Fig. 1.
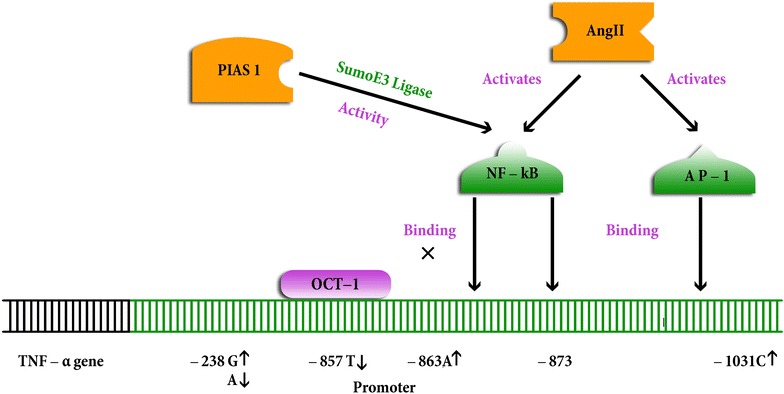
Schematic representation showing some of the molecules thought to be involved in the interaction with TNF-α promoter region. The transcriptional induction of TNF-α is thought to be controlled by some transcription factors, including the transcription factor OCT1, the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), the signal transducer and transcription activator (PIAS1) and activator protein-1 (AP-1). The transcription factor OCT1 can strongly bind with the allele -857T (but not the -857C) and thus blocks the interaction of NF-κB to the nearby region -873 to -863 leading to inhibition of TNF-α transcription. PIAS1 possesses SUMO E3 ligase activity and can repress NF-κB by blocking the DNA-binding activity of NF-κB to TNF-α promoter. Ang II can activate the 2 transcription factors NF-kB and AP-1that are important in mediating TNF-α gene expression. Alleles associated with upregulation of TNF-α gene are designated with arrows with heads directed up while those alleles associated with downregulation are designated with arrows with heads directed down. Molecules involved in the posttranscriptional and posttranslational control of TNF-α are mentioned in the text and not shown here
