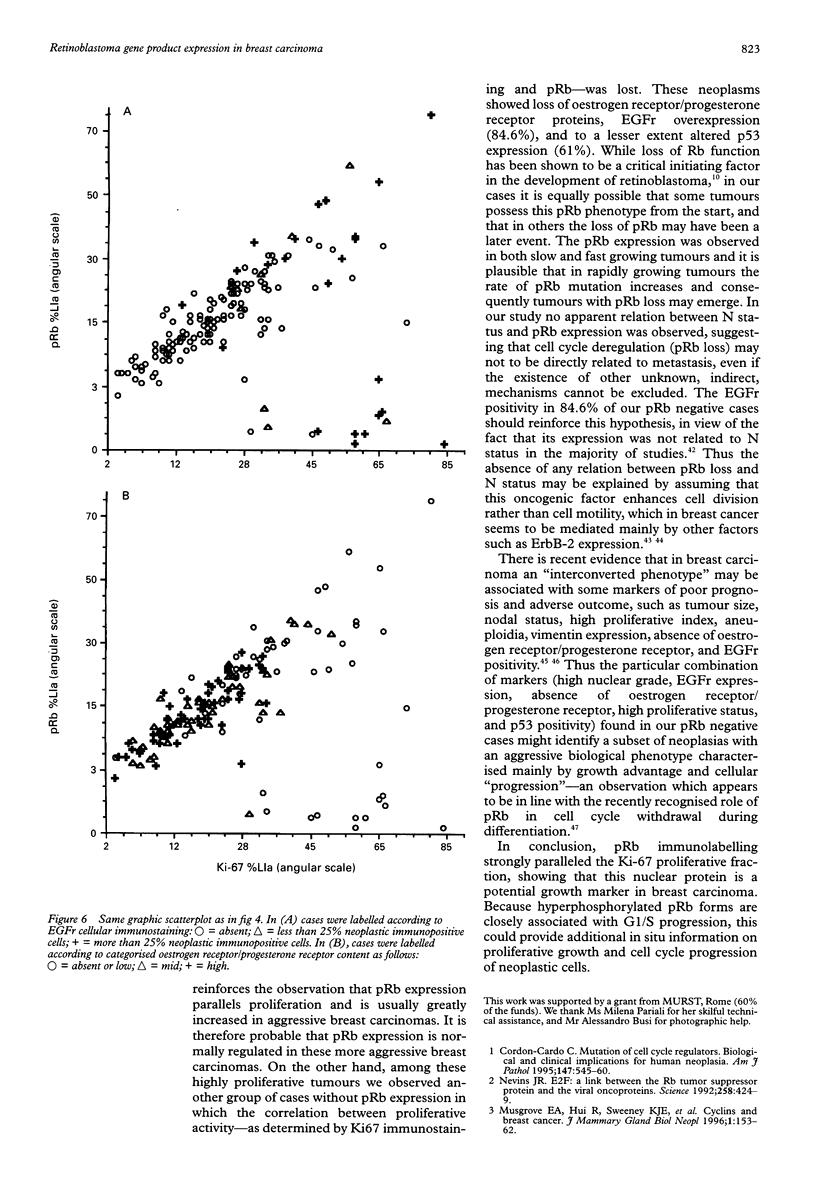
Abstract
AIMS: To investigate the expression of retinoblastoma protein (pRb) in invasive breast tumours and compare its expression with the major biopathological prognostic indicators to identify more aggressive subgroups. MATERIAL: Archival paraffin embedded tissues from 153 consecutive primary breast carcinomas. METHODS: pRb, Ki-67, and oestrogen receptor/progesterone receptor proteins were identified by immunohistochemistry and score values were recorded by image cytometric analysis; p53 and EGFr expression was also evaluated. RESULTS: pRb scores correlated strongly with proliferation activity as determined by Ki-67 staining. Positive relations were also observed between pRb scores, tumour size, nuclear and histological grade, and oestrogen receptor/progesterone receptor content, while abnormal p53 accumulation was not associated with pRb expression. Among the high proliferating carcinomas it was possible to identify 13 cases with loss of pRb expression. CONCLUSIONS: pRb expression paralleled proliferative activity in the majority of breast carcinomas examined, suggesting that in these cases the protein behaves normally in regulating the cell cycle. Conversely in cases with loss of pRb immunostaining, the combined expression of specific highly aggressive factors (EGFr and p53 expression, oestrogen receptor/progesterone receptor negative status, and high K67) seems to characterise a more aggressive phenotype showing growth advantage and cellular "progression" rather than significant nodal involvement.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. J., Tiniakos D. G., McIntosh G. G., Autzen P., Henry J. A., Thomas M. D., Reed J., Horne G. M., Lennard T. W., Angus B. Retinoblastoma protein in human breast carcinoma: immunohistochemical study using a new monoclonal antibody effective on routinely processed tissues. J Pathol. 1996 Sep;180(1):65–70. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199609)180:1<65::AID-PATH607>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedict W. F., Xu H. J., Hu S. X., Takahashi R. Role of the retinoblastoma gene in the initiation and progression of human cancer. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):988–993. doi: 10.1172/JCI114575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi S., Calzolari A., Giannelli E., Giordano A., Zampi G. Expression of retinoblastoma protein in human breast cancer: an immunohistochemical study. Pathologica. 1994 Apr;86(2):146–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg A., Zhang Q. X., Alm P., Olsson H., Sellberg G. The retinoblastoma gene in breast cancer: allele loss is not correlated with loss of gene protein expression. Cancer Res. 1992 May 15;52(10):2991–2994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulet S., Lesty C., Raphael M., Binet J. L., Diebold J. Quantitative study of KI-67 antibody staining in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas using image analysis. Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 1991 Aug;13(4):279–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenee W. K., Dryja T. P., Phillips R. A., Benedict W. F., Godbout R., Gallie B. L., Murphree A. L., Strong L. C., White R. L. Expression of recessive alleles by chromosomal mechanisms in retinoblastoma. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):779–784. doi: 10.1038/305779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli C., Santini D., Chieco P., Taffurelli M., Marrano D., Mancini A. M. Multiple expression patterns of biopathological markers in primary invasive breast carcinoma: a useful tool for elucidating its biological behaviour. Ann Oncol. 1995 Mar;6(3):275–282. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.annonc.a059158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chieco P., Pagnoni M., Romagnoli E., Melchiorri C. A rapid and simple staining method, using toluidine blue, for analysing mitotic figures in tissue sections. Histochem J. 1993 Aug;25(8):569–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C. Mutations of cell cycle regulators. Biological and clinical implications for human neoplasia. Am J Pathol. 1995 Sep;147(3):545–560. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Richon V. M. Expression of the retinoblastoma protein is regulated in normal human tissues. Am J Pathol. 