Abstract
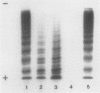
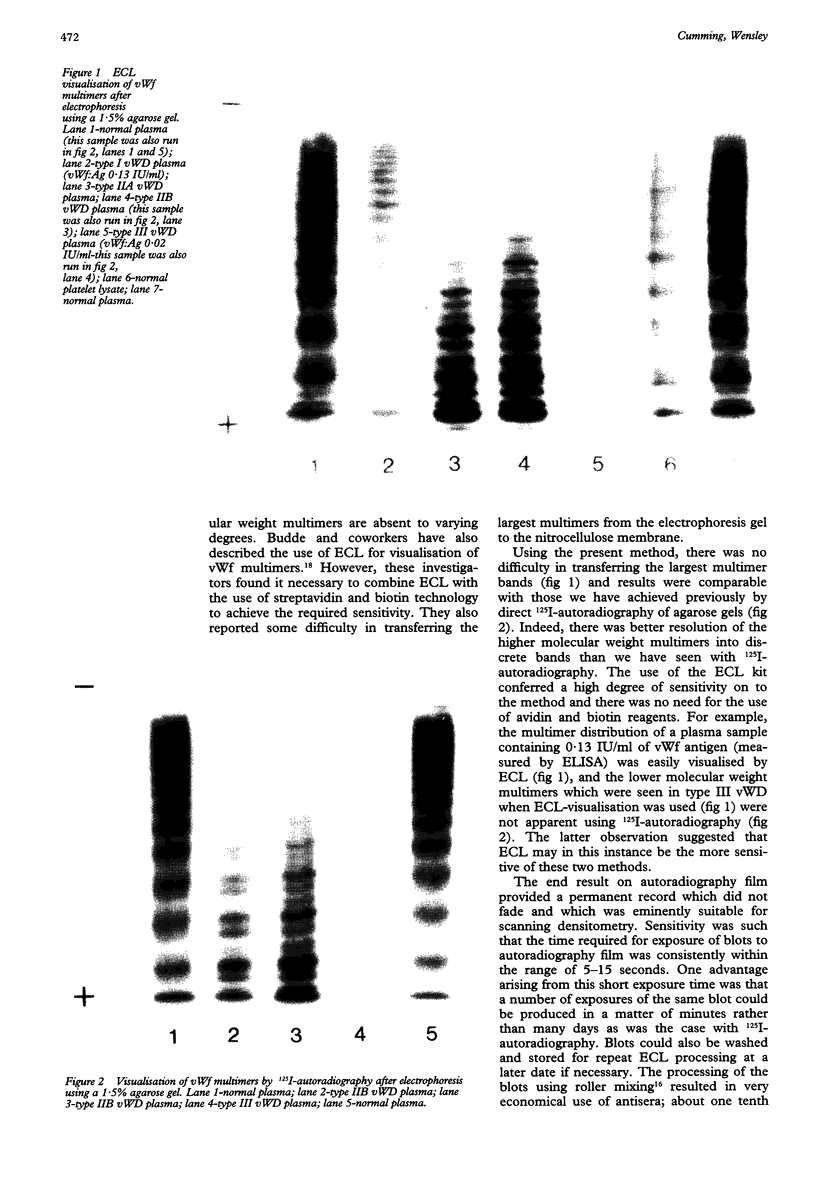
AIMS--To develop a rapid, sensitive, and safe method for the analysis of von Willebrand factor (vWf) multimers in plasma or platelet lysates. METHOD--Analysis of vWf multimers was carried out by sodium dodecyl sulphate-agarose discontinuous gel electrophoresis followed by protein transfer to nitrocellulose membranes by western blotting. Blots were probed using horseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugated rabbit anti-vWf; visualisation of vWf multimers was achieved using a commercially available enhanced chemi-Luminescence (ECL) kit for detecting HRP labelled antibodies on western blots. RESULTS--Electrophoretic transfer of vWf multimers to nitrocellulose membranes, including the higher molecular weight forms, was achieved satisfactorily and there was good resolution of individual multimer bands and of the triplet sub-band structure. Type II vWD variants were readily identifiable. The use of ECL conferred a high degree of sensitivity to the method and the end result on autoradiography film provided a permanent record which did not fade and which was suitable for scanning densitometry. CONCLUSION--The method for vWf multimer analysis described here is sensitive, simple to carry out, uses minimal amounts of reagents, produces results within 48 hours, and does not require the use of potentially hazardous radioactive materials or carcinogenic enzyme substrates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aihara M., Sawada Y., Ueno K., Morimoto S., Yoshida Y., de Serres M., Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H. Visualization of von Willebrand factor multimers by immunoenzymatic stain using avidin-biotin peroxidase complex. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):263–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosstad F., Kjønniksen I., Rønning B., Stormorken H. Visualization of von Willebrand factor multimers by enzyme-conjugated secondary antibodies. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):276–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budde U., Schneppenheim R., Plendl H., Dent J., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Luminographic detection of von Willebrand factor multimers in agarose gels and on nitrocellulose membranes. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Apr 12;63(2):312–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton R. G., Lasham A., Savidge G. F. A new rapid semi-dry blotting technique for multimeric sizing of von Willebrand factor. Thromb Res. 1988 Apr 15;50(2):345–349. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enayat M. S., Hill F. G. Analysis of the complexity of the multimeric structure of factor VIII related antigen/von Willebrand protein using a modified electrophoretic technique. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Aug;36(8):915–919. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.8.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong B. L., Peake I. R. An electroblotting technique for the detection of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor multimers in plasma. Br J Haematol. 1983 Apr;53(4):641–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb07315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Shainoff J. R. Factor VIII-related protein circulates in normal human plasma as high molecular weight multimers. Blood. 1980 Jun;55(6):1056–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi R., Gelfi C., Righetti P. G., Lattuada A., Mannucci P. M. Electroblot and immunoperoxidase staining for rapid screening of the abnormalities of the multimeric structure of von Willebrand factor in von Willebrand's disease. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):246–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. A., Palascak J. E., Thompson M. R., Martelo O. J. A modified SDS agarose gel method for determining factor VIII von Willebrand factor multimers using commercially available reagents. Thromb Res. 1985 Sep 15;39(6):777–780. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeghiero F., Castaman G., Dini E. Epidemiological investigation of the prevalence of von Willebrand's disease. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):454–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. The complex multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1981 Jun;57(6):1140–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Variant von Willebrand's disease: characterization of two subtypes by analysis of multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in plasma and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1318–1325. doi: 10.1172/JCI109795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):895–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneppenheim R., Plendl H., Budde U. Luminography--an alternative assay for detection of von Willebrand factor multimers. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Oct 31;60(2):133–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N., Jones C. N., Thomas P. L. Low volume processing of protein blots in rolling drums. Anal Biochem. 1988 May 1;170(2):393–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90650-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita Y., Harrison J., Abildgaard C. F. von Willebrand factor multimer analysis using a sensitive peroxidase staining method. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Sep 29;62(2):781–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Pietu G., Rabinowitz R., Girma J. P., Rogers J., Meyer D. Heterogeneous abnormalities in the multimeric structure, antigenic properties, and plasma-platelet content of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in subtypes of classic (type I) and variant (type IIA) von Willebrand's disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Mar;101(3):411–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]