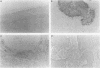
Abstract
AIMS: To determine how epithelial and stromal thymidine phosphorylase expression affects angiogenesis, rapid tumour growth, and decreased apoptotic activity in cervical cancer at varying stages of progression. METHODS: Epithelial and stromal thymidine phosphorylase expression, the microvessel count (reflected by factor VIII related antigen), and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) were assessed immunohistochemically in 25 specimens of normal cervical epithelium, 35 of carcinoma in situ (CIS), 34 of microinvasive carcinoma, and 34 of invasive cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Apoptosis was evaluated by the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labelling (TUNEL) method. The relation of epithelial and stromal thymidine phosphorylase expression to microvessel count, PCNA index, and apoptotic index was examined. RESULTS: Epithelial and stromal thymidine phosphorylase expression progressively increased along a continuum from normal epithelium to invasive squamous cell carcinoma. Epithelial and stromal thymidine phosphorylase expression showed a significant positive correlation with microvessel counts. Within each histological stage, CIS cases with high stromal thymidine phosphorylase expression, invasive squamous cell carcinoma cases with high epithelial thymidine phosphorylase expression, and microinvasive carcinoma cases with high thymidine phosphorylase expression in both epithelium and stroma had a significantly higher microvessel count. High epithelial thymidine phosphorylase expression was associated with a significantly higher PCNA index in CIS and microinvasive carcinoma, but not in invasive squamous cell carcinoma. No significant correlation was seen between apoptotic index and either epithelial or stromal thymidine phosphorylase expression or microvessel count. CONCLUSIONS: Epithelial and stromal thymidine phosphorylase expression may combine to promote angiogenesis during progression of cervical cancer, and epithelial thymidine phosphorylase expression may stimulate tumour cell proliferation in the early stages.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dellas A., Schultheiss E., Almendral A. C., Gudat F., Oberholzer M., Feichter G., Moch H., Torhorst J. Altered expression of mdm-2 and its association with p53 protein status, tumor-cell-proliferation rate and prognosis in cervical neoplasia. Int J Cancer. 1997 Aug 22;74(4):421–425. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19970822)74:4<421::aid-ijc10>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs S. P., Hewett P. W., Johnson I. R., Carmichael J., Murray J. C. Angiogenesis is associated with vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Br J Cancer. 1997;76(11):1410–1415. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1997.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eda H., Fujimoto K., Watanabe S., Ura M., Hino A., Tanaka Y., Wada K., Ishitsuka H. Cytokines induce thymidine phosphorylase expression in tumor cells and make them more susceptible to 5'-deoxy-5-fluorouridine. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1993;32(5):333–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00735915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels K., Fox S. B., Whitehouse R. M., Gatter K. C., Harris A. L. Distinct angiogenic patterns are associated with high-grade in situ ductal carcinomas of the breast. J Pathol. 1997 Feb;181(2):207–212. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199702)181:2<207::AID-PATH758>3.0.CO;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwaki R., Hata K., Iida K., Koike M., Miyazaki K. Immunohistochemical expression of thymidine phosphorylase in human endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 1998 Mar;68(3):247–252. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1997.4929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidi A. J., Abu-Jawdeh G., Berse B., Jackman R. W., Tognazzi K., Dvorak H. F., Brown L. F. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) expression and angiogenesis in cervical neoplasia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Aug 16;87(16):1237–1245. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.16.1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., Levison D. A., Woods A. L., Yu C. C., Kellock D. B., Watkins J. A., Barnes D. M., Gillett C. E., Camplejohn R., Dover R. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunolocalization in paraffin sections: an index of cell proliferation with evidence of deregulated expression in some neoplasms. J Pathol. 1990 Dec;162(4):285–294. doi: 10.1002/path.1711620403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Folkman J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell. 1996 Aug 9;86(3):353–364. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haraguchi M., Miyadera K., Uemura K., Sumizawa T., Furukawa T., Yamada K., Akiyama S., Yamada Y. Angiogenic activity of enzymes. Nature. 1994 Mar 17;368(6468):198–198. doi: 10.1038/368198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatley M. K. What is the value of proliferation markers in the normal and neoplastic cervix? Histol Histopathol. 1998 Jan;13(1):249–254. doi: 10.14670/HH-13.