Abstract
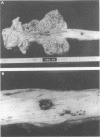
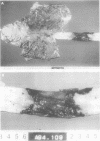
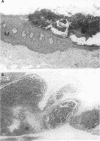
AIMS: To investigate the clinicopathological findings in cases with intraepithelial haemorrhage of the oesophagus (IHO). METHODS: Necropsy records and the histopathology findings in the oesophagus were reviewed for the period 1990 to 1995. Six cases (0.7%) of IHO were found among 919 necropsy cases. Clinical records of these patients and gross and microscopic slides were reviewed in detail. RESULTS: The ages of the IHO cases ranged from 42 to 82 years (average 68 years), with a male to female ratio of 1:2. All cases had underlying haematological disorders with thrombocytopenia, but disseminated intravascular coagulation was not evident in any case. Macroscopically, solitary (two cases) or multiple (four cases) haemorrhagic lesions ranging from 6 to 79 mm in size were identified within the distal oesophagus. Microscopically, there was no inflammatory infiltration, destruction of red blood cells, or submucosal scar formation. CONCLUSIONS: IHO seems to occur shortly before death as a terminal event in haematological disorders. Based on these observations, the term "terminal IHO" can be suggested for this type of oesophageal lesion.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackert J. J., Sherman A., Lustbader I. J., McCauley D. I. Spontaneous intramural hematoma of the esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Oct;84(10):1325–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashman F. C., Hill M. C., Saba G. P., Diaconis J. N. Esophageal hematoma associated with thrombocytopenia. Gastrointest Radiol. 1978 Jun 25;3(2):115–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01887049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atefi D., Horney J. T., Eaton S. B., Shulman M., Whaley W., Galambos J. T. Spontaneous intramural of hematoma of esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 1978 May;24(4):172–174. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(78)73499-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner S. D., Burson L. Esophageal hemorrhage in scleroderma. Am J Gastroenterol. 1966 Dec;46(6):477–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biagi G., Cappelli G., Propersi L., Grossi A. Spontaneous intramural haematoma of the oesophagus. Thorax. 1983 May;38(5):394–395. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.5.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVault K. R., Miller L. S., Yaghsezian H., Spirig A. M., Dhuria M., Armenti F. R., Connell D. C., Martin P., Castell D. O. Acute esophageal hemorrhage from a vagal neurilemoma. Gastroenterology. 1992 Mar;102(3):1059–1061. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Givler R. L. Esophageal lesions in leukemia and lymphoma. Am J Dig Dis. 1970 Jan;15(1):31–36. doi: 10.1007/BF02239344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosimann F., Brönnimann B. Intramural haematoma of the oesophagus complicating sclerotherapy for varices. Gut. 1994 Jan;35(1):130–131. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.1.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nwogu C. E., Conlan A. A. Acute submucosal esophageal hemorrhage. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997 Jul;64(1):247–248. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(97)00507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shay S. S., Berendson R. A., Johnson L. F. Esophageal hematoma. Four new cases, a review, and proposed etiology. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Nov;26(11):1019–1024. doi: 10.1007/BF01314765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratemeier P. H. Massive esophageal hemorrhage in leukemia. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1977 Dec;129(6):1106–1107. doi: 10.2214/ajr.129.6.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschöpe W., Czygan P., Ritz E., Kommerell B., Deppermann D. Intramural hematoma of the esophagus: a complication of carbon tetrachloride intoxication with acute renal failure. Clin Nephrol. 1976 Dec;6(6):526–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]