3 ~0.13 nm) [65] diffused to the embryo through the inner membrane (pore size: 25 nm) [66].
The plasma’s main components, reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, can be detoxified and metabolically controlled by living cells and organisms via glutathione, for example [67]. Experimental supplementation of e.g. catalase protects cells in vitro from excessive oxidation induced by plasma [68, 69]. Also, the chicken embryo possesses strong safeguards against oxidative stress, such as ascorbic acid, α-tocopherol, carotenoid, reduced glutathione, catalase, and superoxide dismutase [70–73]. Yet, reactive species are short-lived and antioxidants need to be present locally in order to counteract the plasma-derived ROS. Moreover, the elevated mortality of chicken embryos following 10 min of kINPen MED plasma treatment suggested a limited control of toxic ROS if their concentration had exceeded a certain local threshold to act systemically, although this was not significantly reflected by AOP measurements at the early (10 min) or late (60 min) sampling time points. Hence, this read-out system may have limitations and future studies should collect the remaining liquid on the egg’s membrane or other egg material after plasma treatment to find markers indicative for ROS-stress. Yet, and assuming a treatment area of 2 cm2, it should be stressed that the long exposure times used in this study exceeded the therapeutically effective duration for the kINPen 09 (5 s per cm2) [49] 15 fold and for the kINPen MED (30–60 s per cm2) [46] 5–10 fold. As these treatment regimens did not cause significant genotoxicity they suggest the kINPen plasma not to be a mutagenic hazard within such treatment times.
However, possible limitations of our model need to be stated. Due to their high reactivity and short-lived nature, introduction of ROS/RNS into biological systems does not fit classical parameters such as bioavailability. Moreover, detecting ROS/RNS-mediated oxidation in 3D tissues is highly challenging. This also complicates the AOP-measurements in whole blood as these do not reflect tissue oxidation. Nonetheless, our provided data may add relevance as a more complex test system was used compared to other studies like Comet-assay or γ-H2AY assay in cell culture models. As future option, the investigation of red blood cells should be carried out sooner (24 h instead of 72 h) after plasma treatment to identify possible repair mechanism in the HET-MN [41].
Conclusion
Regardless of the plasma device used (kINPen 09 and kINPen MED) or the treatment time applied (1.5-10 min), no genotoxic effects of the kINPen plasma were found using the HET-MN model. Also, the global antioxidant defense was not significantly challenged following exposure to the plasma. The data provided with the current study seem to confirm the lack of a genotoxic potential, fostering its presumably safe applications in veterinary and human medicine.
Supporting Information
(XLSX)
Acknowledgments
We thank Simone Zich (Department of Internal Medicine at the University Medicine Greifswald) for the implementation of the May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining methodology.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information file.
Funding Statement
The authors acknowledge that this work was supported by grants funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF): grant numbers 13N9779 (SK, CB, HiB, AS, HaB, AK) and 03Z22DN11 (SB). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Kramer A, Lademann J, Bender C, Sckell A, Hartmann B, Münch S, et al. Suitability of tissue tolerable plasmas (TTP) for the management of chronic wounds. Clin Plas Med. 2013;1(1):11–8. 10.1016/j.cpme.2013.03.002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ulrich C, Kluschke F, Patzelt A, Vandersee S, Czaika VA, Richter H, et al. Clinical use of cold atmospheric pressure argon plasma in chronic leg ulcers: A pilot study. J Wound Care. 2015;24(5):196, 8,–200, 2–3. 10.12968/jowc.2015.24.5.196 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Isbary G, Stolz W, Shimizu T, Monetti R, Bunk W, Schmidt H-U, et al. Cold atmospheric argon plasma treatment may accelerate wound healing in chronic wounds: Results of an open retrospective randomized controlled study in vivo. Clin Plas Med. 2013;1(2):25–30. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schmidt-Bleker A, Winter J, Iseni S, Dünnbier M, Weltmann KD, Reuter S. Reactive species output of a plasma jet with a shielding gas device—combination of FTIR absorption spectroscopy and gas phase modelling. J Phys D: Appl Phys. 2014;47(14):145201 10.1088/0022-3727/47/14/145201. WOS:000333332600003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Iseni S, Zhang S, van Gessel AFH, Hofmann S, van Ham BTJ, Reuter S, et al. Nitric oxide density distributions in the effluent of an RF argon APPJ: effect of gas flow rate and substrate. New J Phys. 2014;16(12):123011 10.1088/1367-2630/16/12/123011. WOS:000346821400011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dünnbier M, Schmidt-Bleker A, Winter J, Wolfram M, Hippler R, Weltmann K, et al. Ambient air particle transport into the effluent of a cold atmospheric-pressure argon plasma jet investigated by molecular beam mass spectrometry. J Phys D: Appl Phys. 2013;46(43):435203. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bekeschus S, Kolata J, Winterbourn C, Kramer A, Turner R, Weltmann KD, et al. Hydrogen peroxide: A central player in physical plasma-induced oxidative stress in human blood cells. Free Radic Res. 2014;48(5):542–9. 10.3109/10715762.2014.892937 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tresp H, Hammer MU, Winter J, Weltmann KD, Reuter S. Quantitative detection of plasma-generated radicals in liquids by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Phys D: Appl Phys. 2013;46(43):435401 10.1088/0022-3727/46/43/435401. WOS:000325679400013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jablonowski H, and von Woedtke Th. Research on plasma medicine-relevant plasma–liquid interaction: What happened in the past five years? Clin Plas Med. 2015;3(2):42–52. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wende K, Barton A, Bekeschus S, Bundscherer L, Schmidt A, Weltmann K-D, et al. Proteomic Tools to Characterize Non-Thermal Plasma Effects in Eukaryotic Cells. Plasma Med. 2013;3(1–2):81–95. 10.1615/PlasmaMed.2014009690 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Schmidt A, von Woedtke T, Bekeschus S. Periodic Exposure of Keratinocytes to Cold Physical Plasma: An In Vitro Model for Redox-Related Diseases of the Skin. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:9816072 10.1155/2016/9816072 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bekeschus S, Masur K, Kolata J, Wende K, Schmidt A, Bundscherer L, et al. Human Mononuclear Cell Survival and Proliferation is Modulated by Cold Atmospheric Plasma Jet. Plasma Process Polym. 2013;10(8):706–13. 10.1002/ppap.201300008. WOS:000327790000005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Graves DB. The emerging role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in redox biology and some implications for plasma applications to medicine and biology. J Phys D: Appl Phys. 2012;45(26):263001 10.1088/0022-3727/45/26/263001. WOS:000305418900001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Winterbourn CC. Reconciling the chemistry and biology of reactive oxygen species. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4(5):278–86. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ahn HJ, Kim KI, Kim G, Moon E, Yang SS, Lee JS. Atmospheric-pressure plasma jet induces apoptosis involving mitochondria via generation of free radicals. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e28154 10.1371/journal.pone.0028154 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bundscherer L, and Bekeschus S, Tresp H, Hasse S, Reuter S, Weltmann K-D, et al. Viability of human blood leucocytes compared with their respective cell lines after plasma treatment. Plasma Med. 2013;3(1–2):71–80. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Weiss M, Gumbel D, Hanschmann EM, Mandelkow R, Gelbrich N, Zimmermann U, et al. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment Induces Anti-Proliferative Effects in Prostate Cancer Cells by Redox and Apoptotic Signaling Pathways. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0130350 10.1371/journal.pone.0130350 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dickinson BC, Chang CJ. Chemistry and biology of reactive oxygen species in signaling or stress responses. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7(8):504–11. 10.1038/nchembio.607 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nowicka AM, Hasse U, Hermes M, Scholz F. Hydroxyl radicals attack metallic gold. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010;49(6):1061–3. 10.1002/anie.200906358 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nowicka AM, Hasse U, Sievers G, Donten M, Stojek Z, Fletcher S, et al. Selective knockout of gold active sites. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010;49(17):3006–9. 