Abstract
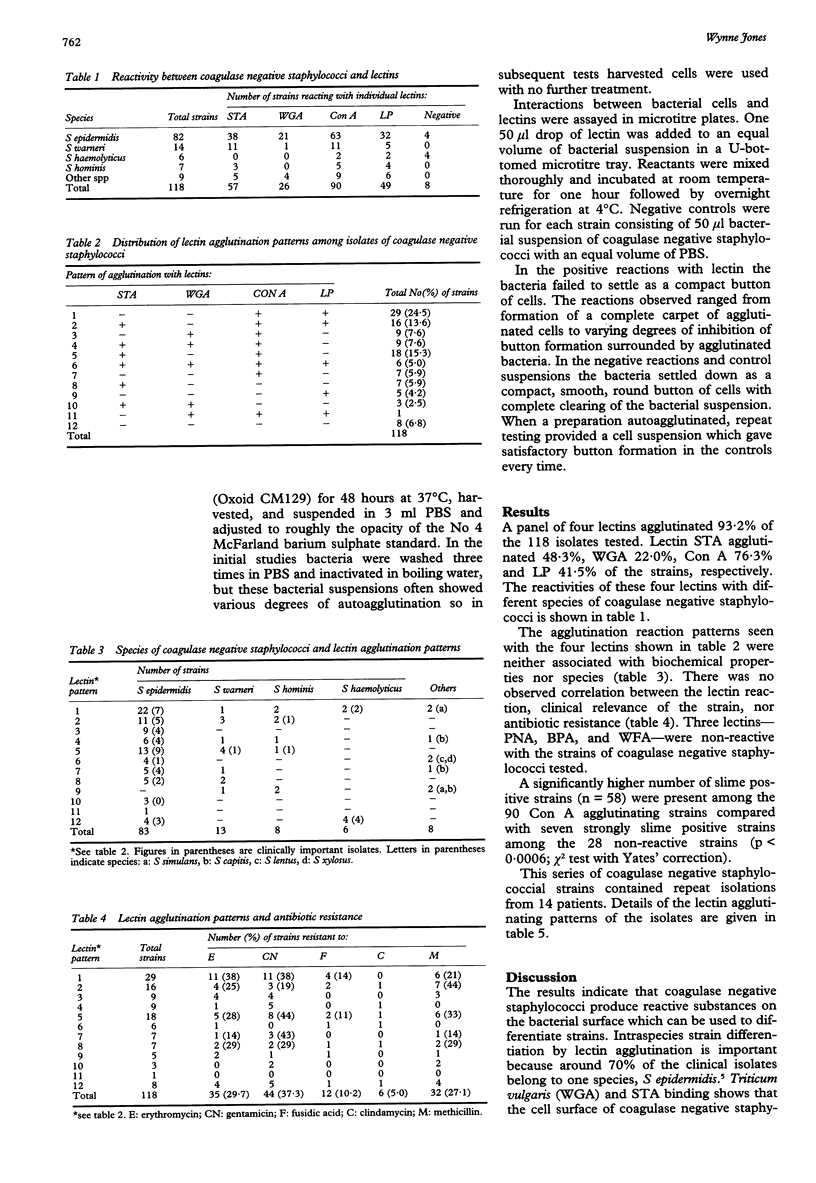
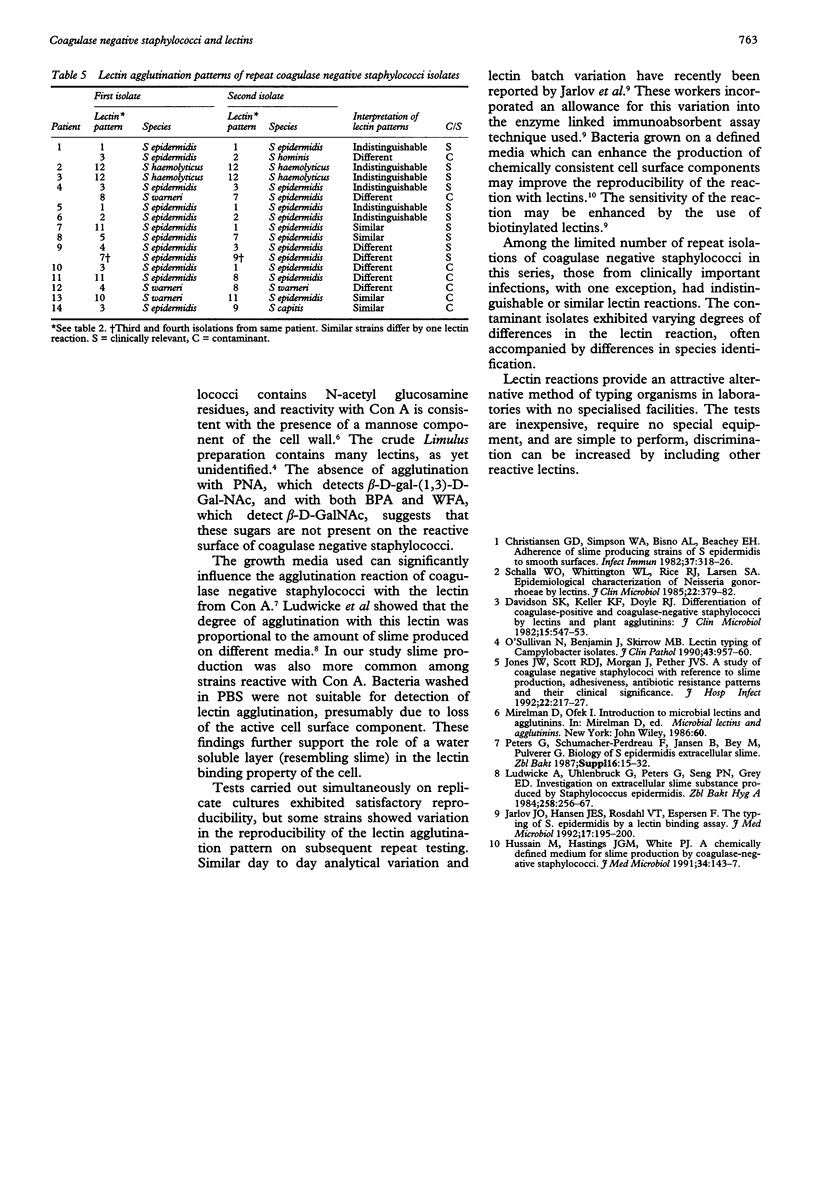
AIMS--To investigate the reaction of 118 blood culture isolates of coagulase negative staphylococci with a panel of seven lectins. METHODS--The interactions between the bacterial suspensions and lectins from Arachnis hypogaea (peanut agglutinin), Bauhina purpurea, Solanum tuberosum (potato starch), Triticum vulgaris (wheat germ agglutinin), Wisteria floribunda, Concanavalin ensiformis and Limulus polphemus (horse-shoe crab agglutinin) were assayed in microtitre plates incubated for 1 hour at room temperature then left overnight at 4 degrees C. Agglutinating activity was detected by examining the pattern of cell settlement compared with that of the controls. RESULTS--Lectins from Solanum tuberosum, Triticum vulgaris, Concanavalin ensiformis and Limulus polyphemus agglutinated 90% of the strains and displayed 11 agglutination patterns which were unrelated to species, clinical relevance, or antibiotic resistance. Fifty three per cent of the isolates fell into three reaction patterns and the other patterns were represented by nine or fewer strains. Replicate cultures investigated simultaneously gave consistent results, but some strains exhibited variation in agglutination patterns on repeat testing. CONCLUSIONS--Based on these observations lectin agglutination patterns seem to offer a method with potential for strain differentiation among coagulase negative staphylococci. Reproducibility may be improved by the use of biotinylated lectins and growing the coagulase negative staphylococci on defined media. Discrimination can be increased by the inclusion of other reactive lectins.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson S. K., Keller K. F., Doyle R. J. Differentiation of coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative staphylococci by lectins and plant agglutinins. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):547–553. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.547-553.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarløv J. O., Hansen J. E., Rosdahl V. T., Espersen F. The typing of Staphylococcus epidermidis by a lectin-binding assay. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Sep;37(3):195–200. doi: 10.1099/00222615-37-3-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. W., Scott R. J., Morgan J., Pether J. V. A study of coagulase-negative staphylococci with reference to slime production, adherence, antibiotic resistance patterns and clinical significance. J Hosp Infect. 1992 Nov;22(3):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(92)90046-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwicka A., Uhlenbruck G., Peters G., Seng P. N., Gray E. D., Jeljaszewicz J., Pulverer G. Investigation on extracellular slime substance produced by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984 Dec;258(2-3):256–267. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(84)80043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan N., Benjamin J., Skirrow M. B. Lectin typing of Campylobacter isolates. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Nov;43(11):957–960. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.11.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalla W. O., Whittington W. L., Rice R. J., Larsen S. A. Epidemiological characterization of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by lectins. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):379–382. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.379-382.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



