Abstract
The deficiency of Adenosine Deaminase 2 (DADA2) is a new autoinflammatory disease characterised by an early onset vasculopathy with livedoid skin rash associated with systemic manifestations, CNS involvement and mild immunodeficiency.
This condition is secondary to autosomal recessive mutations of CECR1 (Cat Eye Syndrome Chromosome Region 1) gene, mapped to chromosome 22q11.1, that encodes for the enzymatic protein adenosine deaminase 2 (ADA2). By now 19 different mutations in CECR1 gene have been detected.
The pathogenetic mechanism of DADA2 is still unclear. ADA2 in a secreted protein mainly expressed by cells of the myeloid lineage; its enzymatic activity is higher in conditions of hypoxia, inflammation and oncogenesis. Moreover ADA2 is able to induce macrophages proliferation and differentiation; it’s deficiency is in fact associated with a reduction of anti-inflammatory macrophages (M2). The deficiency of ADA2 is also associated with an up-regulation of neutrophils-expressed genes and an increased secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The mild immunodeficiency detected in many DADA2 patients suggests a role of this protein in the adaptive immune response; an increased mortality of B cells and a reduction in the number of memory B cells, terminally differentiated B cells and plasmacells has been described in many patients. The lack of the protein is associated with endothelium damage; however the function of this protein in the endothelial homeostasis is still unknown.
From the clinical point of view, this disease is characterized by a wide spectrum of severity. Chronic or recurrent systemic inflammation with fever, elevation of acute phase reactants and skin manifestations (mainly represented by livedo reticularis) is the typical clinical picture. While in some patients the disease is mild and skin-limited, others present a severe, even lethal, disease with multi-organ involvement; the CNS involvement is rather common with ischemic or hemorrhagic strokes. In many patients not only the clinical picture but also the histopathologic features are undistinguishable from those of systemic polyarteritis nodosa (PAN). Of note, patients with an unusual phenotype, mainly dominated by clinical manifestations suggestive for an immune-disrective condition, have been described.
Due to its rarity, the response to treatment of DADA2 is still anecdotal. While steroids can control the disease’s manifestations at high dosage, none of the common immunosuppressive drugs turned out to be effective. Biologic drugs have been used only in few patients, without a clear effectiveness; anti-TNF drugs are those associated to a better clinical response. Hematopoietic stem cells transplantation was effective in patients with a severe phenotype.
Background
The deficiency of Adenosine Deaminase 2 (DADA2) is a recently identified disease, gathered in the family of autoinflammatory diseases, mainly characterised by early-onset polyarteritis, hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes and hypogammaglobulinemia.
In February 2014 two independent studies, one held by the American National Institutes of Health in Bethesda [1] and the other one by the Israeli Sharee Zedek Medical Center in Jerusalem [2], identified this new clinical entity, often familial, characterised by early onset livedoid rash associated with systemic inflammation (fever and elevation of acute phase reactants). Some patients presented ischemic or haemorrhagic cerebral stroke, other vasculopathy-related manifestations (hypertension, gastrointestinal symptoms), hepatosplenomegaly, peripheral neuropathy and mild immunodeficiency.
In many cases both the clinical manifestations and the histological findings were consistent with the diagnosis of polyarteritis nodosa (PAN), with childhood-onset.
The analysis of the whole exome-sequencing (WES) in unrelated affected patients identified autosomal recessive deleterious mutations in CECR1 gene, encoding for adenosine deaminase 2 (ADA2).
The marked reduction of both plasmatic levels and enzymatic activity of ADA2 detected in affected patients respect to healthy donors [1, 2], confirmed the hypothesis that the causative mutation determines the loss-of-function of the protein. The non-affected simple-heterozygous parents displayed intermediate values of both plasmatic levels and enzymatic activity [1].
CECR1 gene
The CECR1 (Cat Eye Syndrome Chromosome Region 1) gene, mapped to chromosome 22q11.1 and constituted by 10 exons [1, 2], encodes for the enzyme adenosine deaminase 2 (ADA2), a protein composed by 4 domains: the signal sequence, the dimerization domain, the putative receptor-binding domain and the catalytic domain.
The mutations detected in CECR1 gene so far are 19, with a different prevalence according to patient’s ethnicity (Table 1, Fig. 1) [1–13]. The G47R mutation has been detected in homozygous state in all patients of Georgian Jewish and Turkish origin. Based on the results of the molecular analysis performed in 246 healthy donors of Georgian Jewish origin, the estimated frequency of this mutation in this population is 10 % [2].
Table 1.
CECR1 mutations so far detected
| Mutation | Exon | HGVS sequence name | Aminoacid substitution | N° of patients | Enzymatic domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1T | 2 | c.2 T > C | Met1Thr | 1 in compound heterozygosis | Signal peptide |
| K13del | 2 | c.37_39del | 37_39del | 2 in compound heterozygosis | Signal peptide (?) |
| 28-kb-deletion | 2 | deletion | deletion | 1 in compound heterozygosis | 5′UTR (5′untranslated region) |
| G47R | 2 | c.139G > A | Gly47Arg | 27 in homozygosis | Dimerization |
| 1 in compound heterozygosis | |||||
| G47A | 2 | c.140G > C | Gly47Ala | 2 in compound heterozygosis | Dimerization |
| G47V | 2 | c.140G > T | Gly47Val | 1 in compound heterozygosis | Dimerization |
| I93T | 2 | c.278 T > C | Ile93Thr | 1 in compound heterozygosis | Dimerization |
| A109D | 3 | c.326C > A | Ala109Asp | 1 in compound heterozygosis | Catalytic |
| H112Q | 3 | c.336C > G | His112Gln | 1 in compound heterozygosis | Catalytic |
| T119A | 3 | c.355A > G | Thr119Ala | 4 in compound heterozygosis | Catalytic |
| G142S | 3 | c.424G > A | Gly142Ser | 4 in compound heterozygosis | Catalytic |
| R169Q | 3 | c.506G > A | Arg169Gln | 15 in homozygosis | PBR (putative receptor-binding) |
| 9 in compound heterozygosis | |||||
| P193L | 4 | c.578C > T | Pro193Leu | 1 in compound heterozygosis | Catalytic (?) |
| M243R | 4 | NA | Met243Arg | 2 in compound heterozygosis | Catalytic |
| P251L | 4 | c.752C > T | Pro251Leu | 4 in compound heterozygosis | Catalytic |
| W264S | 5 | c.791G > C | Trp264Ser | 1 in compound heterozygosis | Catalytic |
| R306* | 6 | c.916C > T | p.Arg306* | 1 in compound heterozygosis | Catalytic (?) |
| N328K | 7 | c.1159C > A | Cys1159Arg | 2 in compound heterozygosis | Catalytic |
| Y453C | 9 | c.1358A > G | Tyr453Cys | 3 in compound heterozygosis | Catalytic |
Legend: HGVS: Human Genome Variation Society
NA not available
Fig. 1.
