Abstract
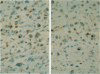
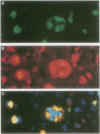
AIM: To investigate whether anaplastic large cell lymphomas (ALCL) expressing cytotoxic proteins have a relatively worse clinical outcome compared with ALCL lacking a cytotoxic phenotype. METHODS: 59 primary cases of ALCL originating from different sites were investigated by immunohistochemistry for the presence of the cytotoxic proteins T cell intracytoplasmic antigen (TIA-1) and granzyme B in the neoplastic cells. Since site of origin and expression of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) strongly influence prognosis, the presence of a cytotoxic phenotype was also investigated in relation to the primary site of origin (lymph node, gut, or skin) and ALK expression. The prognostic value was investigated by analysis of overall and relapse-free survival time, including Cox regression analysis. RESULTS: 39 of 59 ALCL (66%) appeared to have a cytotoxic phenotype as shown by expression of TIA-1 or granzyme B or both in the neoplastic cells. The presence of a cytotoxic phenotype did not have any influence on prognosis. Even when the survival data were corrected for site of origin and stage at presentation or were analysed separately for ALK positive and negative cases, no prognostic influence of a cytotoxic phenotype was observed. CONCLUSIONS: In primary biopsies of patients with ALCL, the presence of a cytotoxic phenotype is not related to clinical outcome of the disease.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnarsson B. A., Kadin M. E. Ki-1 positive large cell lymphoma. A morphologic and immunologic study of 19 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Apr;12(4):264–274. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198804000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Nagler-Anderson C., O'Brien C., Levine H., Watkins S., Slayter H. S., Blue M. L., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with a 15-kDa cytoplasmic granule-associated protein defines a subpopulation of CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):574–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P. TIA-1: structural and functional studies on a new class of cytolytic effector molecule. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;198:131–143. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79414-8_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beljaards R. C., Meijer C. J., Scheffer E., Toonstra J., van Vloten W. A., van der Putte S. C., Geerts M. L., Willemze R. Prognostic significance of CD30 (Ki-1/Ber-H2) expression in primary cutaneous large-cell lymphomas of T-cell origin. A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study in 20 patients. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):1169–1178. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beljaards R. C., Meijer C. J., Van der Putte S. C., Hollema H., Geerts M. L., Bezemer P. D., Willemze R. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: clinicopathological features and prognostic parameters of 35 cases other than mycosis fungoides and CD30-positive large cell lymphoma. J Pathol. 1994 Jan;172(1):53–60. doi: 10.1002/path.1711720110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter M. A., Franklin W. A., Larson R. A., McKeithan T. W., Rubin C. M., Le Beau M. M., Stephens J. K., Vardiman J. W. Morphology in Ki-1(CD30)-positive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is correlated with clinical features and the presence of a unique chromosomal abnormality, t(2;5)(p23;q35). Am J Surg Pathol. 1990 Apr;14(4):305–316. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199004000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrow M. N., Harris T. D., Shaughnessy K. J., Litt G. J. Catalyzed reporter deposition, a novel method of signal amplification. Application to immunoassays. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Dec 20;125(1-2):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulland M. L., Kanavaros P., Wechsler J., Casiraghi O., Gaulard P. Cytotoxic protein expression in natural killer cell lymphomas and in alpha beta and gamma delta peripheral T-cell lymphomas. J Pathol. 1997 Dec;183(4):432–439. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199712)183:4<432::AID-PATH942>3.0.CO;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouaib S., Chehimi J., Bani L., Genetet N., Tursz T., Gay F., Trinchieri G., Mami-Chouaib F. Interleukin 12 induces the differentiation of major histocompatibility complex class I-primed cytotoxic T-lymphocyte precursors into allospecific cytotoxic effectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12659–12663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleege J. C., van Diest P. J., Baak J. P. Computer assisted efficiency testing of different sampling methods for selective nuclear graphic tablet morphometry. Lab Invest. 1990 Aug;63(2):270–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B. Acquisition of specific cytotoxic activity by human T4+ T lymphocytes in culture. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):365–367. doi: 10.1038/308365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foss H. D., Anagnostopoulos I., Araujo I., Assaf C., Demel G., Kummer J. A., Hummel M., Stein H. Anaplastic large-cell lymphomas of T-cell and null-cell phenotype express cytotoxic molecules. Blood. 1996 Nov 15;88(10):4005–4011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris N. L., Jaffe E. S., Stein H., Banks P. M., Chan J. K., Cleary M. L., Delsol G., De Wolf-Peeters C., Falini B., Gatter K. C. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 1994 Sep 1;84(5):1361–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusel J. W., Hanson R. D., Silverman G. A., Ley T. J. Structure and expression of a cluster of human hematopoietic serine protease genes found on chromosome 14q11.2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6152–6158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa N. M., Kanavaros P., van der Valk P., Walboomers J. M., Horstman A., Vos W., Mullink H., Meijer C. J. Expression of c-myc and bcl-2 oncogene products in Reed-Sternberg cells independent of presence of Epstein-Barr virus. J Clin Pathol. 1993 Mar;46(3):211–217. doi: 10.1136/jcp.46.3.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami A., Tian Q., Streuli M., Poe M., Edelhoff S., Disteche C. M., Anderson P. Intron-exon organization and chromosomal localization of the human TIA-1 gene. J Immunol. 1994 May 15;152(10):4937–4945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenacs L., Wellmann A., Sorbara L., Himmelmann A. W., Bagdi E., Jaffe E. S., Raffeld M. Cytotoxic cell antigen expression in anaplastic large cell lymphomas of T- and null-cell type and Hodgkin's disease: evidence for distinct cellular origin. Blood. 1997 Feb 1;89(3):980–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kummer J. A., Kamp A. M., van Katwijk M., Brakenhoff J. P., Radosević K., van Leeuwen A. M., Borst J., Verweij C. L., Hack C. E. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies raised against recombinant human granzymes A and B and showing cross reactions with the natural proteins. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Jul 6;163(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kummer J. A., Vermeer M. H., Dukers D., Meijer C. J., Willemze R. Most primary cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders have a CD4-positive cytotoxic T-cell phenotype. J Invest Dermatol. 1997 Nov;109(5):636–640. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12337633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi D., Ledermann B., Bürki K., Seiler P., Odermatt B., Olsen K. J., Podack E. R., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. Cytotoxicity mediated by T cells and natural killer cells is greatly impaired in perforin-deficient mice. Nature. 1994 May 5;369(6475):31–37. doi: 10.1038/369031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Beau M. M., Bitter M. A., Larson R. A., Doane L. A., Ellis E. D., Franklin W. A., Rubin C. M., Kadin M. E., Vardiman J. W. The t(2;5)(p23;q35): a recurring chromosomal abnormality in Ki-1-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 1989 Dec;3(12):866–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeffler C. M., Smyth M. J., Longo D. L., Kopp W. C., Harvey L. K., Tribble H. R., Tase J. E., Urba W. J., Leonard A. S., Young H. A. Immunoregulation in cancer-bearing hosts. Down-regulation of gene expression and cytotoxic function in CD8+ T cells. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):949–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louahed J., Kermouni A., Van Snick J., Renauld J. C. IL-9 induces expression of granzymes and high-affinity IgE receptor in murine T helper clones. J Immunol. 1995 May 15;154(10):5061–5070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. J., Amarante-Mendes G. P., Shi L., Chuang T. H., Casiano C. A., O'Brien G. A., Fitzgerald P., Tan E. M., Bokoch G. M., Greenberg A. H. The cytotoxic cell protease granzyme B initiates apoptosis in a cell-free system by proteolytic processing and activation of the ICE/CED-3 family protease, CPP32, via a novel two-step mechanism. EMBO J. 1996 May 15;15(10):2407–2416. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Bastard C., Rimokh R., Dastugue N., Huret J. L., Kristoffersson U., Magaud J. P., Nezelof C., Tilly H., Vannier J. P. CD30-positive large cell lymphomas ('Ki-1 lymphoma') are associated with a chromosomal translocation involving 5q35. Br J Haematol. 1990 Feb;74(2):161–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matutes E., Coelho E., Aguado M. J., Morilla R., Crawford A., Owusu-Ankomah K., Catovsky D. Expression of TIA-1 and TIA-2 in T cell malignancies and T cell lymphocytosis. J Clin Pathol. 1996 Feb;49(2):154–158. doi: 10.1136/jcp.49.2.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. W., Kirstein M. N., Valentine M. B., Dittmer K. G., Shapiro D. N., Saltman D. L., Look A. T. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Science. 