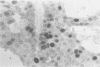
Abstract
AIM--To investigate the association between proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunostaining and various clinicopathological variables, and its prognostic value in breast carcinoma. METHODS--A monoclonal antibody PC10 was applied to formalin fixed, paraffin wax embedded tissue in 144 cases of primary breast cancer. PCNA immunostaining was scored by counting 1000 cells; the percentage of positive stained cells was recorded as the PCNA labelling index (PCNA-LI). RESULTS--The PCNA-LI varied from 0-77% with a mean of 18%. When tumours were separated on the basis of the mean value, 93 had a low PCNA-LI of less or equal than 18% and 47 a high PCNA-LI of more than 18%. There was no significant correlation between PCNA-LI and all prognostic factors included in this study. Moreover, PCNA-LI failed to show any prognostic value for overall and disease free survival. CONCLUSION--PCNA immunostaining is not correlated with clinicopathological variables and patient survival in breast cancer.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battersby S., Anderson T. J. Correlation of proliferative activity in breast tissue using PCNA/cyclin. Hum Pathol. 1990 Jul;21(7):781–781. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Frank R., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H. Cyclin/PCNA is the auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase-delta. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):515–517. doi: 10.1038/326515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Macdonald-Bravo H. Existence of two populations of cyclin/proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle: association with DNA replication sites. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1549–1554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Macdonald-Bravo H. Induction of the nuclear protein 'cyclin' in quiescent mouse 3T3 cells stimulated by serum and growth factors. Correlation with DNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3177–3181. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. L., Allen C., Henson D. E. Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer. 1989 Jan 1;63(1):181–187. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890101)63:1<181::aid-cncr2820630129>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Celis A. Cell cycle-dependent variations in the distribution of the nuclear protein cyclin proliferating cell nuclear antigen in cultured cells: subdivision of S phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3262–3266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltrera M. D., Gown A. M. PCNA/cyclin expression and BrdU uptake define different subpopulations in different cell lines. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Jan;39(1):23–30. doi: 10.1177/39.1.1670579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson A. E., Norton J. A., Weinberg D. S. Comparative assessment of proliferation and DNA content in breast carcinoma by image analysis and flow cytometry. Am J Pathol. 1990 May;136(5):1115–1124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairman M. P. DNA polymerase delta/PCNA: actions and interactions. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jan;95(Pt 1):1–4. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.3.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figge C., Reifenberger G., Vogeley K. T., Messing M., Roosen N., Wechsler W. Immunohistochemical demonstration of proliferating cell nuclear antigen in glioblastomas: pronounced heterogeneity and lack of prognostic significance. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1992;118(4):289–295. doi: 10.1007/BF01208618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher B., Bauer M., Wickerham D. L., Redmond C. K., Fisher E. R., Cruz A. B., Foster R., Gardner B., Lerner H., Margolese R. Relation of number of positive axillary nodes to the prognosis of patients with primary breast cancer. An NSABP update. Cancer. 1983 Nov 1;52(9):1551–1557. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19831101)52:9<1551::aid-cncr2820520902>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galand P., Degraef C. Cyclin/PCNA immunostaining as an alternative to tritiated thymidine pulse labelling for marking S phase cells in paraffin sections from animal and human tissues. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1989 Sep;22(5):383–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1989.tb00223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R. L., Coltrera M. D., Gown A. M. Analysis of proliferative grade using anti-PCNA/cyclin monoclonal antibodies in fixed, embedded tissues. Comparison with flow cytometric analysis. Am J Pathol. 1989 Apr;134(4):733–739. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Lemke H., Baisch H., Wacker H. H., Schwab U., Stein H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1710–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haag D., Goerttler K., Tschahargane C. The proliferative index (PI) of human breast cancer as obtained by flow cytometry. Pathol Res Pract. 1984 Mar;178(4):315–322. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(84)80020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. A., Levison D. A., Woods A. L., Yu C. C., Kellock D. B., Watkins J. A., Barnes D. M., Gillett C. E., Camplejohn R., Dover R. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunolocalization in paraffin sections: an index of cell proliferation with evidence of deregulated expression in some neoplasms. J Pathol. 1990 Dec;162(4):285–294. doi: 10.1002/path.1711620403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haneda H., Katabami M., Miyamoto H., Isobe H., Shimizu T., Ishiguro A., Moriuti T., Takasaki Y., Kawakami Y. The relationship of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen protein to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) resistance of a murine leukemia cell line P388/CDDP. Oncology. 1991;48(3):234–238. doi: 10.1159/000226934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haybittle J. L., Blamey R. W., Elston C. W., Johnson J., Doyle P. J., Campbell F. C., Nicholson R. I., Griffiths K. A prognostic index in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1982 Mar;45(3):361–366. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S., Filipe M. I., Hall P. A., Waseem N., Lane D. P., Levison D. A. Prognostic value of proliferating cell nuclear antigen in gastric carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Aug;44(8):655–659. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.8.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., Gatti C., Travali S., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen cyclin and thymidine kinase mRNA levels by growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10175–10179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamel O. W., LeBrun D. P., Davis R. E., Berry G. J., Warnke R. A. Growth fraction estimation of malignant lymphomas in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue using anti-PCNA/Cyclin 19A2. Correlation with Ki-67 labeling. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jun;138(6):1471–1477. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Bernstein R. M., Franza B. R., Jr, Garrels J. I. Identity of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cyclin. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):374–376. doi: 10.1038/309374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi K., Fritzler M. J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to a nuclear antigen in proliferating cells. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2228–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Mathews M. B. Regulation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13856–13864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Kurki P., Celis J. E., Nakamura R. M., Tan E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to a nuclear protein (PCNA/cyclin) associated with DNA replication. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Feb;168(2):475–486. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins B. A., de la Vega D., Ogata K., Tan E. M., Nakamura R. M. Immunohistochemical detection of proliferating cell nuclear antigen in solid human malignancies. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987 Sep;111(9):841–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestrini R., Sanfilippo O., Tedesco G. Kinetics of human mammary carcinomas and their correlation with the cancer and the host characteristics. Cancer. 1974 Oct;34(4):1252–1258. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197410)34:4<1252::aid-cncr2820340435>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki Y., Deng J. S., Tan E. M. A nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation and blast transformation. J Exp Med. 1981 Dec 1;154(6):1899–1909. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.6.1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubiana M., Courdi A. Cell proliferation kinetics in human solid tumors: relation to probability of metastatic dissemination and long-term survival. Radiother Oncol. 1989 May;15(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(89)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waseem N. H., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Structural conservation and the detection of a nucleolar form. J Cell Sci. 1990 May;96(Pt 1):121–129. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A. L., Hall P. A., Shepherd N. A., Hanby A. M., Waseem N. H., Lane D. P., Levison D. A. The assessment of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunostaining in primary gastrointestinal lymphomas and its relationship to histological grade, S+G2+M phase fraction (flow cytometric analysis) and prognosis. Histopathology. 1991 Jul;19(1):21–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dierendonck J. H., Wijsman J. H., Keijzer R., van de Velde C. J., Cornelisse C. J. Cell-cycle-related staining patterns of anti-proliferating cell nuclear antigen monoclonal antibodies. Comparison with BrdUrd labeling and Ki-67 staining. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1165–1172. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]