Abstract
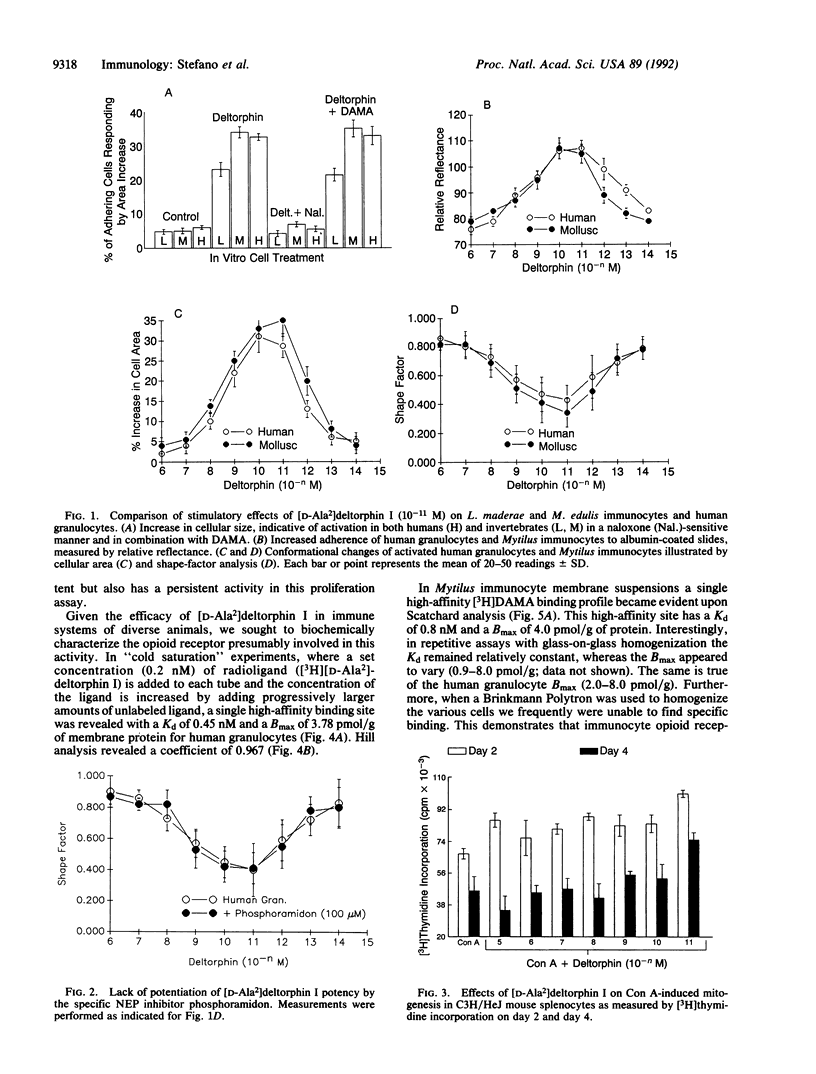
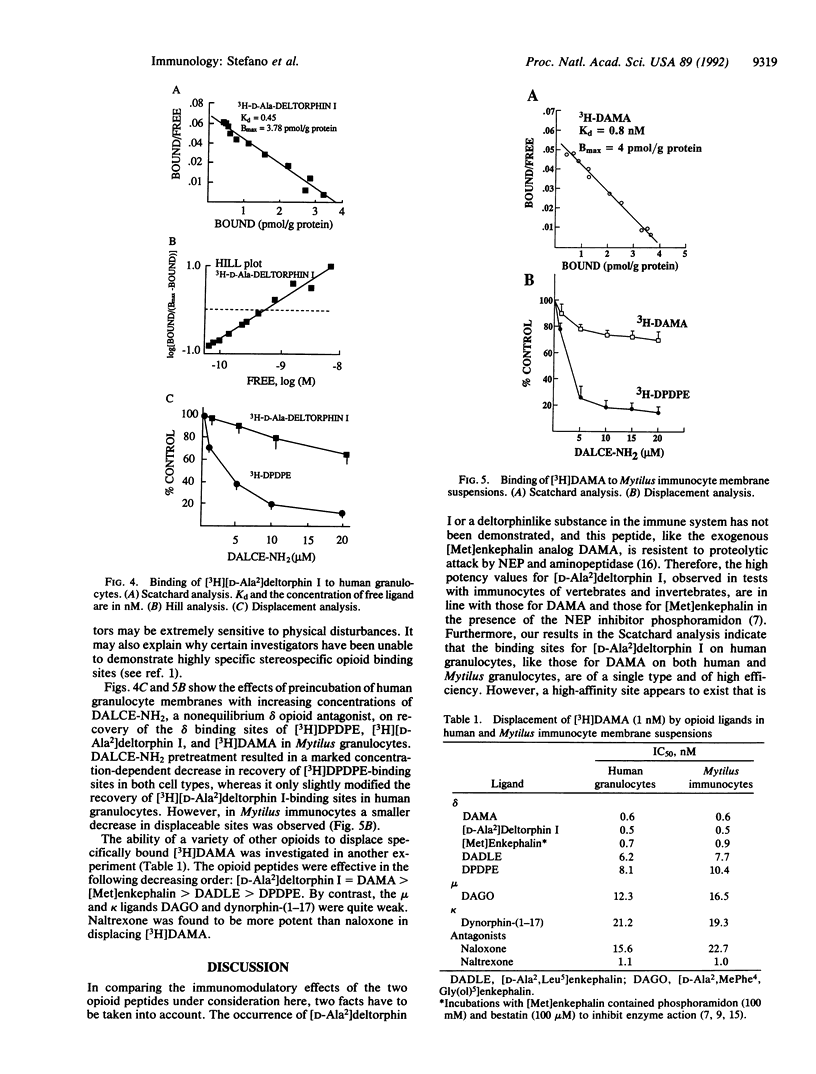
The effects of the opioid neuropeptide [D-Ala2]deltorphin I, isolated from amphibian skin, on immunoregulatory activities were studied in representatives of vertebrates and invertebrates. The high potency of this compound parallels that of [Met]enkephalin, which was previously demonstrated in vertebrate plasma and invertebrate hemolymph. The addition of [D-Ala2]deltorphin I at 10(-11) M to human granulocytes or immunocytes of the mollusc Mytilus edulis resulted in cellular adherence and conformational changes indicative of cellular activation. This value is in line with the concentrations obtained with [Met]enkephalin, tested in the presence of the specific neutral endopeptidase 24.11 inhibitor phosphoramidon, and this opioid's synthetic analog [D-Ala2, Met5]enkephalin which, like [D-Ala2]deltorphin I, is resistant to proteolytic degradation. Both ligands appear to be acting on the same population of immunocytes. The same relationship was estimated to exist in the insect Leucophaea maderae, in which the high viscosity of the hemolymph makes the quantification of reactive cells more difficult than in Mytilus. In addition, [D-Ala2]deltorphin I is as potent as beta-endorphin in affecting the proliferation of lymphocytes in response to mitogen. Saturation experiments with unlabeled ligands and the radioligands [3H][D-Ala2]deltorphin I and [3H][D-Ala2,Met5]enkephalinamide revealed the presence of two high-affinity binding sites on human granulocytes, one sensitive to the nonequilibrium delta opioid antagonist [D-Ala2,Leu5,Cys6]enkephalinamide and the other relatively insensitive. The results obtained with [D-Ala2]deltorphin I support the view that the special role played by endogenous [Met]enkephalin in immunobiological activities of vertebrates and invertebrates is mediated by a special subtype of delta opioid receptor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowen W. D., Hellewell S. B., Kelemen M., Huey R., Stewart D. Affinity labeling of delta-opiate receptors using [D-Ala2,Leu5,Cys6]enkephalin. Covalent attachment via thiol-disulfide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13434–13439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. L., Van Epps D. E. Opioid peptides modulate production of interferon gamma by human mononuclear cells. Cell Immunol. 1986 Nov;103(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erspamer V., Melchiorri P., Falconieri-Erspamer G., Negri L., Corsi R., Severini C., Barra D., Simmaco M., Kreil G. Deltorphins: a family of naturally occurring peptides with high affinity and selectivity for delta opioid binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5188–5192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J. Regulatory peptide metabolism at cell surfaces: the key role of endopeptidase-24.11. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1986;45(11-12):1503–1513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kream R. M., Zukin R. S., Stefano G. B. Demonstration of two classes of opiate binding sites in the nervous tissue of the marine mollusc Mytilus edulis. Positive homotropic cooperativity of lower affinity binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9218–9224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Stefano G. B., D'Adamio L., Switzer S. N., Howard F. D., Sinisterra J., Scharrer B., Reinherz E. L. Downregulation of enkephalin-mediated inflammatory responses by CD10/neutral endopeptidase 24.11. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):394–396. doi: 10.1038/347394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Stefano G. B., Switzer S. N., Griffin J. D., Reinherz E. L. CD10 (CALLA)/neutral endopeptidase 24.11 modulates inflammatory peptide-induced changes in neutrophil morphology, migration, and adhesion proteins and is itself regulated by neutrophil activation. Blood. 1991 Oct 1;78(7):1834–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano G. B., Cadet P., Scharrer B. Stimulatory effects of opioid neuropeptides on locomotory activity and conformational changes in invertebrate and human immunocytes: evidence for a subtype of delta receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6307–6311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano G. B., Leung M. K., Zhao X. H., Scharrer B. Evidence for the involvement of opioid neuropeptides in the adherence and migration of immunocompetent invertebrate hemocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):626–630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano G. B. Role of opioid neuropeptides in immunoregulation. Prog Neurobiol. 1989;33(2):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(89)90038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Kutvirt S. L. Modulation of human neutrophil adherence by beta-endorphin and met-enkephalin. J Neuroimmunol. 1987 Jul-Aug;15(3):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(87)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagon I. S., Gibo D., McLaughlin P. J. Expression of zeta (zeta), a growth-related opioid receptor, in metastatic adenocarcinoma of the human cerebellum. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Feb 21;82(4):325–327. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.4.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagon I. S., Goodman S. R., McLaughlin P. J. Characterization of zeta (zeta): a new opioid receptor involved in growth. Brain Res. 1989 Mar 20;482(2):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Epps D. E., Saland L. Beta-endorphin and met-enkephalin stimulate human peripheral blood mononuclear cell chemotaxis. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3046–3053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