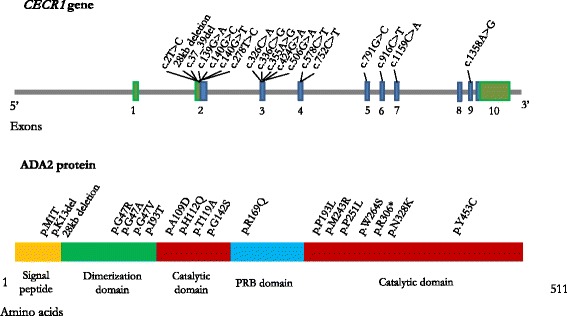
Cat Eye Syndrome Chromosome Region 1 (CECR1) gene and Adenosine Deaminase 2 (ADA2) protein with the mutations by now detected
Conversely, the R169Q is the mutation more frequently detected in the European Caucasian population [1, 2, 7, 12, 13].
The mutations so far detected affect the Signal peptide (n = 2), the 5’ untranslated region (n = 1), the dimerization domain (n = 4), the putative receptor binding (n = 1) and the catalytic domain (n = 11) (Table 1, Fig. 1) [1–13]. Moreover two patients with a homozygous deletion on 22.11.1 chromosome (encompassing CECR1 gene) have been recently described [14].
ADA2 protein and pathogenetic mechanisms
The enzyme Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) plays a key role in the purine metabolism converting adenosine to inosine and 2′-deoxyadenosine to 2′-deoxyinosine [15].
The two major ADA isoforms are ADA1, whose deficiency is cause of a severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) [16], and ADA2.
Even if the two proteins have partial structural homology, the two isoenzymes differ in many aspects: the affinity of ADA2 for molecules of adenosine and deoxy-adenosine is about 100 times lower than that of ADA1; consequently, at physiological concentrations of substrate, the deaminase activity of ADA2 is almost absent [17].
While ADA1 is monomeric and acts primarily intracellularly, ADA2 is dimeric and secreted in the extracellular environment where it exerts its main functions. For this reason ADA2 is clearly detectable in the plasma. Finally, while ADA1 is ubiquitally expressed in all cell types, ADA2 is mostly expressed by monocytes and other cells of the myeloid lineage [17].
ADA2 is more stable at high temperatures and the optimum pH for its activity is generally acid (about 6.5), which suggests a specialized role of this enzyme in conditions of hypoxia, inflammation and oncogenesis; in these conditions its deaminase activity is higher [17] (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
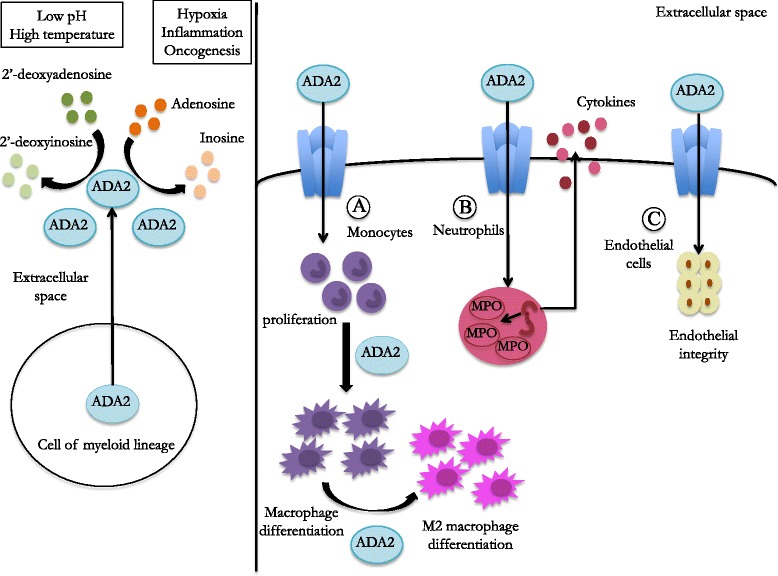
Production and physiological role of Adenosine Deaminase 2 (ADA2). ADA2 is produced and secreted by cells of myeloid lineage; it exerts its enzymatic activity in the extracellular space, especially in the presence of a low pH or high temperature. On monocytes (a) ADA2 acts as growth-factor with an autocrine activity: it induces monocytes’ proliferation and promote the differentiation of M2 anti-inflammatory macrophages. On neutrophils (b) ADA2 induces the gene of expression of some pro-inflammatory proteins, such as myeloperoxidase (MPO) and neutrophils’ activations, leading to the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. There are indirect evidences of a possible role of ADA2 as growth-factor for endothelial cells (c)
The capacity of binding receptors involved in the signal transduction of different pathways (such as proteoglycans), confers to ADA2 a growth-factor like action; for this reason ADA2 is considered an Adenosine Deaminase-related Growth-Factor (ADGF) [17–19] (Fig. 2).
ADA2 displays also an autocrine activity: the protein, released by activated monocytes, is able to induce monocyte proliferation and macrophage differentiation [20]; CECR1 silencing in myeloid cells is in fact associated to a reduced differentiation of monocytes to macrophages [1]. This activity has been demonstrated to be mediated by the direct binding of cellular receptors, and therefore to be independent from the enzymatic activity [20] (Fig. 2).
ADA2 seems to be also involved in the balance between pro-inflammatory (M1) and anti-inflammatory (M2) monocytes; its absence has been in fact associated with a defect in differentiation of M2 macrophages, which leads to a prevalence of pro-inflammatory M1 cells [1].
Microarray analysis in two DADA2 patients showed a marked up-regulation of neutrophils-expressed genes. Intracellular staining revealed an increased expression of myeloperoxidase (MPO) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells compared to controls [8] (Fig. 2). According with these findings, the assessment of cytokine levels performed in the serum of few described patients revealed an increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines: in the two patients carrying a homozygous deletion of 22q11.1 chromosome increased levels of both IL-1β and TNFα were detected [14], while in another case the detection of IL-6 revealed increased levels [7]. These data are in contrast with the results obtained in the NIH study, in which the cytokine assay performed in the supernatants of the whole blood cell cultured with different stimuli did not reveal any significant difference between patients and healthy donors [1]. Further studies on larger series of patients are therefore needed in order to investigate the cytokines’ pattern in DADA2; in particular the cytokines’ production should be assessed in stimulated PBMCs and should take into consideration the disease activity.