1994 Mar 4;263(5151):1281–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.8122112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzio M., Chinnaiyan A. M., Kischkel F. C., O'Rourke K., Shevchenko A., Ni J., Scaffidi C., Bretz J. D., Zhang M., Gentz R. FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death--inducing signaling complex. Cell. 1996 Jun 14;85(6):817–827. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller C., Tschopp J. Resistance of CTL to perforin-mediated lysis. Evidence for a lymphocyte membrane protein interacting with perforin. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 15;153(6):2470–2478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhuber G., Vogelsang H., Stolte M., Muthenthaler S., Kummer J. A., Kummer A. J., Radaszkiewicz T. Evidence that intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes are activated cytotoxic T cells in celiac disease but not in giardiasis. Am J Pathol. 1996 May;148(5):1351–1357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudejans J. J., Jiwa N. M., Kummer J. A., Ossenkoppele G. J., van Heerde P., Baars J. W., Kluin P. M., Kluin-Nelemans J. C., van Diest P. J., Middeldorp J. M. Activated cytotoxic T cells as prognostic marker in Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1997 Feb 15;89(4):1376–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulford K., Lamant L., Morris S. W., Butler L. H., Wood K. M., Stroud D., Delsol G., Mason D. Y. Detection of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and nucleolar protein nucleophosmin (NPM)-ALK proteins in normal and neoplastic cells with the monoclonal antibody ALK1. Blood. 1997 Feb 15;89(4):1394–1404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan L. T., Tewari M., O'Rourke K., Dixit V., Snipas S. J., Poirier G. G., Ray C., Pickup D. J., Salvesen G. S. Proteolytic activation of the cell death protease Yama/CPP32 by granzyme B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Mar 5;93(5):1972–1976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.5.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raap A. K., van de Corput M. P., Vervenne R. A., van Gijlswijk R. P., Tanke H. J., Wiegant J. Ultra-sensitive FISH using peroxidase-mediated deposition of biotin- or fluorochrome tyramides. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Apr;4(4):529–534. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.4.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandlund J. T., Pui C. H., Roberts W. M., Santana V. M., Morris S. W., Berard C. W., Hutchison R. E., Ribeiro R. C., Mahmoud H., Crist W. M. Clinicopathologic features and treatment outcome of children with large-cell lymphoma and the t(2;5)(p23;q35). Blood. 1994 Oct 15;84(8):2467–2471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiota M., Nakamura S., Ichinohasama R., Abe M., Akagi T., Takeshita M., Mori N., Fujimoto J., Miyauchi J., Mikata A. Anaplastic large cell lymphomas expressing the novel chimeric protein p80NPM/ALK: a distinct clinicopathologic entity. Blood. 1995 Sep 1;86(5):1954–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfeld A. G., Diebold J., Noel H., Kapanci Y., Rilke F., Kelényi G., Sundstrom C., Lennert K., van Unnik J. A., Mioduszewska O. Updated Kiel classification for lymphomas. Lancet. 1988 Feb 6;1(8580):292–293. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J., Bird C. H., Sutton V., McDonald L., Coughlin P. B., De Jong T. A., Trapani J. A., Bird P. I. A cytosolic granzyme B inhibitor related to the viral apoptotic regulator cytokine response modifier A is present in cytotoxic lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1996 Nov 1;271(44):27802–27809. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.44.27802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susskind B., Shornick M. D., Iannotti M. R., Duffy B., Mehrotra P. T., Siegel J. P., Mohanakumar T. Cytolytic effector mechanisms of human CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Hum Immunol. 1996 Jan;45(1):64–75. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(95)00151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. S., Engelhard V. H. Perforin-dependent cytotoxic activity and lymphokine secretion by CD4+ T cells are regulated by CD8+ T cells. J Immunol. 1997 Sep 1;159(5):2091–2099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Utsunomiya Y., Inoue Y., Kimura N., Fujita S. Monoclonal proliferation of CD4+ large granular lymphocytes with cytolytic activity. Br J Haematol. 1995 Oct;91(2):419–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1995.tb05314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin P. C., Kummer J. A., van der Valk P., van Heerde P., Kluin P. M., Willemze R., Ossenkoppele G. J., Radaszkiewicz T., Meijer C. J. Granzyme B-expressing peripheral T-cell lymphomas: neoplastic equivalents of activated cytotoxic T cells with preference for mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue localization. Blood. 1994 Dec 1;84(11):3785–3791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]