Abstract
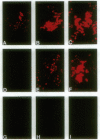
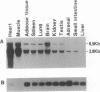
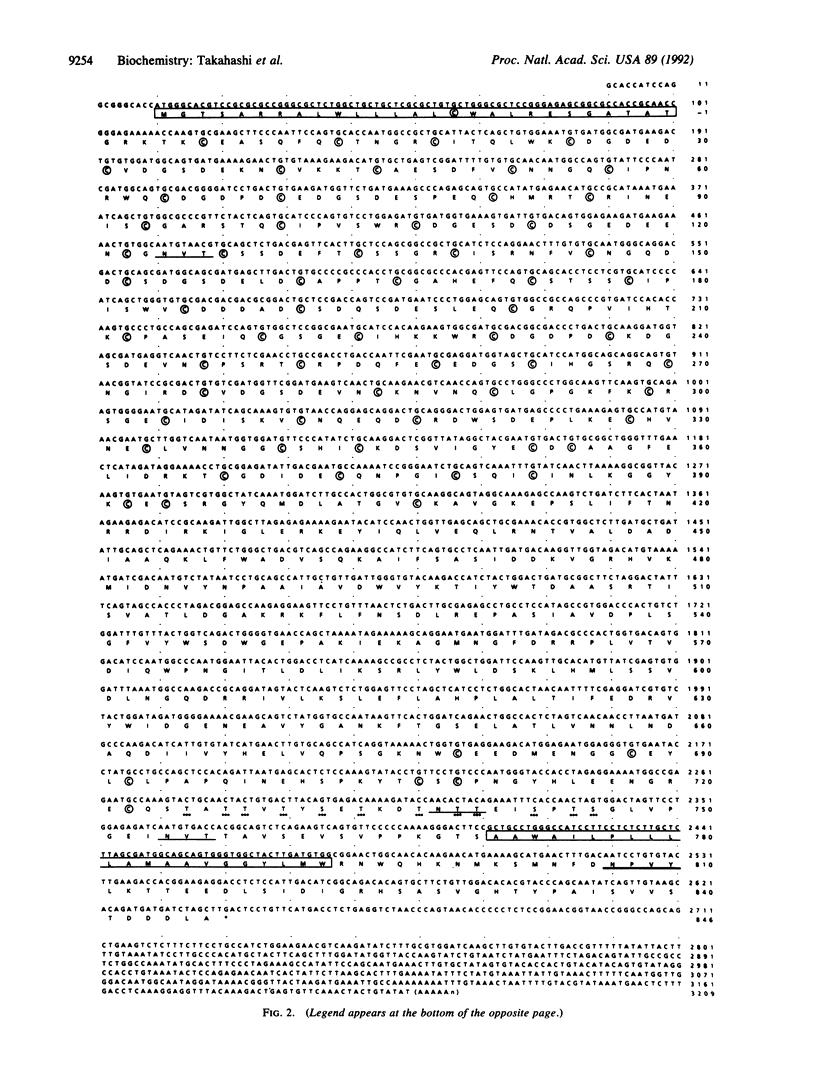
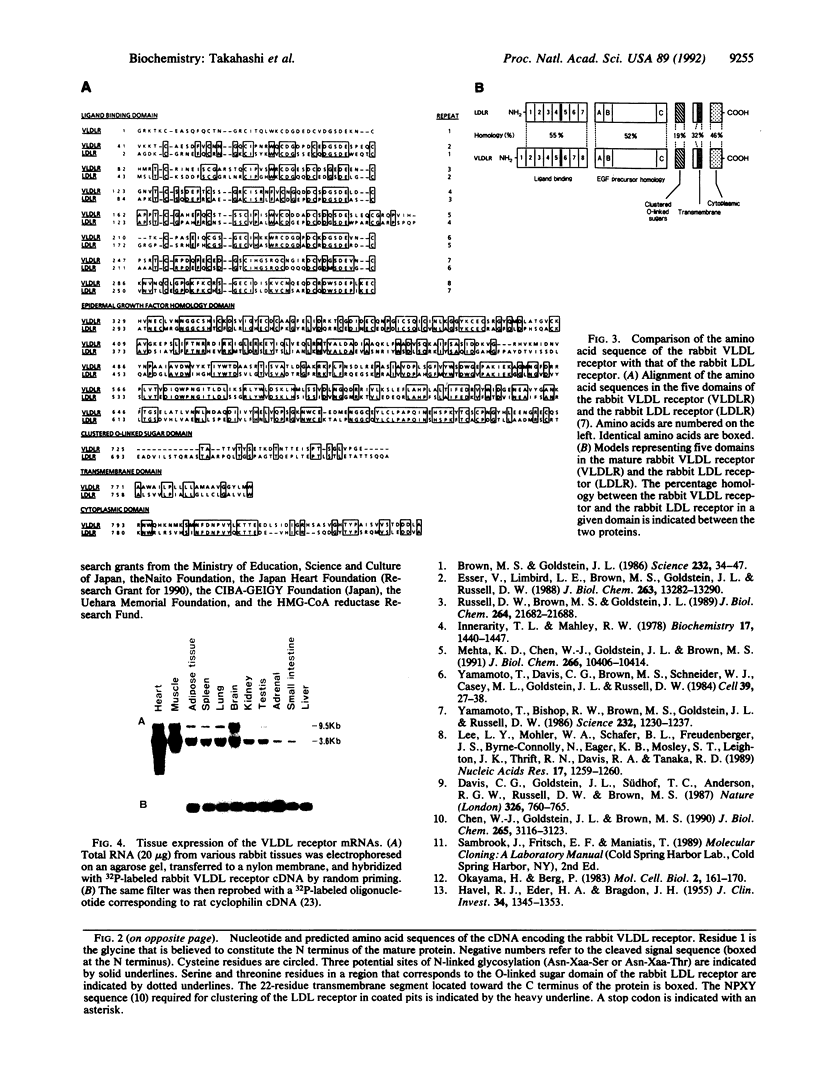
A cDNA that expresses a receptor for very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) was isolated from a rabbit heart cDNA library and characterized. The deduced amino acid sequence of the cDNA revealed that the cDNA encodes a protein with striking homology to the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor. Like the LDL receptor, the mature protein consists of the following five domains spanning 846 amino acids: 328 N-terminal amino acids including an 8-fold repeat of 40 amino acids homologous to the ligand binding repeat of the LDL receptor; 396 amino acid residues homologous to the epidermal growth factor precursor including three cysteine-rich repeats; a region immediately outside of the plasma membrane rich in serines and threonines; 22 amino acids traversing the plasma membrane; and 54 amino acids including the NPVY sequence that is required for clustering of the LDL receptor in coated pits and that projects into the cytoplasm. LDL-receptor-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cells transfected with the cDNA bound and internalized VLDL, beta-migrating VLDL, and intermediate density lipoprotein but did not bind LDL with high affinity. The 3.6- and 9.5-kilobase mRNAs for the VLDL receptor are highly abundant in heart, muscle, and adipose tissue. Barely detectable amounts of the mRNAs were present in liver. Based on the structural features, ligand specificity, and tissue expression of the mRNAs, we suggest that this VLDL receptor may mediate uptake of apolipoprotein E-containing lipoproteins enriched with triglyceride in nonhepatic tissues that are active in fatty acid metabolism.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. NPXY, a sequence often found in cytoplasmic tails, is required for coated pit-mediated internalization of the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3116–3123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., Goldstein J. L., Südhof T. C., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Brown M. S. Acid-dependent ligand dissociation and recycling of LDL receptor mediated by growth factor homology region. Nature. 1987 Apr 23;326(6115):760–765. doi: 10.1038/326760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser V., Limbird L. E., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Mutational analysis of the ligand binding domain of the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13282–13290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Binding and degradation of low density lipoproteins by cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5153–5162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Enhanced binding by cultured human fibroblasts of apo-E-containing lipoproteins as compared with low density lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1440–1447. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Mahley R. W. Binding of arginine-rich (E) apoprotein after recombination with phospholipid vesicles to the low density lipoprotein receptors of fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4186–4190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley D. M., Krieger M. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of low density lipoprotein: somatic cell mutants define multiple genes required for expression of surface-receptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5454–5458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Basu S. K., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L. Saturation and suppression of hepatic lipoprotein receptors: a mechanism for the hypercholesterolemia of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. Y., Mohler W. A., Schafer B. L., Freudenberger J. S., Byrne-Connolly N., Eager K. B., Mosley S. T., Leighton J. K., Thrift R. N., Davis R. A. Nucleotide sequence of the rat low density lipoprotein receptor cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1259–1260. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta K. D., Chen W. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low density lipoprotein receptor in Xenopus laevis. I. Five domains that resemble the human receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10406–10414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Weinstein J. N., Mahley R. W. Acetoacetylated lipoproteins used to distinguish fibroblasts from macrophages in vitro by fluorescence microscopy. Arteriosclerosis. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):177–185. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.1.3.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Different combinations of cysteine-rich repeats mediate binding of low density lipoprotein receptor to two different proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21682–21688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibui T., Uchida-Kamizono M., Okazaki H., Kondo J., Murayama S., Morimoto Y., Nagahari K., Teranishi Y. High-level secretion of human apolipoprotein E produced in Escherichia coli: use of a secretion plasmid containing tandemly polymerized ompF-hybrid gene. J Biotechnol. 1991 Feb;17(2):109–120. doi: 10.1016/0168-1656(91)90002-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Bishop R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Deletion in cysteine-rich region of LDL receptor impedes transport to cell surface in WHHL rabbit. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1230–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3010466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]