It has been also postulated that the deregulation of purinergic stimulation, due to the decrease of the enzymatic activity of ADA2, may play a pro-inflammatory role. Adenosine is in fact an important signaling molecule that can modulate the inflammatory response; its concentration in tissues is normally low and increases in condition of cellular stress, ischemia or inflammation [21]. The accumulation of adenosine can influence the inflammatory response by binding several receptors that lead to inflammation, tissue damage and fibrosis [21]. However, the plasmatic levels of adenosine and deoxiadenosine in few DADA2 patients has been detected within the normal range [1, 2].
Since hypogammaglobulinemia has been described in some patients, adaptive immunity has been investigated in ADA2 patients. A reduction in the number of memory B cells, terminally differentiated B cells and plasmacells has been described [1, 7]; moreover co-culture experiments have enlightened an increased mortality of B cells [1]. Not univocal results have been detected concerning the T cells function. In fact, while in the NIH study ADA2 mutations seem not to affect T lymphocyte number and activation [1], in a more recent study an increase of regulatory T cells and a decrease of CD8+ and CD4 + memory T cells have been detected in one patient with DADA2 [7]. In addition a reduced number of Th1, Th2 and follicular T helper (Tfh) cells has been observed in the same patient.
The reason why endothelium represents the main target of inflammation in DADA2 is still largely unknown. ADA2 acts as a growth-factor for endothelial cells. In fact, even if it has been demonstrated that endothelial cells do not express CECR1 gene, the deficiency of ADA2 is associated to a damage of vascular endothelium and to an over expression of activation markers [1]. The knockdown animal model for CECR1 gene (zebrafish) displays cerebral haemorrhages without morphologic alteration in the vascular structure; these episodes recovered following the transfection of non-mutant human CECR1 messenger RNA [1]. In the same way, monocytes of patients with DADA2 led to destruction of co-cultured human microvascular endothelial cells [1].
Due to the rarity of the disease, all available data on the pathogenic consequences of ADA2 defect in humans come from few patients; further studies are therefore needed in order to better enlighten the activity of ADA2 in the innate and adaptive immune response and its role in the endothelium homeostasis.
Clinical manifestations
DADA2 can be defined as an inflammatory vasculopathy with a wide range of clinical manifestations, possibly associated with an immunodeficiency of variable severity.
The disease is mainly characterized by chronic or recurrent systemic inflammation with fever and elevation of acute phase reactants, usually associated with different possible skin manifestations, ranging from the most frequent livedo reticularis (Fig. 3) to maculopapular rash, nodules, purpura, erythema nodosum, Raynaud’s phenomenon, ulcerative lesions, digital necrosis [1, 2].
Fig. 3.
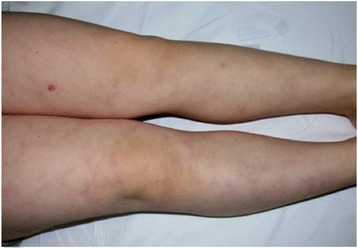
Livedo reticularis in a patient with DADA2
The clinical picture is wide, ranging form a mild disease with a late onset skin-limited involvement to a very severe systemic phenotype (even fatal) with an early onset and a multi-organ involvement (Tables 2 and 3).
Table 2.
Clinical manifestation of DADA2 patients so far described
| Report |
CECR1
Mutation |
Ethnicity | Age at onset | Fever | Skin | CNS/PNS | Gastro-intestinal | Immune/Hematologic system | ANA | ANCA | Hypertension | Other | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Navon et al. | 1 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 2 m | Yes | Ulcerations at extremities | No | Intestinal necrosis | No | neg | neg | Yes | Coronary aneurysms |
| 2 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 5 y | No | Livedo reticularis, nodules, purpuric rash | No | Intestinal vasculitis | No | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 3 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 7 m | Yes | Livedo reticularis, papulo-nodular rash, Raynaud’s phenomenon | Ischemic stroke, peripheral paresis of cranial nerves | No | No | neg | neg | Yes | Arthritis | |
| 4 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 3,5 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, nodules, purpuric rash, erythema nodosum | Cranial nerve paralysis | No | No | pos | ND | No | No | |
| 5 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 2,5 y | No | Maculopapular rash, nodules | Neurosensorial hearing loss | No | No | neg | neg | No | Arthritis | |
| 6 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 2 m (died at 9 m) | Yes | Digital necrosis | Ventricular haemorrhage | Aneurism of celiac artery | No | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 7 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 2 m | Yes | Livedo reticularis, Raynaud’s phenomenon | No | Abdominal pain | No | neg | ND | No | No | |
| 8 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 6,5 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, nodules, Raynaud’s phenomenon | No | Abdominal pain | No | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 9 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 9 y | No | Livedo reticularis | No | No | No | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 10 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 10 y | No | Livedo reticularis, nodules, Raynaud’s phenomenon, leg ulcers | No | No | No | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 11 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 59 y | No | Leg ulcers | No | No | No | neg | ND | No | No | |
| 12 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | childhood (died at 30 y) | No | Livedo reticularis, nodules, Raynaud’s phenomenon, leg ulcers with amputation | No | No | No | ND | ND | No | No | |
| 13 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 1 y | No | Livedo reticularis, nodules, Raynaud’s phenomenon | Sensitive polyneuropathy | No | No | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 14 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 4 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, purpuric rash, skin nodules. | No | No | No | pos | ND | No | No | |
| 15 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 1 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis | No | Abdominal pain | No | neg | neg | Yes | Mesenteric and renal infarcts | |