10.1002/anie.201000485 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.De Haan JB, Crack PJ, Flentjar N, Iannello RC, Hertzog PJ, Kola I. An imbalance in antioxidant defense affects cellular function: the pathophysiological consequences of a reduction in antioxidant defense in the glutathione peroxidase-1 (Gpx1) knockout mouse. Redox Rep. 2003;8(2):69–79. 10.1179/135100003125001378 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kim GJ, Kim W, Kim KT, Lee JK. DNA damage and mitochondria dysfunction in cell apoptosis induced by nonthermal air plasma. Appl Phys Lett. 2010;96(2):021502 10.1063/1.3292206. WOS:000273689400013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tarricone E, Brun P, Vono M, Cardin R, Zuin M, Martines E, et al. Investigation of the effects of atmospheric pressure cold plasma on human cells and tissues. Ital J Anat Embryol. 2012;117(2):186 10.13128/IJAE-12308. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kalghatgi S, Azizkhan-Clifford J. DNA Damage in Mammalian Cells by Atmospheric Pressure Microsecond-Pulsed Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma Is Not Mediated Via Lipid Peroxidation. Plasma Med. 2011;1(2):167–77. 10.1615/PlasmaMed.2011003798 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.García-Alcantara E, Lopez-Callejas R, Serment-Guerrero J, Peña-Eguiluz R, Muñoz-Castro A, Rodriguez-Mendez B, et al. Toxicity and Genotoxicity in HeLa and E. coli Cells Caused by a Helium Plasma Needle. Appl Phys Res. 2013;5(5):p21. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Morales-Ramirez P, Cruz-Vallejo V, Pena-Eguiluz R, Lopez-Callejas R, Rodriguez-Mendez BG, Valencia-Alvarado R, et al. Assessing cellular DNA damage from a helium plasma needle. Radiat Res. 2013;179(6):669–73. 10.1667/RR3223.1 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wu AS, Kalghatgi S, Dobrynin D, Sensenig R, Cerchar E, Podolsky E, et al. Porcine intact and wounded skin responses to atmospheric nonthermal plasma. J Surg Res. 2013;179(1):e1–e12. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ptasinska S, Bahnev B, Stypczynska A, Bowden M, Mason NJ, Braithwaite NS. DNA strand scission induced by a non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma jet. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2010;12(28):7779–81. 10.1039/c001188f . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Blackert S, Haertel B, Wende K, von Woedtke T, Lindequist U. Influence of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma on cellular structures and processes in human keratinocytes (HaCaT). J Dermatol Sci. 2013;70(3):173–81. 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.01.012 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Guo Z, Kozlov S, Lavin MF, Person MD, Paull TT. ATM activation by oxidative stress. Science. 2010;330(6003):517–21. 10.1126/science.1192912 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Choucroun P, Gillet D, Dorange G, Sawicki B, Dewitte JD. Comet assay and early apoptosis. Mutat Res. 2001;478(1–2):89–96. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Goldstein JC, Waterhouse NJ, Juin P, Evan GI, Green DR. The coordinate release of cytochrome c during apoptosis is rapid, complete and kinetically invariant. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2(3):156–62. WOS:000085771300015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Boxhammer V, Li YF, Koritzer J, Shimizu T, Maisch T, Thomas HM, et al. Investigation of the mutagenic potential of cold atmospheric plasma at bactericidal dosages. Mutat Res. 2013;753(1):23–8. 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2012.12.015 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Welz C, Becker S, Li Y-F, Shimizu T, Jeon J, Schwenk-Zieger S, et al. Effects of cold atmospheric plasma on mucosal tissue culture. J Phys D: Appl Phys. 2013;46(4):045401 10.1088/0022-3727/46/4/045401. WOS:000313591300025. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wende K, Bekeschus S, Schmidt A, Jatsch L, Hasse S, Weltmann KD, et al. Risk assessment of a cold argon plasma jet in respect to its mutagenicity. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2016;798–799:48–54. 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.02.003 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bender C, Matthes R, Kindel E, Kramer A, Lademann J, Weltmann K-D, et al. The Irritation Potential of Nonthermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma in the HET-CAM. Plasma Process Polym. 2010;7(3–4):318–26. 