Abstract
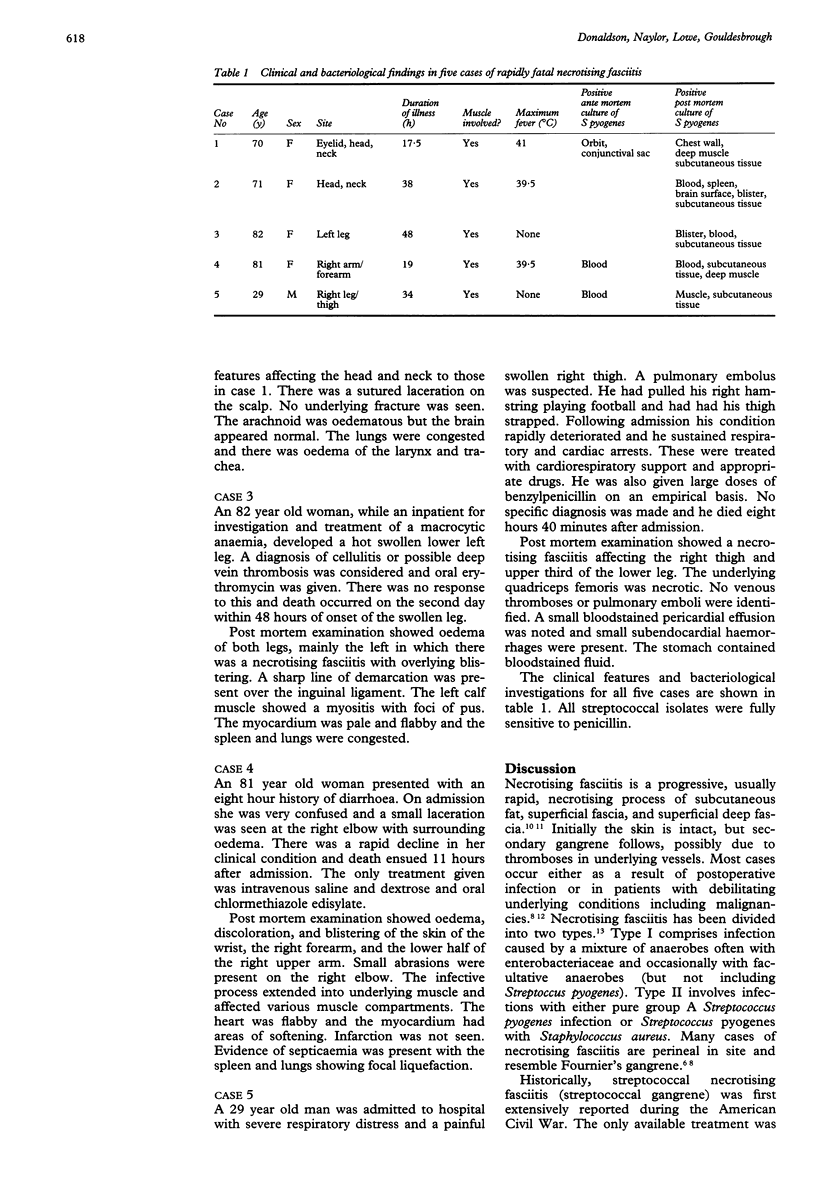
AIMS--To describe the morbid anatomical and bacteriological features in a series of five cases of rapidly fatal Streptococcus pyogenes necrotising fasciitis. METHODS--Post mortem and bacteriological examinations were made of five patients dying within 48 hours from rapidly fatal necrotising fasciitis. RESULTS--All five cases died rapidly from a toxic Streptococcus toxin syndrome as a result of developing necrotising fasciitis following trivial injury. CONCLUSIONS--Necrotising fasciitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes infection can be rapidly fatal. This is probably the result of a toxic shock syndrome. Rapid, early diagnosis and swift and probably empirical treatment is required to avoid a fatal outcome.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnholt J., Andersen I., Søndergaard G. Necrotic bullous erysipelas. Acta Med Scand. 1988;223(2):191–192. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1988.tb15786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahna M., Canalis R. F. Necrotizing fasciitis. (Streptococcal gangrene) of the face. Report of a case and review of the literature. Arch Otolaryngol. 1980 Oct;106(10):648–651. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1980.00790340056015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailie F. B., Linehan I. P., Hadfield G. J., Gillett A. P., Bailey B. N. Infective cutaneous gangrene--urgency in diagnosis and treatment. Ann Plast Surg. 1987 Sep;19(3):238–246. doi: 10.1097/00000637-198709000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker F. G., Leppard B. J., Seal D. V. Streptococcal necrotising fasciitis: comparison between histological and clinical features. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Mar;40(3):335–341. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.3.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartter T., Dascal A., Carroll K., Curley F. J. 'Toxic strep syndrome'. A manifestation of group A streptococcal infection. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Jun;148(6):1421–1424. doi: 10.1001/archinte.148.6.1421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beathard G. A., Guckian J. C. Necrotizing fasciitis due to group A beta-hemolytic streptococci. Arch Intern Med. 1967 Jul;120(1):63–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibler M. R., Rouan G. W. Cryptogenic group A streptococcal bacteremia: experience at an urban general hospital and review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):941–951. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone L. A., Woodard D. R., Schlievert P. M., Tomory G. S. Clinical and bacteriologic observations of a toxic shock-like syndrome due to Streptococcus pyogenes. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):146–149. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruickshank J. G., Hart R. J., George M., Feest T. G. Fatal streptococcal septicaemia. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jun 13;282(6280):1944–1945. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6280.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson O. J., Pers M. Streptococcal gangrene of the eyelids. Case reports. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986;20(3):331–335. doi: 10.3109/02844318609004497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedden W. F. Six Cases of Acute Infective Gangrene of the Extremities. Proc R Soc Med. 1909;2(CLIN):213–218. doi: 10.1177/003591570900200178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledingham I. M., Tehrani M. A. Diagnosis, clinical course and treatment of acute dermal gangrene. Br J Surg. 1975 May;62(5):364–372. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintiliani R., Engh G. A. Overwhelming sepsis associated with group A beta hemolytic streptococci. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971 Oct;53(7):1391–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea W. J., Wyrick W. J., Jr Necrotizing fasciitis. Ann Surg. 1970 Dec;172(6):957–964. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197012000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees R. C. Cytokines as biological response modifiers. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Feb;45(2):93–98. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.2.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimailho A., Riou B., Richard C., Auzepy P. Fulminant necrotizing fasciitis and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):143–146. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse T. M., Malangoni M. A., Schulte W. J. Necrotizing fasciitis: a preventable disaster. Surgery. 1982 Oct;92(4):765–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson P. Do streptococci cause toxic shock? BMJ. 1990 Nov 3;301(6759):1006–1007. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6759.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal D. V., Leppard B. Necrotizing fasciitis-a disease of temperate and warm climates. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(3):392–395. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaunak S., Wendon J., Monteil M., Gordon A. M. Septic scarlet fever due to Streptococcus pyogenes cellulitis. Q J Med. 1988 Nov;69(259):921–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Tanner M. H., Winship J., Swarts R., Ries K. M., Schlievert P. M., Kaplan E. Severe group A streptococcal infections associated with a toxic shock-like syndrome and scarlet fever toxin A. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):1–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollerman G. H. Changing group A streptococci. The reappearance of streptococcal 'toxic shock'. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Jun;148(6):1268–1270. doi: 10.1001/archinte.148.6.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB H. E., HOOVER N. W., NICHOLS D. R., WEED L. A. Streptococcal gangrene. Arch Surg. 1962 Dec;85:969–973. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1962.01310060105019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder E. L., Mendez J., Khatib R. Spontaneous gangrenous myositis induced by Streptococcus pyogenes: case report and review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Mar-Apr;9(2):382–385. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.2.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