| 16 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 18 y | No | No | No | No | No | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 17 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 28 y | Yes | Raynaud’s phenomenon, purpuric rash, leg ulcers with digital amputation | Polyneuropathy | No | No | neg | neg | Yes | Panniculitis | |
| 18 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 2 y | No | Skin nodules | Polyneuropathy | No | No | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 19 | G47R/G47R | Georgian | 16 y | No | Raynaud’s phenomenon, ulceration of extremities | No | No | No | pos | neg | Yes | No | |
| 20 | R169Q/P251L | European Caucasian | 1 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis | Ischemic stroke, cranial nerves (II,VI,VII) paralysis | No | No | neg | ND | Yes | No | |
| 21 | R169Q/P251L | European Caucasian | 12 y | No | No | Ischemic stroke, VII cranial nerve paralysis | No | No | pos | neg | No | No | |
| 22 | R169Q/P251L | European Caucasian | 1 y | No | Livedo reticularis, skin rash at extremities | Ischemic stroke VI cranial nerve paralysis, neurosensorial hearing loss |
No | No | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 23 | R169Q/P251L | European Caucasian | 3 m | No | Livedo reticularis, vasculitic exanthema of lower extremities | VII cranial nerve paralysis | No | No | ND | ND | No | Epididymitis | |
| 24 | G47V/W264S | Turkish | 10 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis | No | No | No | neg | ND | Yes | Myalgia, abdominal and renal aneurysm | |
| Zhou et al. | 1 | A109D/Y453C | European Caucasian | 2 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis | Ischemic stroke | Splenomegaly | No | pos | neg | No | No |
| 2 | G47A/Y453C | European Caucasian | 1 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, erythematous and urticarial rash | Ischemic and haemorrhagic strokes | Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly. Portal hypertension. | Pancytopenia, hypoIg | pos | neg | No | No | |
| 3 | R169Q/deletion | European Caucasian | 1,5 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, urticarial rash | Ischemic and haemorrhagic strokes | Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, chronic gastritis | Leucopoenia, hypoIg | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 4 | G47A/H112Q | European Caucasian | 5 m | Yes | Livedo reticularis, urticarial rash | Ischemic and haemorrhagic strokes | Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, portal hypertension. | Pancytopenia, HypoIg | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 5 | R169Q/Y453C | European Caucasian | 1,5 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis | Ischemic stroke | Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly. | Leucopoenia, hypoIg | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 6 | M1T/I93T | European Caucasian | 1,5 y (died 16 y) | Yes | Non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis |
Ischemic stroke | Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly. portal hypertension. | No | neg | neg | Yes | Evans syndrome | |
| 7 | G47R/G47R | Turkish | 3,5 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, erythema nodosum | Ischemic stroke III cranial nerve paralysis |
No | No | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 8 | G47R/G47R | Tukish | 4 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, erythema nodosum | Ischemic stroke | Bowel perforation | No | neg | neg | No | Macrophage activation syndrome | |
| 9 | G47R/G47R | Turkish | 9 y (died 22 y) | Yes | Livedo reticularis, ulceration of extremities | No | Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly | Leucopoenia | pos | neg | No | Renal amyloidosis, necrotising pneumonia | |
| van Montfrans et al. | 1 | R169Q/R169Q | NA | 6 m | No | Livedo reticularis | No | Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly | Granulocytopenia, red-cell aplasia | NA | NA | No | No |
| 2 | R169Q/R169Q | NA | 6 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis | Stroke | Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly | HypoIg, lymphopenia | NA | NA | No | No | |
| Bras et al. | 1 | T119A/G142S | European Caucasian | >10 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, ulcerations of extremities | Stroke | No | No | NA | NA | No | No |
| 2 | T119A/G142S | European Caucasian | >10 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, ulcerations of extremities | Stroke | No | No | NA | NA | No | No | |
| 3 | T119A/G142S | European Caucasian | >10 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, ulcerations of extremities | Stroke | No | No | NA | NA | No | No | |
| 4 | T119A/G142S | European Caucasian | >10 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, ulcerations of extremities | Stroke | No | No | NA | NA | No | No | |
| Van Eyck et al. | 1 | G47R/G47R | NA | 5 y | Yes | No | No | Splenomegaly | Lymphadenopathy, anaemia, thrombocytosis | NA | NA | No | |
| Garg et al. | 1 | G47R/R306* | Turkish | 1,5 y (died 5 y) | Yes | Skin rash | Hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke. intraparenchymal haemorrhage |
No | No | neg | neg | No | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| Van Eyck et al. | 1 | R169Q/R169Q | African/ Caucasian | 6 m | No | No | Haemorrhagic stroke | Splenomegaly | Pancytopenia, hypoIg, lymphadenopathy, recurrent viral infections | NA | NA | No | No |
| 2 | R169Q/R169Q | African/ Caucasian | 5 m | No | No | TIA | Bowel perforation (ulcerative bowel disease, no signs of vasculitis) | Leucopoenia, hypoIg, lymphadenopathy, recurrent viral infections | NA | NA | No | No | |
| Belot et al. | 1 | R169Q/P193L | European Caucasian | First year | Yes | Livedo reticularis, ulceration of extremities | TIA, ischemic stroke, sensitive polyneuropathy, intracerebral haemorrhage. | Bowel stenosis | HypoIg | neg | neg | No | Oral aphtae |
| 2 | G47R/G47R | Asian | 1 m | Yes | Erythema nodosum, vasculitic rash | Intracerebral haemorrhage, Ischemic stroke, Optic neuritis | No | No | NA | NA | Yes | Dactylitis, aneurysm of abdominal vessels | |
| Westendorp et al. | 1 | R169Q/R169Q | European Caucasian | 3 y | No | Livedo reticularis, nodules | Ischemic stroke, peripheral neuropathy neurosensorial hearing loss |
No | No | NA | NA | No | No |
| 2 | R169Q/R169Q | European Caucasian | 2 y | No | Livedo reticularis | Ischemic stroke | No | No | NA | NA | No | Autism | |