10.1002/ppap.200900119. WOS:000276547700017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hammann A, Huebner NO, Bender C, Ekkernkamp A, Hartmann B, Hinz P, et al. Antiseptic efficacy and tolerance of tissue-tolerable plasma compared with two wound antiseptics on artificially bacterially contaminated eyes from commercially slaughtered pigs. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2010;23(6):328–32. 10.1159/000314724 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lademann J, Ulrich C, Patzelt A, Richter H, Kluschke F, Klebes M, et al. Risk assessment of the application of tissue-tolerable plasma on human skin. Clin Plas Med. 2013;1(1):5–10. 10.1016/j.cpme.2013.01.001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Levi-Montalcini R, Hamburger V. Selective growth stimulating effects of mouse sarcoma on the sensory and sympathetic nervous system of the chick embryo. J Exp Zool. 1951;116(2):321–61. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wolf T, Luepke N-P. Formation of micronuclei in incubated hen's eggs as a measure of genotoxicity. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis. 1997;394(1–3):163–75. 10.1016/s1383-5718(97)00136-8. WOS:000071034400019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wolf T, Niehaus-Rolf C, Luepke N-P. Some new methodological aspects of the hen’s egg test for micronucleus induction (HET-MN). Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis. 2002;514(1–2):59–76. 10.1016/s1383-5718(01)00317-5. WOS:000173829400007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Alls A, Cover M, Benton W, Krauss W. Treatment of Hatching Eggs for Disease Prevention: Factors Affecting Permeability and a Visual Detection of Drug Absorption. Avian Dis. 1964;8(2):245–56. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Reid WM, Maag TA, Boyd FM, Kleckner AL, Schmittle S. Embryo and baby chick mortality and morbidity induced by a strain of Escherichia coli. Poult Sci. 1961;40(6):1497–502. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bekeschus S, Schmidt A, Weltmann K-D, von Woedtke T. The plasma jet kINPen—A powerful tool for wound healing. Clin Plas Med. 2016;4(1). 10.1016/j.cpme.2016.01.001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Weltmann KD, Kindel E, Brandenburg R, Meyer C, Bussiahn R, Wilke C, et al. Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet for Medical Therapy: Plasma Parameters and Risk Estimation. Contrib Plasma Phys. 2009;49(9):631–40. 10.1002/ctpp.200910067. WOS:000272204200004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bussiahn R, Lembke N, Gesche R, von Woedtke T, Weltmann K-D. Plasmaquellen für biomedizinische Applikationen. Hyg Med. 2013;38:212–6. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hamilton JW, Denison MS, Bloom SE. Development of basal and induced aryl hydrocarbon (benzo[a]pyrene) hydroxylase activity in the chicken embryo in ovo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983;80(11):3372–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Heinrich-Hirsch B, Hofmann D, Webb J, Neubert D. Activity of aldrinepoxidase, 7-ethoxycoumarin-O-deethylase and 7-ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase during the development of chick embryos in ovo. Arch Toxicol. 1990;64(2):128–34. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bender C, Partecke LI, Kindel E, Doring F, Lademann J, Heidecke CD, et al. The modified HET-CAM as a model for the assessment of the inflammatory response to tissue tolerable plasma. Toxicol In Vitro. 2011;25(2):530–7. 10.1016/j.tiv.2010.11.012 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Chang TK, Weber GF, Crespi CL, Waxman DJ. Differential activation of cyclophosphamide and ifosphamide by cytochromes P-450 2B and 3A in human liver microsomes. Cancer Res. 1993;53(23):5629–37. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wolf T, Niehaus-Rolf C, Banduhn N, Eschrich D, Scheel J, Luepke NP. The hen's egg test for micronucleus induction (HET-MN): novel analyses with a series of well-characterized substances support the further evaluation of the test system. Mutat Res. 2008;650(2):150–64. 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2007.11.009 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Piaton E, Fabre M, Goubin-Versini I, Bretz-Grenier M-F, Courtade-Saïdi M, Vincent S, et al. , editors. [Technical recommendations and best practice guidelines for May-Grunwald-Giemsa staining: Literature review and insights from the quality assurance]. Ann Pathol; 2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lucas AM, Jamroz C. Atlas of avian hematology. Atlas of Avian Hematology. 1961.
