Abstract
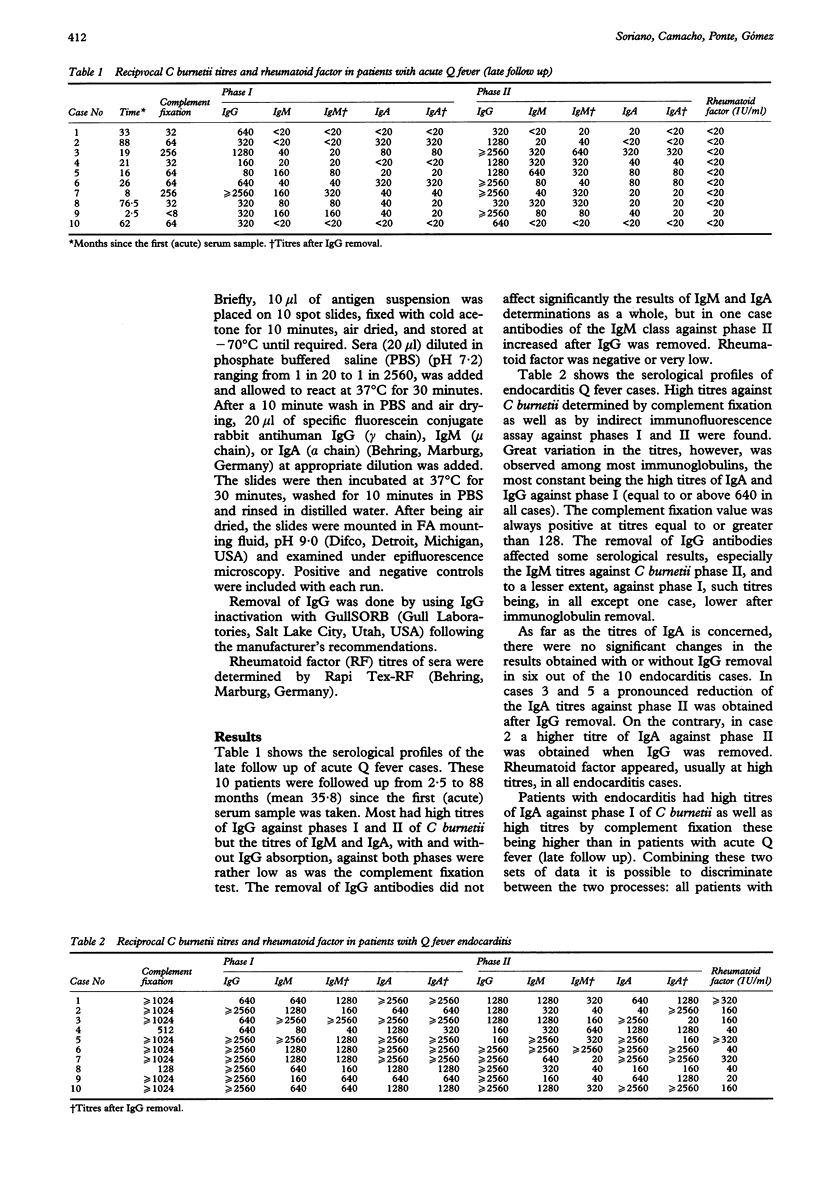
AIMS--To differentiate the serological profiles of chronic (endocarditis) Q fever from the late follow up of acute cases. METHODS--Twenty patients (10 diagnosed with acute and 10 with endocarditis Q fever) were studied. Those diagnosed with acute infection were followed up from 2.5 to 88 months (mean 35.8 months). Serological variables included indirect immunofluorescence against phase I and II of Coxiella burnetii (IgM, IgG, and IgA), complement fixation and rheumatoid factor (RF). RESULTS--All patients with titres of IgA against phase I, after IgG removal, equal to or above 320 and a complement fixation value equal to or above 128 had endocarditis. No patient with acute Q fever had such a serological profile. CONCLUSIONS--The combination of IgA against phase I and complement fixation values may be sufficient to differentiate the serological profile of chronic (endocarditis) Q fever from the late follow up of acute cases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dupuis G., Péter O., Peacock M., Burgdorfer W., Haller E. Immunoglobulin responses in acute Q fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):484–487. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.484-487.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlinger E. Immunofluorescence serology. A tool for prognosis of Q-fever. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;3(4):343–351. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(85)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Guerrero M. L., Muelas J. M., Aguado J. M., Renedo G., Fraile J., Soriano F., De Villalobos E. Q fever endocarditis on porcine bioprosthetic valves. Clinicopathologic features and microbiologic findings in three patients treated with doxycycline, cotrimoxazole, and valve replacement. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Feb;108(2):209–213. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field P. R., Hunt J. G., Murphy A. M. Detection and persistence of specific IgM antibody to Coxiella burnetii by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: a comparison with immunofluorescence and complement fixation tests. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):477–487. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiset P., Ormsbee R. A. The antibody response to antigens of Coxiella burneti. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1968 Apr;206(3):321–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrow J. S., Pike M. C. The long-term prognosis of severe infantile malnutrition. Lancet. 1967 Jan 7;1(7480):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. G., Field P. R., Murphy A. M. Immunoglobulin responses to Coxiella burnetii (Q fever): single-serum diagnosis of acute infection, using an immunofluorescence technique. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):977–981. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.977-981.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough R. C., 3rd, Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M., Rogers W. R., Bennetts R. W., Raaf J., Krause A., Gardner C. Q fever endocarditis in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Sep;91(3):400–402. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-3-400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Laxdal T., Quie P. G., Williams R. C., Jr Rheumatoid factors in subacute bacterial endocarditis--bacterium, duration of disease or genetic predisposition? Ann Intern Med. 1968 Apr;68(4):746–756. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-4-746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL O. W., STALLMAN N. D. The incidence and significance of phase 1 complement-fixing antibody in Q fever. J Hyg (Lond) 1962 Sep;60:359–364. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400020477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock M. G., Philip R. N., Williams J. C., Faulkner R. S. Serological evaluation of O fever in humans: enhanced phase I titers of immunoglobulins G and A are diagnostic for Q fever endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1089–1098. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1089-1098.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M. G., Burgdorfer W. Microimmunofluorescence test for the serological study of rocky mountain spotted fever and typhus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jan;3(1):51–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.1.51-61.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Levy P. Y., Harlé J. R., Etienne J., Massip P., Goldstein F., Micoud M., Beytout J., Gallais H., Remy G. Chronic Q fever: diagnosis and follow-up. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:51–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Urvölgyi J., Etienne J., Roturier M., Puel J., Chaudet H. Diagnosis of endocarditis in acute Q-fever by immunofluorescence serology. Acta Virol. 1988 Jan;32(1):70–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A., Suni J., Wager O. Rheumatoid factor in acute viral infections: interference with determination of IgM, IgG, and IgA antibodies in an enzyme immunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):250–255. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelman D. W. Q fever: a study of 111 consecutive cases. Med J Aust. 1982 Jun 26;1(13):547-8, 551, 553. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1982.tb124169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tellez A., Sainz C., Echevarria C., de Carlos S., Fernandez M. V., Leon P., Brezina R. Q fever in Spain: acute and chronic cases, 1981-1985. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):198–202. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turck W. P., Howitt G., Turnberg L. A., Fox H., Longson M., Matthews M. B., Das Gupta R. Chronic Q fever. Q J Med. 1976 Apr;45(178):193–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. G., Neilson G. H., Galea E. G., Stafford G., O'Brien M. F. Q fever endocarditis in Queensland. Circulation. 1976 Apr;53(4):680–684. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.53.4.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winner S. J., Eglin R. P., Moore V. I., Mayon-White R. T. An outbreak of Q fever affecting postal workers in Oxfordshire. J Infect. 1987 May;14(3):255–261. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(87)93560-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