| Gonzales Santiago et al. | 1 | K13del/N328K | European Caucasian | 2 y | Yes | Livedo racemosa | No | No | HypoIg | NA | neg | No | No |
| 2 | K13del/N328K | European Caucasian | 5 y | No | Nodules, erytema of lower extremities | No | No | HypoIg, recurrent infections | NA | NA | No | No | |
| Batu et al. | 1 | G47R/G47R | Turkish | 6,5 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, | No | Abdominal pain | No | NA | NA | No | No |
| 2 | G47R/G47R | Turkish | 4 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, erythema nodosum, necrotic ulcers | Stroke | Abdominal pain, hypertransaminasemia | No | pos | NA | Yes | Glomerulosclerosis | |
| 3 | G47R/G47R | Turkish | 10 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis | No | Abdominal pain | No | NA | NA | No | No | |
| Van Montfrans et al. | 1 | R169Q/R169Q | European Caucasian | 1 y | Yes | Livedo reticularis, erythema nodosum, eczema, Raynaud phenomenon | Ischemic stroke, III cranial nerve paralysis | Abdominal pain, hepatomegaly | Adenopathy, hypoIg, pancytopenia | neg | neg | No | Oral aphtae, arthralgia GH deficiency |
| 2 | R169Q/R169Q | European Caucasian | Birth | No | Livedo reticularis, eczema | No | Abdominal pain, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly | HypoIg, anaemia | ND | ND | No | Jugular vein thrombosis, GH deficiency | |
| 3 | R169Q/R169Q | European Caucasian | 6 y | No | Livedo reticularis, ulceration of extremities and trunk | No | Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly | Adenopathy, anaemia | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 4 | R169Q/R169Q | European Caucasian | 3 y | No | Livedo racemosa, erythema nodosum, Raynaud phenomenon | Ischemic stroke, VI cranial nerve paralysis | Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly | HypoIg, recurrent infections, anaemia | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 5 | R169Q/R169Q | European Caucasian | 1y | No | Eczema | Ischemic stroke, IV cranial nerve paralysis | Splenomegaly | HypoIg, anaemia, leucopoenia | neg | ND | No | Autism | |
| 6 | R169Q/R169Q | European Caucasian | 9 m | Yes | Eczema | Ischemic stroke, IV cranial nerve paralysis | Abdominal pain, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly | HypoIg, pancytopenia | pos | pos | Yes | Oral aphtae, arthralgia | |
| 7 | R169Q/R169Q | European Caucasian | 8 y | Yes | Rash | Ischemic stroke, III cranial nerve paralysis | Abdominal pain, acute liver failure | HypoIg, recurrent infections, anaemia,lymphopenia | neg | neg | No | Oral aphtae, arthralgia | |
| 8 | R169Q/R169Q | African/Caucasian | 6 m | No | Eczema | Intracranial haemorrhage | Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly | HypoIg, adenopath, thrombocytopenia, leucopoenia | neg | neg | No | No | |
| 9 | R169Q/R169Q | African/Caucasian | 5 m | No | No | No | Bowel ulcerations, colitis, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly | HypoIg, recurrent infections, adenopathy | neg | neg | No | No | |
| Fellmann et al. | 1 | Homozygous 22q11.1 deletion (IL17RA and CECR1) | Asian | Birth (Died 16 y) | No | Ichthyosiform rash, oro-vaginal ulcerations | No | No | Recurrent infection (C. Albicans, S. aureus), neutropenia | neg | neg | No | Chronic systemic inflammation, failure to thrive |
| 2 | Homozygous 22q11.1 deletion (IL17RA and CECR1) | Asian | 2 y | No | Ichthyosiform rash | No | Splenomegaly | Oro-vaginal candidiasis, Staphylococcal skin infections | neg | neg | No | Retinal vasculitis | |
| Schepp et al. | 1 | R169Q/ M243R |
NA | 18 y | No | No | No | Splenomegaly | HypoIg, recurrent respiratory infections | NA | NA | No | Arthralgia |
| 2 | R169Q/M243R | NA | 2 m (Died 17 y) | Yes | Erythema nodosum | Intracranial haemorrhage | Splenomegaly | HypoIg, lymphopenia, recurrent urinary tract and respiratory infections | neg | NA | No | Arthritis Failure to thrive. |
|
Legend: CNS central nervous system
PNS peripheral nervous system
TIA transitory ischemic attack
GH growth hormone
HypoIg Hypogammaglobulinemia
ND not done
NA not available
Table 3.
genotype/phenotype correlation in DADA2
| Mutation | Exon | N° of patients | Associated symptoms (% of patients) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1T | 2 | 1 in heterozygosis | Fever Skin: Non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis CNS/PNS: ischemic stroke Visceral: involvement: hepatomegaly, splenomegaly. portal hypertension, hypertension (100 %) |
| K13del | 2 | 2 in heterozygosis | Fever (50 %) Skin: Livedo racemosa (50 %), skin nodules (50 %) Immune/hematologic system: hypogammaglobulinemia (100 %), recurrent infections (50 %) |
| 28-kb-deletion | 2 | 1 in heterozygosis | Fever Skin: Livedo reticularis, urticarial rash CNS/PNS: ischemic and haemorrhagic strokes Visceral involvement: hepatomegaly, splenomegaly. chronic gastritis Immune/hematologic system: leukopenia, hypogammaglobulinemia (100 %) |
| G47R | 2 | 27 in homozygosis | Fever (64 %) Skin: Livedo reticularis (60 %), skin nodules (35 %), ulcerations at extremities/digital necrosis (32 %), Raynaud’s phenomenon (28 %), purpuric/vasculitic rash (18 %), erythema nodosum (18 %), panniculitis (3 %) CNS/PNS: ischemic stroke (21 %), hemorrhagic stroke (7 %), intracranial haemorrhage (11 %), cranial nerve paralysis (14 %), polineuropathy (11 %), neurosensorial hearing loss (3 %). Visceral involvement: abdominal pain (21 %), intestinal vasculitis (14 %), hepatomegaly (3 %), splenomegaly (7 %), hypertransaminasemia (3 %), hypertension (25 %). Immune/hematologic system: Leucopoenia (3 %), anaemia (3 %), lymphadenopathy (3 %). |
| 1 in heterozygosis | |||
| G47A | 2 | 2 in heterozygosis | Fever (100 %) Skin: Livedo reticularis (100 %), urticarial rash (100 %) CNS/PNS: ischemic and haemorrhagic strokes (100 %) Visceral involvement: hepatomegaly (100 %), splenomegaly (100 %), portal hypertension (100 %) Immune/hematologic system: Pancytopenia (100 %), hypogammaglobulinemia (100 %). |
| G47V | 2 | 1 in heterozygosis | Fever Skin: Livedo reticularis Visceral involvement: hypertension, abdominal and renal aneurysm (100 %). |
| I93T | 2 | 1 in heterozygosis | Fever Skin: Non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis CNS/PNS: ischemic stroke Visceral: involvement: hepatomegaly, splenomegaly. portal hypertension, hypertension (100 %) |
| A109D | 3 | 1 in heterozygosis | Fever Skin: Livedo reticularis CNS/PNS: ischemic stroke Visceral involvement: splenomegaly (100 %). |
