Abstract
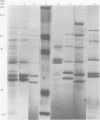
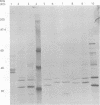
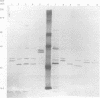
AIMS: To develop a new typing system for group B streptococci based on 35S-methionine-labelled protein profiles of bacterial proteins. METHODS: 377 clinical isolates of group B streptococci were examined by incorporation of 35S-methionine into bacterial proteins under strict anaerobic conditions. After sodium dodecylsulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, autoradiography was performed. The patterns produced were visually analysed and categorised into clusters of organisms based on the pattern of band production between 32-46 kilodaltons. RESULTS: 294 of the typed strains classified into seven different groups designated a-g. 32 strains failed to incorporate 35S-methionine sufficiently to be grouped and 11 strains did not fall into one of the seven identified groups. Typability, reproducibility, and discrimination of the system was evident. CONCLUSIONS: This typing system may help to distinguish between colonising and invasive strains of the organism.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ancona R. J., Ferrieri P., Williams P. P. Maternal factors that enhance the acquisition of group-B streptococci by newborn infants. J Med Microbiol. 1980 May;13(2):273–280. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony B. F., Okada D. M., Hobel C. J. Epidemiology of the group B streptococcus: maternal and nosocomial sources for infant acquisitions. J Pediatr. 1979 Sep;95(3):431–436. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony B. F., Okada D. M. The emergence of group B streptococci in infections of the newborn infant. Annu Rev Med. 1977;28:355–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.28.020177.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer K. M., Gadzala C. A., Kelly P. D., Gotoff S. P. Selective intrapartum chemoprophylaxis of neonatal group B streptococcal early-onset disease. III. Interruption of mother-to-infant transmission. J Infect Dis. 1983 Nov;148(5):810–816. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.5.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton R. A., Baker C. J. Role of adherence in the pathogenesis of neonatal group B streptococcal infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):837–843. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.837-843.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman L. G., Christensen P., Christensen K., Fryklund B., Helgesson A. M., Svenningsen N. W., Tullus K. Prevention of excess neonatal morbidity associated with group B streptococci by vaginal chlorhexidine disinfection during labour. The Swedish Chlorhexidine Study Group. Lancet. 1992 Jul 11;340(8811):65–69. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90393-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun C. S., Brady L. J., Boyle M. D., Dillon H. C., Ayoub E. M. Group B streptococcal C protein-associated antigens: association with neonatal sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):786–791. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman G. Typing of Streptococcus agalactiae (Lancefield group B). Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;7(2):226–231. doi: 10.1007/BF01963093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson B. D., Stapleton P., Ludlam H. Ribotyping of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Jun;36(6):414–419. doi: 10.1099/00222615-36-6-414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Baker C. J., Troup N. J., Tompkins L. S. Restriction endonuclease analysis of human and bovine group B streptococci for epidemiologic study. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1352–1356. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1352-1356.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Bressack M., Troup N. J., Tompkins L. S. Infant with two relapses of group B streptococcal sepsis documented by DNA restriction enzyme analysis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Oct;7(10):729–732. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198810000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Hastings M. J., Clare A. J., Bloxham B., Marwood R., Rivers R. P., Stringer J. Nosocomial transmission of group B streptococci. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Aug 15;283(6289):459–461. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6289.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faro S. Group B beta-hemolytic streptococci and puerperal infections. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Mar 15;139(6):686–689. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(81)90486-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores A. E., Ferrieri P. Molecular species of R-protein antigens produced by clinical isolates of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):1050–1054. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.1050-1054.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings M. J., Easmon C. S., Neill J., Bloxham B., Rivers R. P. Group B streptococcal colonisation and the outcome of pregnancy. J Infect. 1986 Jan;12(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(86)94775-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard S. R., O'Farrell S., Holland D., Crook S., Barnett M. J., Tabaqchali S. The epidemiology of Clostridium difficile with use of a typing scheme: nosocomial acquisition and cross-infection among immunocompromised patients. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):159–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerqvist C. G., Sundell H., Gettins P. Molecular basis for group B beta-hemolytic streptococcal disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):51–55. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff L. C., Michel J. L., Kasper D. L. A monoclonal antibody identifies a protective C-protein alpha-antigen epitope in group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):204–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.204-210.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder C. J., Zanen H. C. Neonatal group B streptococcal meningitis. Arch Dis Child. 1984 May;59(5):439–443. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.5.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano Y., Nagano N., Takahashi S., Murono K., Fujita K., Taguchi F., Okuwaki Y. Restriction endonuclease digest patterns of chromosomal DNA from group B beta-haemolytic streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Nov;35(5):297–303. doi: 10.1099/00222615-35-5-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poxton I. R., Aronsson B., Möllby R., Nord C. E., Collee J. G. Immunochemical fingerprinting of Clostridium difficile strains isolated from an outbreak of antibiotic-associated colitis and diarrhoea. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Jun;17(3):317–324. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. The development of a phage-typing system for group-B streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):133–143. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S. Epidemiologic markers of Clostridium difficile. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12 (Suppl 2):S192–S199. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_2.s192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., Holland D., O'Farrell S., Silman R. Typing scheme for Clostridium difficile: its application in clinical and epidemiological studies. Lancet. 1984 Apr 28;1(8383):935–938. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92392-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]