FIG 2 .
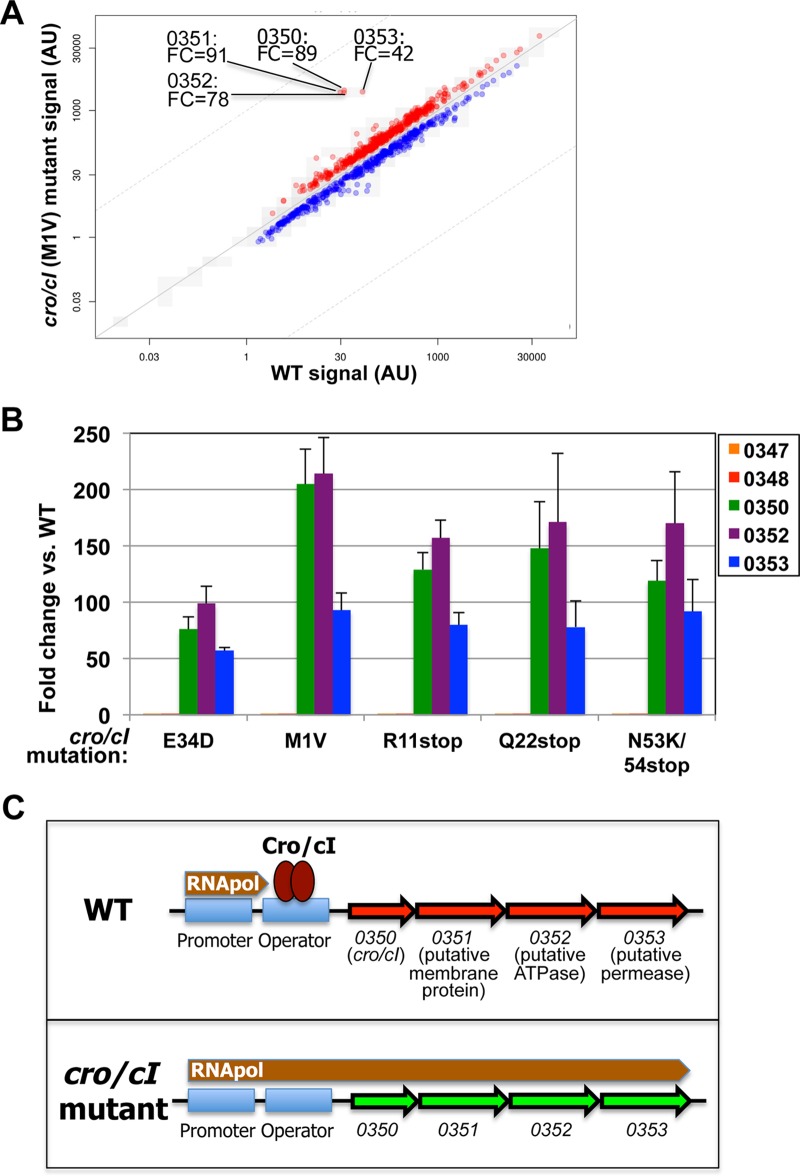
cro/cI mutations enhance the expression of all 4 genes in the cro/cI-ABC transporter operon. (A) RNA sequencing showing differential expression of 4 genes in S. aureus USA300 cro/cI(M1V) mutant (strain GNE0117) versus WT USA300. This revealed a significant enhancement in transcript expression of four genes sharing an operon, including SAUSA300_0350 (cro/cI) itself (89-fold enhanced) and three genes encoding a putative ABC transporter, i.e., SAUSA300_0351 (0351, product annotated as a putative membrane protein; 91-fold upregulated), SAUSA300_0352 (0352, encoding a putative ATPase; 78-fold), and SAUSA300_0353 (0353, encoding a putative permease; 42-fold). Similar results were obtained for three other cro/cI mutants, i.e., cro/cI(R11stop) (strain GNE0215), cro/cI(E34D) (strain GNE0214), and cro/cI(N53K/54stop) (strain GNE0217) mutants. FC, fold change compared to expression in WT USA300; AU, arbitrary units. Table S3 in the supplemental material shows all other genes that were upregulated by at least twofold. (B) Transcript expression of genes upstream of or inside the cro/cI operon was quantified by qRT-PCR in five different USA300 cro/cI mutants (with E34D, M1V, R11stop, Q22stop, and N53K/54stop mutations). This confirmed the robust (>50-fold) overexpression of genes located inside the cro/cI operon, i.e., SAUSA300_0350 (cro/cI), SAUSA300_0352, and SAUSA300_0353. The expression of two genes located immediately upstream of cro/cI, i.e., SAUSA300_0347 (annotated as tatC) and SAUSA300_0348 (tatA), was not affected. Shown is the fold change for each mutant versus the expression in WT USA300, representing the average ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent values. (C) Hypothetical model for the role of cro/cI-mediated regulation of the putative ABC transporter in S. aureus resistance to compound 103. In WT S. aureus (top), Cro/CI protein binds to the operator sequence, suppressing transcription of the ABC transporter by blocking RNA polymerase activity, analogous to the effects of Cro of lambda phage (15). In a cro/cI mutant (bottom), either no Cro/CI protein or a nonfunctional Cro/CI protein is produced, enabling polymerase activity that leads to overexpression of the ABC transporter, which causes resistance to compound 103.