| H112Q | 3 | 1 in heterozygosis | Fever Skin: Livedo reticularis, urticarial rash CNS/PNS: ischemic and haemorrhagic strokes Visceral involvement: hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, portal hypertension Immune/hematologic system: Pancytopenia, hypogammaglobulinemia (100 %). |
| T119A | 3 | 4 in heterozygosis | Fever (100 %) Skin: Livedo reticularis, ulceration of extremities (100 %) CNS/PNS: ischemic and haemorrhagic strokes (100 %) |
| G142S | 3 | 4 in heterozygosis | Fever (100 %) Skin: Livedo reticularis, ulceration of extremities (100 %) CNS/PNS: ischemic and haemorrhagic strokes (100 %) |
| R169Q | 3 | 15 in homozygosis | Fever (37 %) Skin: Livedo reticularis (58 %), skin nodules (4 %), ulcerations at extremities/digital necrosis (8 %), Raynaud’s phenomenon (8 %), purpuric/vasculitic rash (13 %), erythema nodosum (13 %), eczema (20 %) CNS/PNS: ischemic stroke (54 %), hemorrhagic stroke (13 %), intracranial haemorrhage (13 %), cranial nerve paralysis (37 %), polineuropathy (8 %), neurosensorial hearing loss (8 %). Visceral involvement: abdominal pain (17 %), bowel ulcerations (8 %), chronic gastritis (4 %), bowel stenosis (4 %), colitis (4 %), hepatomegaly (45 %), splenomegaly (58 %), acute liver failure (4 %), hypertension (8 %). Immune/hematologic system: hypogammaglobulinemia (62 %), pancytopenia (8 %), leucopoenia (20 %), lymphopenia (13 %), granulocytopenia (4 %), anaemia (25 %), thrombocytopenia (4 %), lymphadenopathy (25 %), recurrent infections (29 %). |
| 9 in heterozygosis | |||
| P193L | 4 | 1 in heterozygosis | Fever Skin: Livedo reticularis, ulcerations at extremities CNS/PNS: ischemic stroke, TIA, intracranial haemorrhage, polineuropathy Visceral involvement: bowel stenosis, oral aphtae Immune/hematologic system: hypogammaglobulinemia (100 %). |
| M243R | 4 | 2 in heterozygosis | Fever (50 %) Skin: erythema nodosum (50 %) CNS/PNS: intracranial haemorrhage (50 %) Visceral involvement: splenomegaly (100 %) Immune/hematologic system: hypogammaglobulinemia (100 %), recurrent infections (100 %). |
| P251L | 4 | 4 in heterozygosis | Fever (25 %) Skin: Livedo reticularis (75 %), vasculitic rash (50 %) CNS/PNS: ischemic stroke (75 %), cranial nerve paralysis (100 %), neurosensorial hearing loss (25 %). Visceral involvement: hypertension (25 %), epididymitis (25 %) |
| W264S | 5 | 1 in heterozygosis | Fever Skin: Livedo reticularis Visceral involvement: hypertension, abdominal and renal aneurysm (100 %). |
| R306* | 6 | 1 in heterozygosis | Fever Skin: rash CNS/PNS: ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, intracranial haemorrhage (100 %) |
| N328K | 7 | 2 in heterozygosis | Fever (50 %) Skin: Livedo racemosa (50 %), skin nodules (50 %) Immune/hematologic system: hypogammaglobulinemia (100 %), recurrent infections (50 %) |
| Y453C | 9 | 3 in heterozygosis | Fever (100 %) Skin: Livedo reticularis (100 %), urticarial rash (33 %) CNS/PNS: ischemic stroke (100 %), haemorrhagic strokes (33 %) Visceral involvement: hepatomegaly (66 %), splenomegaly (100 %), portal hypertension (33 %) Immune/hematologic system: Pancytopenia (66 %), hypogammaglobulinemia (66 %). |
In most patients, a neurological involvement, affecting both the peripheral and central nervous system, has been described.
The severity of the CNS involvement is rather variable. In some patients a transitorily ischemic attack (TIA) has been described (with negative cerebral CT and/or MRI), while others developed an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke (in few cases a ventricular haemorrhage has also been detected). Typically, the strokes associated to DADA2 are lacunar with a wide range of clinical manifestations ranging from clinically silent episodes in few cases, to severe ones leading to a permanent disability [1, 2, 10, 12].
The neuropathy ranges from a transient mononeuritis (such as a cranial nerve transient paralysis) to a permanent polyneuropathy; moreover, few patients suffered from optic neuritis. In few cases, persistent neurosensorial hearing loss has also been described [1, 2, 12].
Most patients have gastrointestinal manifestations: abdominal pain, significant weight loss, chronic gastritis, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, portal hypertension, bowel perforation or stenosis.
While nephrogenic hypertension is rather common in this condition, in few patients focal glomerulosclerosis and renal amyloidosis have also been described [11]. Lung involvement with necrotising pneumonia (lethal) has been reported in one patient [11].
The blood tests usually reveal an elevation of acute phase reactants (ERS, CRP), low haemoglobin levels and neutrophilic leukocytosis [1, 2]; however in few patients cytopenia (pancytopenia, leucopoenia) has been detected [1, 7, 12]. Auto-antibody are usually negative.
As stated above, a mild immunodeficiency can be observed; some patients present hypogammaglobulinemia that may affect IgM or all Ig subclasses [1, 13]. Of note, despite the low immunoglobulins’ levels, only few cases displayed an increased susceptibility to infections, that was rather severe in exceptional cases [1, 3, 7, 12, 13].
MRI is the most useful tool in the diagnosis of cerebral strokes; in fact CT scan as well as conventional angiography may not detect the smaller lacunar strokes and therefore underestimate the entity of involvement of the CNS [1].
Some patients underwent an angiographic investigation, that revealed the presence of stenosis and/or aneurysms of abdominal artery, particularly mesenteric, celiac, hepatic and renal arteries; the histological analysis, when done, revealed a necrotizing vasculitis [1, 2].
In patients with symptoms suggestive for organ involvement but without pathologic finding in not-invasive radiologic studies, conventional angiography can be of help revealing aneurism and or stenosis in the middle sizes arteries.
Skin biopsy revealed, in most cases, a non-granulomatous, necrotizing vasculitis of small and medium-sized vessels, with the same histopathologic features of polyarteritis nodosa [1, 2, 9].
In few cases the histology was less specific showing a leucocytoclastic vasculitis or a panniculitis.
Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is, according to the Chapel Hill classification, a “Necrotizing arteritis of medium or small arteries without glomerulonephritis or vasculitis in arterioles, capillaries, or venules, and not associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs)” [22]. It’s gathered in the medium-sized vessels vasculitis, even if it can affect arteries of any size [22].