- 54.Bruns GA, Ingram VM. The erythroid cells and haemoglobins of the chick embryo. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973;266(877):225–305. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Müller W-U, Streffer C. Micronucleus Assays In: Obe G, editor. Advances in Mutagenesis Research. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 1994. p. 1–134. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Benkhai H, Lemanski S, Below H, Heiden JU, Below E, Lademann J, et al. Can physical stress be measured in urine using the parameter antioxidative potential? GMS Krankenhhyg Interdiszip. 2010;5(2). PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2951104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Greywe D, Kreutz J, Banduhn N, Krauledat M, Scheel J, Schroeder KR, et al. Applicability and robustness of the hen's egg test for analysis of micronucleus induction (HET-MN): results from an inter-laboratory trial. Mutat Res. 2012;747(1):118–34. 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2012.04.012 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Lassila O, Martin C, Toivanen P, Dieterlen-Lievre F. Erythropoiesis and lymphopoiesis in the chick yolk-sac-embryo chimeras: contribution of yolk sac and intraembryonic stem cells. Blood. 1982;59(2):377–81. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sorrell JM, Weiss L. Development of the embryonic chick phagocytic system: intraembryonic erythrophagocytosis induced by phenylhydrazine. J Morphol. 1982;171(2):183–94. 10.1002/jmor.1051710206 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yassine F, Fedecka-Bruner B, Dieterlen-Lievre F. Ontogeny of the chick embryo spleen—a cytological study. Cell Differ Dev. 1989;27(1):29–45. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sheng G. Primitive and definitive erythropoiesis in the yolk sac: a bird's eye view. Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(6–7):1033–43. 10.1387/ijdb.103105gs . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Darzynkiewicz Z. Radiation-induced DNA synthesis in nuclei of hen erythrocytes reactivated in heterokaryons. Exp Cell Res. 1971;69(2):477–81. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Nouspikel T, Hanawalt PC. DNA repair in terminally differentiated cells. DNA Repair (Amst). 2002;1(1):59–75. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Somashekaraiah BV, Padmaja K, Prasad AR. Lead-induced lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense components of developing chick embryos. Free Radic Biol Med. 1992;13(2):107–14. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Busing WR, Levy HA. Crystal and Molecular Structure of Hydrogen Peroxide: A Neutron-Diffraction Study. The Journal of Chemical Physics. 1965;42(9):3054 10.1063/1.1696379. WOS:A19656468000012. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kutchai H, Steen JB. Permeabilty of the shell and shell membraes of hens' eggs during development. Respir Physiol. 1971;11(3):265–78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bekeschus S, von Woedtke T, Kramer A, Weltmann K-D, Masur K. Cold Physical Plasma Treatment Alters Redox Balance in Human Immune Cells. Plasma Med. 2013;3(4):267–78. 10.1615/PlasmaMed.2014011972 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Partecke LI, Evert K, Haugk J, Doering F, Normann L, Diedrich S, et al. Tissue tolerable plasma (TTP) induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer. 2012;12(1):473 10.1186/1471-2407-12-473 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bekeschus S, Iseni S, Reuter S, Masur K, Weltmann K-D. Nitrogen Shielding of an Argon Plasma Jet and Its Effects on Human Immune Cells. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci. 2015;43(3):776–81. 10.1109/tps.2015.2393379. WOS:000352358400012. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Wilson JX, Jaworski EM. Effect of oxygen on ascorbic acid uptake and concentration in embryonic chick brain. Neurochem Res. 1992;17(6):571–6. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Gaál T, Mézes M, Noble RC, Dixon J, Speake BK. Development of antioxidant capacity in tissues of the chick embryo. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 1995;112(4):711–6. 10.1016/0305-0491(95)00125-5. WOS:A1995TN31300019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Surai PF, Noble RC, Speake BK. Tissue-specific differences in antioxidant distribution and susceptibility to lipid peroxidation during development of the chick embryo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1304(1):1–10. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Surai PF. Tissue-specific changes in the activities of antioxidant enzymes during the development of the chicken embryo. Br Poult Sci. 1999;40(3):397–405. 10.1080/00071669987511 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(XLSX)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information file.