Abstract
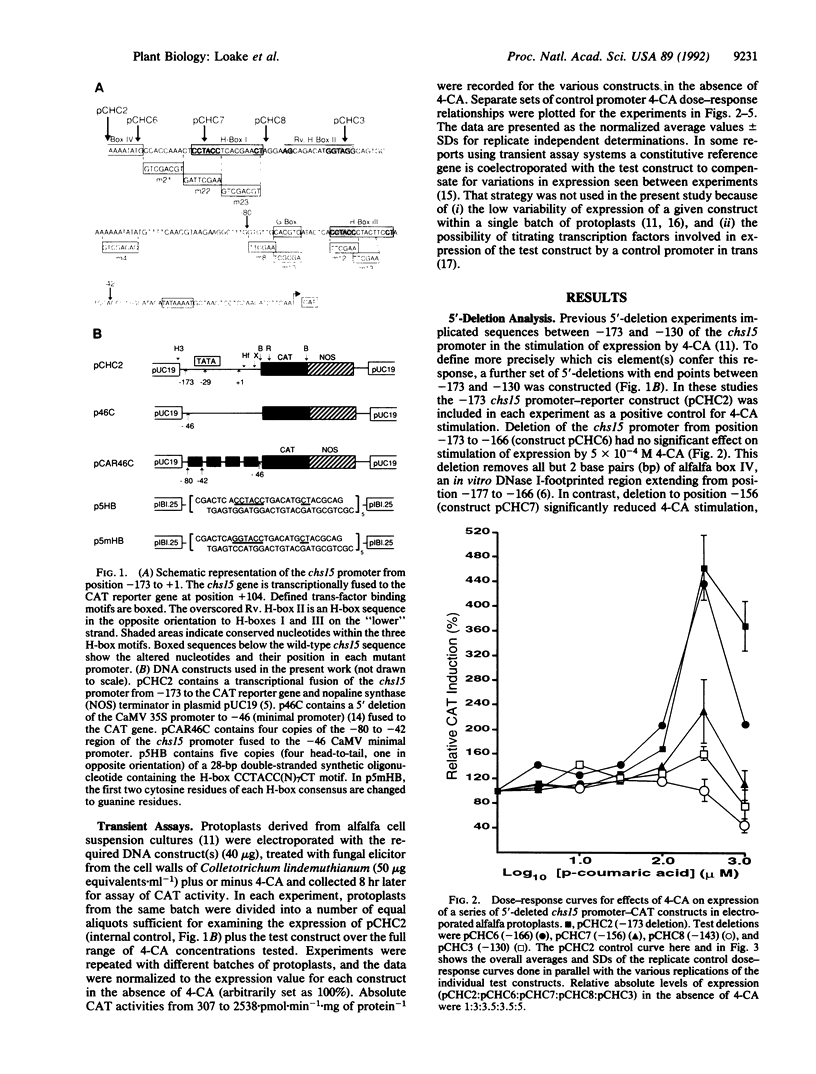
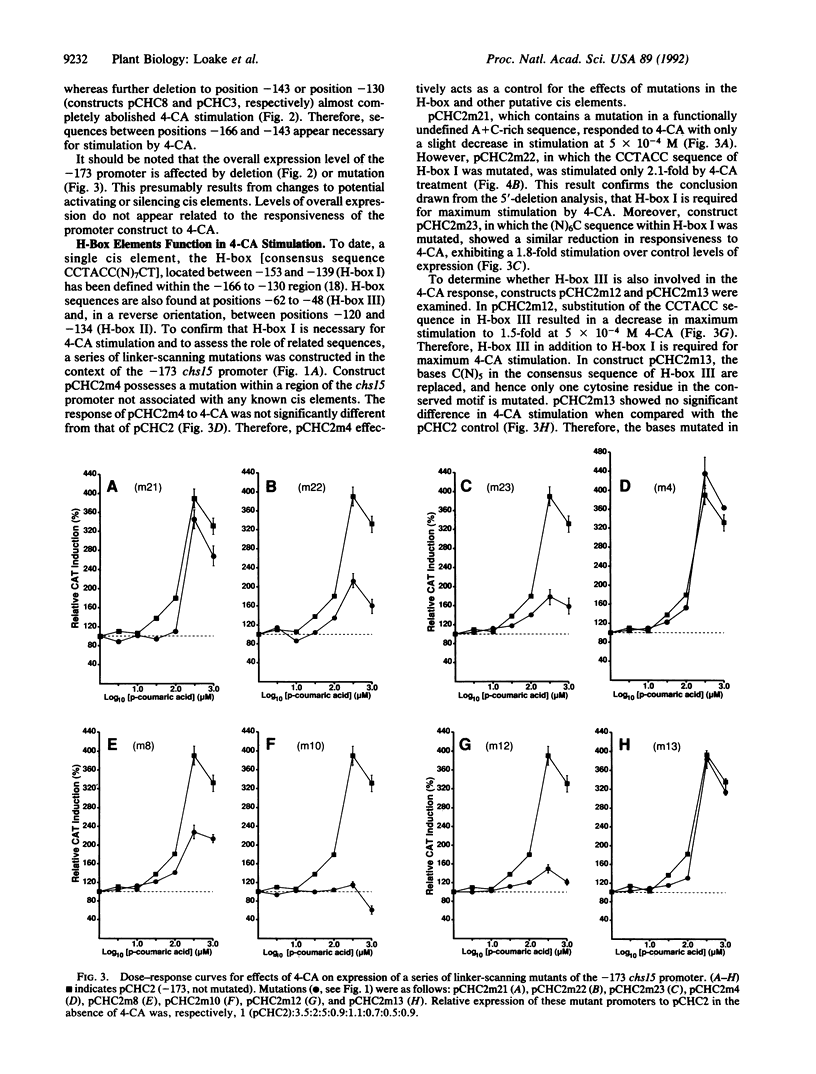
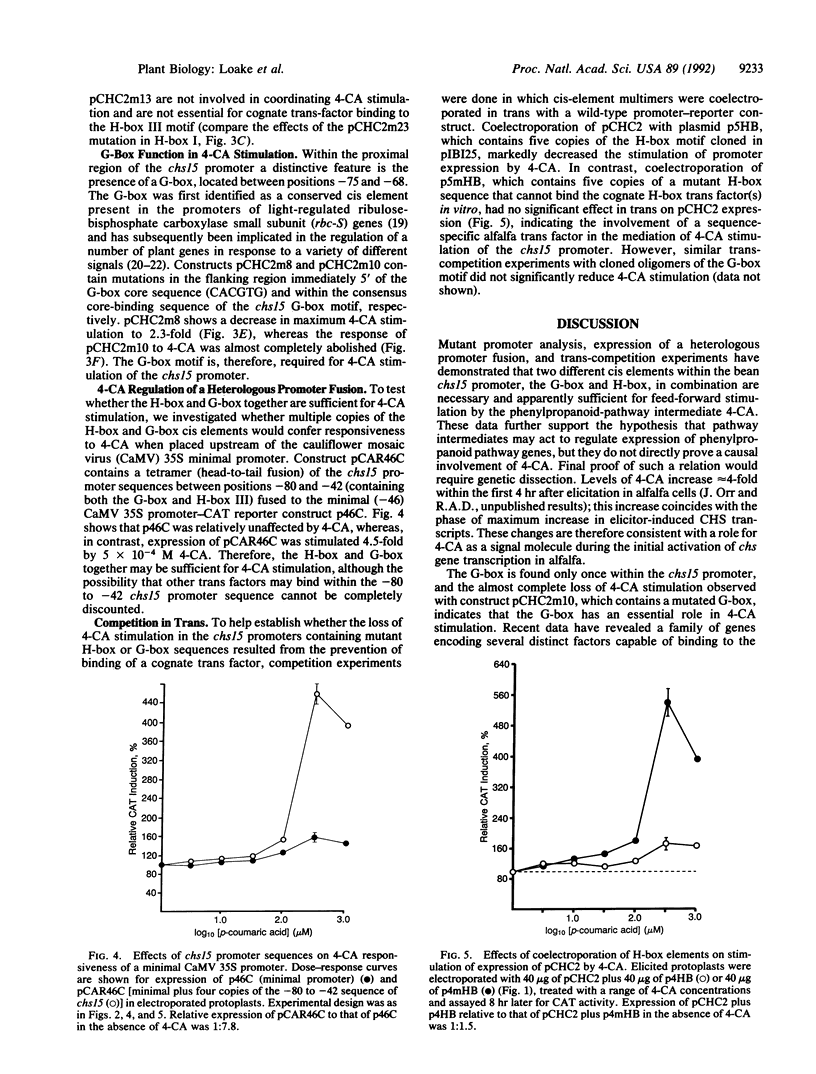
The phenylpropanoid pathway intermediate p-coumaric acid (4-CA) stimulates expression of the bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) chalcone synthase (malonyl-CoA:4-coumaroyl-CoA, EC 2.3.1.74) chs15 gene promoter in electroporated protoplasts of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). We have analyzed the effects of 5' deletions, mutations, and competition with promoter sequences in trans on the expression of a chs15 promoter-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene fusion in elicited alfalfa protoplasts. Two distinct sequence elements, the H-box (consensus CCTACC(N)7CT) and the G-box (CACGTG), are required for stimulation of the chs15 promoter by 4-CA. Furthermore, a 38-base-pair chs15 promoter sequence containing both cis elements conferred responsiveness to 4-CA on the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S minimal promoter. The H-box and G-box in combination establish the complex developmental pattern of chs15 expression and are also involved in stress induction. Hence, potential internal pathway regulation through feed-forward stimulation by 4-CA operates by modulation of the signal pathways for developmental and environmental regulation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrhein N., Gerhardt J. Superinduction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in gherkin hypocotyls caused by the inhibitor, L-alpha-aminooxy-beta-phenylpropionic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 3;583(4):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Chua N. H. The Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S Promoter: Combinatorial Regulation of Transcription in Plants. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):959–966. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block A., Dangl J. L., Hahlbrock K., Schulze-Lefert P. Functional borders, genetic fine structure, and distance requirements of cis elements mediating light responsiveness of the parsley chalcone synthase promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5387–5391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Harrison M. J. Activation, structure, and organization of genes involved in microbial defense in plants. Adv Genet. 1990;28:165–234. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60527-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Cashmore A. R. Mutation of either G box or I box sequences profoundly affects expression from the Arabidopsis rbcS-1A promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1717–1726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Clouse S. D., Dixon R. A., Lawton M. A., Lamb C. J. Glutathione and fungal elicitor regulation of a plant defense gene promoter in electroporated protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6738–6742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano G., Pichersky E., Malik V. S., Timko M. P., Scolnik P. A., Cashmore A. R. An evolutionarily conserved protein binding sequence upstream of a plant light-regulated gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiltinan M. J., Marcotte W. R., Jr, Quatrano R. S. A plant leucine zipper protein that recognizes an abscisic acid response element. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):267–271. doi: 10.1126/science.2145628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. J., Choudhary A. D., Dubery I., Lamb C. J., Dixon R. A. Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). 8. Cis-elements and trans-acting factors for the quantitative expression of a bean chalcone synthase gene promoter in electroporated alfalfa protoplasts. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 May;16(5):877–890. doi: 10.1007/BF00015079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loake G. J., Choudhary A. D., Harrison M. J., Mavandad M., Lamb C. J., Dixon R. A. Phenylpropanoid pathway intermediates regulate transient expression of a chalcone synthase gene promoter. Plant Cell. 1991 Aug;3(8):829–840. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.8.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lois R., Dietrich A., Hahlbrock K., Schulz W. A phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene from parsley: structure, regulation and identification of elicitor and light responsive cis-acting elements. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1641–1648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavandad M., Edwards R., Liang X., Lamb C. J., Dixon R. A. Effects of trans-Cinnamic Acid on Expression of the Bean Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase Gene Family. Plant Physiol. 1990 Oct;94(2):671–680. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty D. R., Hattori T., Carson C. B., Vasil V., Lazar M., Vasil I. K. The Viviparous-1 developmental gene of maize encodes a novel transcriptional activator. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):895–905. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeda K., Salinas J., Chua N. H. A tobacco bZip transcription activator (TAF-1) binds to a G-box-like motif conserved in plant genes. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1793–1802. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07704.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe S. A., Tobin E. M. Deletion analysis of a phytochrome-regulated monocot rbcS promoter in a transient assay system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2683–2686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder T. B., Hedrick S. A., Bell J. N., Liang X. W., Clouse S. D., Lamb C. J. Organization and differential activation of a gene family encoding the plant defense enzyme chalcone synthase in Phaseolus vulgaris. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):219–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00325687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid J., Doerner P. W., Clouse S. D., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Developmental and environmental regulation of a bean chalcone synthase promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell. 1990 Jul;2(7):619–631. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.7.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Lefert P., Becker-André M., Schulz W., Hahlbrock K., Dangl J. L. Functional architecture of the light-responsive chalcone synthase promoter from parsley. Plant Cell. 1989 Jul;1(7):707–714. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.7.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Lefert P., Dangl J. L., Becker-André M., Hahlbrock K., Schulz W. Inducible in vivo DNA footprints define sequences necessary for UV light activation of the parsley chalcone synthase gene. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):651–656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields S. E., Wingate V. P., Lamb C. J. Dual control of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase production and removal by its product cinnamic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):389–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