Being DADA2 a vasculitis with a genetic basis, it has been proposed to group this disease in the vasculitis with a probable cause according to the Chapel Hill classification [11, 22].
Notably, most of the DADA2 patients not only received the histological diagnosis of PAN but also met the EULAR/PRINTO/PRES diagnostic criteria for childhood polyarteritis nodosa (Table 4) [23].
Table 4.
EULAR/PRINTO/PRES classification criteria for childhood Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) [23]
| Histopathology or angiographic abnormalities (mandatory) plus one of the five following criteria: | - Histology: necrotising vasculitis in medium or small-sized arteries. - Angiography: aneurysm, stenosis or occlusion of a medium or small sized artery, |
|
| EULAR/PRINTO/PRES classification criteria for childhood Polyarteritis nodosa (c-PAN) | 1. Skin involvement | Livedo reticularis, skin nodules, superficial ulcers, peripheral tissue necrosis |
| 2. Myalgia/muscle tenderness | Muscle pain or tenderness | |
| 3. Hypertension | Blood pressure > 95th centile | |
| 4. Peripheral neuropathy | Sensory or motor neuropathy | |
| 5. Renal involvement | Proteinuria, haematuria, impaired function |
Unusual phenotypes
Even if most of the patients with DADA2 have a clinical phenotype consistent with a systemic inflammatory vasculopathy, a recent report has enlighten that the disease may be dominated by clinical manifestations suggestive for an immune-disrective condition, such as cytopenia, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly and immunodeficiency with severe viral infections [7]. The two patients described did not present skin involvement and one of them developed a vascular involvement only after bone-marrow transplantation. Of note, the mutations found in these two patients were the same described in patients with a “typical” inflammatory clinical picture.
Similarly a third patient with a lymphoprolipherative clinical picture, resembling Castleman’s syndrome, has been reported by the same group [5].
A more recent clinical series of 9 DADA2 patients with the homozygous R169Q mutation has enlightened that the presence of cytopenia is a common finding of the disease, together with the common inflammatory manifestations [12].
In the two patients carrying homozygous 22q11.1 deletion, encompassing both copies of the IL-17 receptor A (IL17RA) and the CECR1 gene, the clinical phenotype was dominated by muco-cutaneous infections and dermatitis associated to persistent inflammation and, in one patient, vasculitis responding to steroids [14]. Livedo reticularis, stroke and other DADA2 clinical manifestations were not described.
Finally two brothers with a clinical picture consistent with the diagnosis of common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) were found to be affected by DADA2 by whole exome-sequencing; of note only one of them displayed clinical sign and symptoms consistent with a vasculopathy [13].
Outcome
Being a disease of recent identification, the clinical outcome has not been well investigated. However, from the clinical data by now available is clear that the spectrum of severity of the disease is wide, ranging from patients with neonatal onset and a severe organ involvement to patients with onset in the adulthood and the presence of only skin manifestations (Tables 2 and 3); of note, even between patients carrying the same mutations in CECR1 gene the clinical picture can be widely different (Tables 2 and 3).
The disease turned out to be lethal in seven out of the 65 patients by now described [1, 2, 6, 13, 14]: in three cases the severity of the visceral involvement was lethal [1, 2], two patients died for respiratory complications following intracranial haemorrhage [6, 13], while one patient developed necrotising pneumonia [1, 11]; finally one of the two patients carrying the homozygous deletion on 22.11.1 chromosome died for septic shock.
Treatment
DADA2 is a newly recognised condition and the number of patients so far described is limited; for this reason the response to treatment is largely anecdotal and still controversial (Table 5).
Table 5.
Treatment administrated and clinical response in the described DADA2 patients (1-14)
| Therapy | Case report (number of treated patients) | Response to treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Steroids (orally or i.v.) | Navon et al. (17) | In 2 cases complete control of the disease with on demand steroidal therapy. In other patients steroid-dependence. |
| Zhou et al. (9) | Partial control of diseases manifestations with high doses of corticosteroids | |
| Van Eyck et al. (2) | Steroid-dependence | |
| Belot et al. (2) | Steroid-dependence | |
| Garg et al. (1) | Steroid-dependence | |
| Van Montfrans et al. (6) | Partial response in 3 patients | |
| Schepp et al. (1) | Partial response | |
| cyclophosphamide (orally or i.v.) | Navon et al. (9) | Good response in 2 patients. |
| Zhou et al. (7) | Not specified | |
| Belot et al. (2) | Partial response | |
| Garg et al. (1) | Poor response | |
| Batu et al. (4) | Poor response | |
| Azathioprine | Navon et al. (7) | No patients with complete response |
| Van Eyck et al. (2) | Poor response | |
| Belot et al. (1) | Good response in association to methotrexate | |
| Batu et al. (3) | Poor response | |
| Van Montfrans et al. (5) | Not specified | |
| Methotrexate | Navon et al. (3) | Good response in association with other immunosuppressive and biologics |
| Belot et al. (1) | Good response in association with azathioprine | |
| Batu et al. (3) | Poor response | |
| Schepp et al. (1) | Partial response | |
| Cyclosporine | Van Eyck et al. (1) | Poor response |
| Colchicine | Batu et al. (5) | Good response in one patient, none response in 4 patients |
| Mycophenolate | Zhou et al. (2) | Not specified |
| Van Eyck et al. (1) | Poor response | |
| Belot et al. (1) | Partial response in association with cyclophosphamide | |
| Batu et al. (2) | Good response in one patient, poor in the other | |
| Sirolimus | Van Eyck et al. (2) | Good response in one patient Poor response in one patient |
| Tacrolimus | Van Eyck et al. (2) | Good response in one patient Poor response in one patient |
| I.v. immunoglobulins | Navon et al. (1) | Not specified |
| Zhou et al. (5) | Not specified | |
| Van Eyck et al. (2) | Prophylactic dosage | |
| Belot et al. (1) | Prophylactic dosage | |
| Schepp et al. (2) | Prophylactic dosage | |
| Anakinra | Zhou et al. (5) | Not specified |
| Garg et al. (1) | Initial partial response than relapse | |
| Van Montfrans et al. (1) | Good response | |
| Canakinumab | Garg et al. (1) | Initial partial response than relapse |
| Etanercept | Navon et al. (5) | Complete response in 5 patients Partial response in 1 patient |
| Zhou et al. (6) | Not specified | |
| van Montfrans et al. (3) | Partial response in 1 pateint Complete response in 2 patients |
|
| Batu et al. (3) | Partial response in 2 patients, complete in 1 | |
| Adalimumab | Navon et al. (3) | Complete response in 2 patients, exacerbation in 1 patient |
| Infliximab | Navon et al. (2) | Complete response in 1 patient Partial response in 1 patient |
| Tocilizumab | Zhou et al. (1) | Not specified |
| Van Eyck et al. (1) | Complete response | |
| Batu et al. (1) | Poor response | |
| Rituximab | Zhou et al. (1) | Poor response |
| Belot et al. (1) | Poor response |
Being an inflammatory condition, high doses of steroids are usually able to control the clinical manifestations [1, 2, 8, 9, 11, 12]. However, due to the severity of the condition, a steroid-dependence is often described. None of the most common immunosuppressive drugs (cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, methotrexate) was effective [1, 2, 6, 8, 11, 13].