1994 Mar;144(3):500–510. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Potter C. R. The neu-oncogene: more than a prognostic indicator? Hum Pathol. 1994 Dec;25(12):1264–1268. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dei Tos A. P., Maestro R., Doglioni C., Piccinin S., Libera D. D., Boiocchi M., Fletcher C. D. Tumor suppressor genes and related molecules in leiomyosarcoma. Am J Pathol. 1996 Apr;148(4):1037–1045. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M. K., Cliby W. A., Xu H. J., DeLacey K. A., Hu S. X., Keeney G. L., Li J., Podratz K. C., Jenkins R. B., Benedict W. F. Evidence of functional RB protein in epithelial ovarian carcinomas despite loss of heterozygosity at the RB locus. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 1;54(3):610–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou Q. P. Putative roles of retinoblastoma protein in apoptosis. Apoptosis. 1997;2(1):5–18. doi: 10.1023/a:1026498820543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston C. W., Ellis I. O. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 1991 Nov;19(5):403–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faccioli S., Chieco P., Gramantieri L., Stecca B. A., Bolondi L. Cytometric measurement of cell proliferation in echo-guided biopsies from focal lesions of the liver. Mod Pathol. 1996 Feb;9(2):120–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S. B., Harris A. L. The epidermal growth factor receptor in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 1997 Apr;2(2):131–141. doi: 10.1023/a:1026399613946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., T'Ang A. The role of the retinoblastoma gene in breast cancer development. Cancer Treat Res. 1992;61:59–68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3500-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas-Kogan D. A., Kogan S. C., Levi D., Dazin P., T'Ang A., Fung Y. K., Israel M. A. Inhibition of apoptosis by the retinoblastoma gene product. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 1;14(3):461–472. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbour J. W., Lai S. L., Whang-Peng J., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D., Kaye F. J. Abnormalities in structure and expression of the human retinoblastoma gene in SCLC. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):353–357. doi: 10.1126/science.2838909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix M. J., Seftor E. A., Seftor R. E., Trevor K. T. Experimental co-expression of vimentin and keratin intermediate filaments in human breast cancer cells results in phenotypic interconversion and increased invasive behavior. Am J Pathol. 1997 Feb;150(2):483–495. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. Valeur pronostique d'une variable continue et point de césure optimal. Bull Cancer. 1993 Aug;80(8):649–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. M., Yandell D. W., Park S. H., Canning S., Whyte P., Buchkovich K., Harlow E., Weinberg R. A., Dryja T. P. Point mutational inactivation of the retinoblastoma antioncogene. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):937–940. doi: 10.1126/science.2521957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jares P., Campo E., Pinyol M., Bosch F., Miquel R., Fernandez P. L., Sanchez-Beato M., Soler F., Perez-Losada A., Nayach I. Expression of retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) in mantle cell lymphomas. Correlation with cyclin D1 (PRAD1/CCND1) mRNA levels and proliferative activity. Am J Pathol. 1996 May;148(5):1591–1600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., To H., Shew J. Y., Bookstein R., Scully P., Lee W. H. Inactivation of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene in human breast cancers. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):218–221. doi: 10.1126/science.3388033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bookstein R. E., Lee E. Y. Molecular biology of the human retinoblastoma gene. Immunol Ser. 1990;51:169–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Shew J. Y., Hong F. D., Sery T. W., Donoso L. A., Young L. J., Bookstein R., Lee E. Y. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein associated with DNA binding activity. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):642–645. doi: 10.1038/329642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Heyman M., Wang Y., Falkmer U., Hising C., Székely L., Einhorn S. Molecular analysis of the retinoblastoma gene in primary ovarian cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 1994 Sep 1;58(5):663–667. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910580508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez J. C., Piris M. A., Sánchez-Beato M., Villuendas R., Orradre J. L., Algara P., Sánchez-Verde L., Martínez P. Retinoblastoma (Rb) gene product expression in lymphomas. Correlation with Ki67 growth fraction. J Pathol. 1993 Apr;169(4):405–412. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx J. The cell cycle: spinning farther afield. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1490–1492. doi: 10.1126/science.1828620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh G. G., Anderson J. J., Milton I., Steward M., Parr A. H., Thomas M. D., Henry J. A., Angus B., Lennard T. W., Horne C. H. Determination of the prognostic value of cyclin D1 overexpression in breast cancer. Oncogene. 1995 Sep 7;11(5):885–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musgrove E. A., Hui R., Sweeney K. J., Watts C. K., Sutherland R. L. Cyclins and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 1996 Apr;1(2):153–162. doi: 10.1007/BF02013639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen N. H., Emdin S. O., Cajander J., Landberg G. Deregulation of cyclin E and D1 in breast cancer is associated with inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein. Oncogene. 1997 Jan 23;14(3):295–304. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1200833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietiläinen T., Lipponen P., Aaltomaa S., Eskelinen M., Kosma V. M., Syrjänen K. Expression of retinoblastoma gene protein (Rb) in breast cancer as related to established prognostic factors and survival. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A(3):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(94)00463-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santini D., Ceccarelli C., Mazzoleni G., Pasquinelli G., Jasonni V. M., Martinelli G. N. Demonstration of cytokeratin intermediate filaments in oocytes of the developing and adult human ovary. Histochemistry. 1993 Apr;99(4):311–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00269104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santini D., Ceccarelli C., Taffurelli M., Pileri S., Marrano D. Differentiation pathways in primary invasive breast carcinoma as suggested by intermediate filament and biopathological marker expression. J Pathol. 1996 Aug;179(4):386–391. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199608)179:4<386::AID-PATH631>3.0.CO;2-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawan A., Randall B., Angus B., Wright C., Henry J. A., Ostrowski J., Hennessy C., Lennard T. W., Corbett I., Horne C. H. Retinoblastoma and p53 gene expression related to relapse and survival in human breast cancer: an immunohistochemical study. J Pathol. 1992 Sep;168(1):23–28. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki S., Kawakita N., Yanai A., Kitada T., Sakai Y., Nakatani K., Yamada T., Sakaguchi H., Kuroki T. Expression of the retinoblastoma gene product in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1995 Apr;26(4):366–374. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- T'Ang A., Varley J. M., Chakraborty S., Murphree A. L., Fung Y. K. Structural rearrangement of the retinoblastoma gene in human breast carcinoma. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):263–266. doi: 10.1126/science.3175651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudel M., Mulligan L., Cavenee W., Margolese R., Côté J., Gariépy G. Retinoblastoma and p53 gene product expression in breast carcinoma: immunohistochemical analysis and clinicopathologic correlation. Hum Pathol. 1992 Dec;23(12):1388–1394. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90059-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley J. M., Armour J., Swallow J. E., Jeffreys A. J., Ponder B. A., T'Ang A., Fung Y. K., Brammar W. J., Walker R. A. The retinoblastoma gene is frequently altered leading to loss of expression in primary breast tumours. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):725–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]