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzman D. Apoptosis provides new targets for chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Aug 21;88(16):1098–1100. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.16.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa F., Miyazono K., Hellman U., Drexler H., Wernstedt C., Hagiwara K., Usuki K., Takaku F., Risau W., Heldin C. H. Identification of angiogenic activity and the cloning and expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):557–562. doi: 10.1038/338557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koukourakis M. I., Giatromanolaki A., Kakolyris S., O'Byrne K. J., Apostolikas N., Skarlatos J., Gatter K. C., Harris A. L. Different patterns of stromal and cancer cell thymidine phosphorylase reactivity in non-small-cell lung cancer: impact on tumour neoangiogenesis and survival. Br J Cancer. 1998 May;77(10):1696–1703. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1998.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C., Tanigawa N. Spontaneous apoptosis is inversely related to intratumoral microvessel density in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1997 Jan 15;57(2):221–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moghaddam A., Zhang H. T., Fan T. P., Hu D. E., Lees V. C., Turley H., Fox S. B., Gatter K. C., Harris A. L., Bicknell R. Thymidine phosphorylase is angiogenic and promotes tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):998–1002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Oka K., Ishikawa A., Morita S. Correlation of cervical carcinoma c-erb B-2 oncogene with cell proliferation parameters in patients treated with radiation therapy for cervical carcinoma. Cancer. 1997 Feb 1;79(3):513–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida M., Hino A., Mori K., Matsumoto T., Yoshikubo T., Ishitsuka H. Preparation of anti-human thymidine phosphorylase monoclonal antibodies useful for detecting the enzyme levels in tumor tissues. Biol Pharm Bull. 1996 Nov;19(11):1407–1411. doi: 10.1248/bpb.19.1407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obermair A., Bancher-Todesca D., Bilgi S., Kaider A., Kohlberger P., Müllauer-Ertl S., Leodolter S., Gitsch G. Correlation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and microvessel density in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997 Aug 20;89(16):1212–1217. doi: 10.1093/jnci/89.16.1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorke E. A. Antisense human papillomavirus (HPV) E6/E7 expression, reduced stability of epidermal growth factor, and diminished growth of HPV-positive tumor cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997 Sep 3;89(17):1243–1246. doi: 10.1093/jnci/89.17.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. H. Cervical and vulva cancer: changes in FIGO definitions of staging. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1996 May;103(5):405–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1996.tb09764.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji Y., Saegusa M., Takano Y., Ohbu M., Okayasu I. Correlation of apoptosis with tumour cell differentiation, progression, and HPV infection in cervical carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 1996 Feb;49(2):134–138. doi: 10.1136/jcp.49.2.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Bucana C. D., Akagi Y., Liu W., Cleary K. R., Mai M., Ellis L. M. Significance of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor in the angiogenesis of human gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1998 Feb;4(2):429–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Bucana C. D., Liu W., Yoneda J., Kitadai Y., Cleary K. R., Ellis L. M. Platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor in human colon cancer angiogenesis: role of infiltrating cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Aug 21;88(16):1146–1151. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.16.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebayashi Y., Akiyama S., Akiba S., Yamada K., Miyadera K., Sumizawa T., Yamada Y., Murata F., Aikou T. Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of an angiogenic factor, thymidine phosphorylase, in human colorectal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Aug 21;88(16):1110–1117. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.16.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toi M., Hoshina S., Taniguchi T., Yamamoto Y., Ishitsuka H., Tominaga T. Expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1995 Apr 21;64(2):79–82. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910640202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumo K., Kodama J., Seki N., Nakanishi Y., Miyagi Y., Kamimura S., Yoshinouchi M., Okuda H., Kudo T. Different angiogenic pathways in human cervical cancers. Gynecol Oncol. 1998 Jan;68(1):38–44. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1997.4876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda M., Ueki K., Kumagai K., Terai Y., Okamoto Y., Ueki M., Otsuki Y. Apoptosis and tumor angiogenesis in cervical cancer after preoperative chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1998 Jun 1;58(11):2343–2346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]