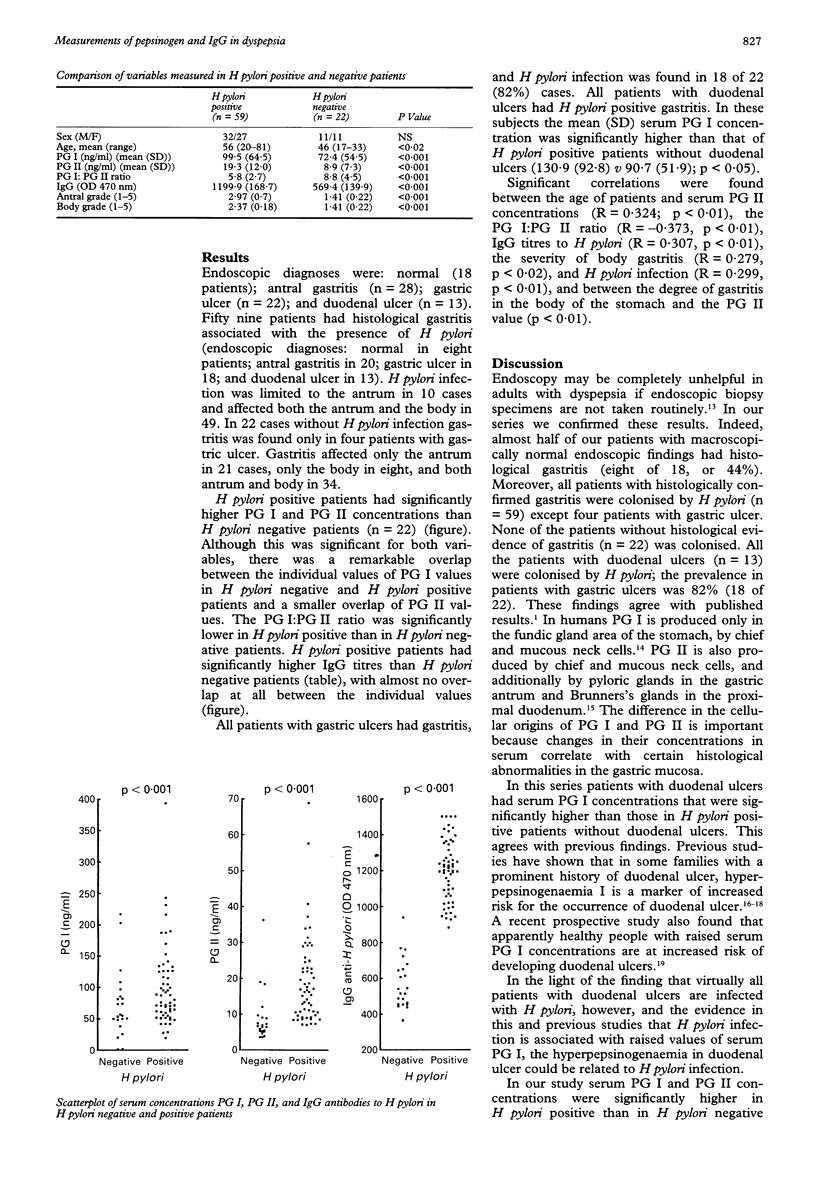
Abstract
AIMS--To investigate the association between histologically confirmed gastritis, carriage of Helicobacter pylori and pepsinogen (PG) I and PG II concentrations. METHODS--Prospective study of 81 dyspeptic patients undergoing upper gastrointestinal endoscopy was made. The extent of gastric mucosal inflammation and the presence of H pylori was determined, and serology to evaluate PG I and II concentrations and IgG titres to H pylori was carried out. RESULTS--The presence of H pylori was strongly correlated with high IgG antibody titres to H pylori and gastritis. Patients who were H pylori positive had significantly higher PG I and PG II concentrations and a significantly lower PG I:PG II ratio than patients who were negative for H pylori. In 13 patients with duodenal ulcer and H pylori positive gastritis serum PG I concentrations were significantly higher than in H pylori positive patients without duodenal ulcer. Significant correlations were found between the age of patients and serum PG II, the PG I:PG II ratio, IgG antibodies to H pylori, the severity of body gastritis and H pylori infection, and between the degree of gastritis in the body of the stomach and the PG II concentration. CONCLUSIONS--Serum PG I and II concentrations, together with a fall in the PG I:PG II ratio, could be used as predictors of H pylori infection as well as serum IgG antibody response to H pylori.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Karnes W. E., Jr, Samloff I. M., Siurala M., Kekki M., Sipponen P., Kim S. W., Walsh J. H. Positive serum antibody and negative tissue staining for Helicobacter pylori in subjects with atrophic body gastritis. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jul;101(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90474-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984 Jun 16;1(8390):1311–1315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91816-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oderda G., Vaira D., Dell'Olio D., Holton J., Forni M., Altare F., Ansaldi N. Serum pepsinogen I and gastrin concentrations in children positive for Helicobacter pylori. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Sep;43(9):762–765. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.9.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oderda G., Vaira D., Holton J., Dowsett J. F., Ansaldi N. Serum pepsinogen I and IgG antibody to Campylobacter pylori in non-specific abdominal pain in childhood. Gut. 1989 Jul;30(7):912–916. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.7.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I., Petersen G., Samloff I. M., McConnell R. B., Ellis A., Spence M. A., Rimoin D. L. Genetic heterogeneity of hyperpepsinogenemic I and normopepsinogenemic I duodenal ulcer disease. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Sep;91(3):372–377. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-3-372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I., Sones J. Q., Samloff I. M., Richardson C. T., Gursky J. M., Walsh J. H., Rimoin D. L. Duodenal-ulcer disease associated with elevated serum pepsinogen I: an inherited autosomal dominant disorder. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 11;300(2):63–66. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901113000203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M. Cellular localization of group I pepsinogens in human gastric mucosa by immunofluorescence. Gastroenterology. 1971 Aug;61(2):185–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M., Liebman W. M. Cellular localization of the group II pepsinogens in human stomach and duodenum by immunofluorescence. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jul;65(1):36–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M. Pepsinogens I and II: purification from gastric mucosa and radioimmunoassay in serum. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jan;82(1):26–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M. Pepsinogens I and II: purification from gastric mucosa and radioimmunoassay in serum. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jan;82(1):26–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M., Stemmermann G. N., Heilbrun L. K., Nomura A. Elevated serum pepsinogen I and II levels differ as risk factors for duodenal ulcer and gastric ulcer. Gastroenterology. 1986 Mar;90(3):570–576. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)91110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. L., Calam J., Rotter J. I., Vaillant C., Samloff I. M., Cook A., Simkin E., Dockray G. J. Family studies of hypergastrinemic, hyperpepsinogenemic I duodenal ulcer. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Oct;95(4):421–425. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-4-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaira D., Holton J., Osborn J., Dowsett J., McNeil I., Hatfield A. Use of endoscopy in patients with dyspepsia. BMJ. 1989 Jul 22;299(6693):237–237. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6693.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaira D., Holton J. Serum immunoglobulin G antibody levels for Campylobacter pylori diagnosis. Gastroenterology. 1989 Oct;97(4):1069–1070. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenendaal R. A., Biemond I., Peña A. S., van Duijn W., Kreuning J., Lamers C. B. Influence of age and Helicobacter pylori infection on serum pepsinogens in healthy blood transfusion donors. Gut. 1992 Apr;33(4):452–455. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.4.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R., Truelove S. C., Gear M. W. The histological diagnosis of chronic gastritis in fibreoptic gastroscope biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jan;25(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