Navon et al. reported ten patients treated with anti-TNF drugs (etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab) with complete response in 8, even after the failure of immunosuppressive therapies [2]; good results with anti-TNF agents were also reported in other small series [3, 11, 12]. By now, the reason why this drug is effective is still unclear.
According to the report of Zhou et al., neither immunosuppressive nor biologic drugs were able to completely control the disease manifestations in all treated patients; the enzymatic substitutive treatment (fresh frozen plasma or recombinant enzyme) was postulated to be of help. This approach was tempted in two patients reported by Batu et al. with a transient good response in one and a not-satisfactory response in the other [11].
A possible role of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been postulated to be effective by Zhou et al. and Navon et al., being able to provide ADA2 producing monocytes and therefore to normalize the plasmatic levels of the enzyme [1, 2]. This therapeutic strategy, performed in one of the two patients reported by Van Eyck et al. [7] and in a patient reported by the NIH group [3], was able to normalize the plasmatic levels of ADA2 and to control the disease manifestations [3, 7]; early complications occurred in one of them. More recently two additive patients who displayed a complete response to HSCT have been described [12].
Van Eyck et al. conclude that HSCT should be suggested only for those patients with a severe disease, since DADA2 patients present an increased risk of HSCT-related complications due to the persistent inflammation and the compromised endothelial integrity [7]. Of note, the other patient described in this paper displayed a complete response to treatment with sirolimus; the authors assume that this drug may be of help in the control of the clinical manifestations related to ADA2-deficiency, being able to reduce the M1 macrophage differentiation and the production of IL-6 [7].
Conclusion
In conclusion DADA2 is a genetic condition mainly characterized by an inflammatory vasculopathy resembling polyarteritis nodosa (PAN). From the clinical data so far available, the age at onset, the disease manifestations and severity are widely variable. Further clinical studies are therefore needed in order to better understand the phenotypic viability of this condition and the genotype-phenotype correlation.
In light of the data by now available, we consider the genetic analysis of CECR1 gene suggested in the following clinical pictures: patients with an inflammatory vasculopathy with early onset in infancy, patients with a diagnosis of PAN or cPAN with early onset and/or severe organ involvement (above all stroke), especially in case of a positive family history or consanguinity/endogamy in the parents. Moreover DADA2 should be ruled out in patients with an immune-disreactive condition without an underlying diagnosis, especially in presence of signs or symptoms of vasculitis.
Finally, a better enlightenment of the pathogenetic mechanisms of the disease is needed; these data will be of help also in the identification of an effective treatment.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article (and its additional files).
Authors’ contributions
RC carried out the review of the available papers on the disease, performed the revision of the genetic and clinical manifestations and drafted the manuscript. FP and FS reviewed the pathogenetic studies of the disease and draft the pathogenesis chapter of the review. MG conceived of the review, participated in its design and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
Marco Gattorno received speaker’s fees from Sobi and Novartis and grant for the Eurofever project from Sobi and Novartis.
Consent for publication
The consent to publish the clinical image (Fig. 3) has been obtained from the patient’s parents.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Contributor Information
Roberta Caorsi, Email: robertacaorsi@hotmail.it.
Federica Penco, Email: federica.penco@hotmail.it.
Francesca Schena, Email: fransche79@gmail.com.
Marco Gattorno, Email: marcogattorno@gaslini.org.
References
- 1.Zhou Q, Yang D, Ombrello AK, et al. Early-onset stroke and vasculopathy associated with mutations in ADA2. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:911–920. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1307361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Navon Elkan P, Pierce SB, Segel R, et al. Mutant adenosine deaminase 2 in a polyarteritis nodosa vasculopathy. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:921–931. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1307362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.van Montfrans J, Zavialov A, Zhou Q. Mutant ADA2 in vasculopathies. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(5):478. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1405506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bras J, Guerreiro R, Santo GC. Mutant ADA2 in vasculopathies. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(5):478–80. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1405506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Van Eyck L, Liston A, Wouters C. Mutant ADA2 in vasculopathies. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(5):480. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1405506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Garg N, Kasapcopur O, Foster J, 2nd, et al. Novel adenosine deaminase 2 mutations in a child with a fatal vasculopathy. Eur J Pediatr. 2014;173(6):827–30. doi: 10.1007/s00431-014-2320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Van Eyck L, Jr, Hershfield MS, Pombal D, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation rescues the immunologic phenotype and prevents vasculopathy in patients with adenosine deaminase 2 deficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135(1):283–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.10.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Belot A, Wassmer E, Twilt M, et al. Mutations in CECR1 associated with a neutrophil signature in peripheral blood. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2014;12:44. doi: 10.1186/1546-0096-12-44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gonzalez Santiago TM, Zavialov A, Saarela J, et al. Dermatologic features of ADA2 deficiency in cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;1. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 10.Westendorp WF, Nederkoorn PJ, Aksentijevich I, et al. Unexplained early-onset lacunar stroke and inflammatory skin lesions: consider ADA2 deficiency. Neurology. 2015;84(20):2092–3. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Batu ED, Karadag O, Taskiran EZ, et al. A case series of adenosine deaminase 2-deficient patients emphasizing treatment and genotype-phenotype correlations. J Rheumatol. 2015;42(8):1532–4. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.150024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Van Montfrans JM, Hartman EA, Braun KP, et al. Phenotypic variability in patients with ADA2 deficiency due to identical homozygous R169Q mutations. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 13.Schepp J, Bulashevska A, Mannhardt-Laakmann W, et al. Deficiency of adenosine deaminase 2 causes antibody deficiency. J Clin Immunol. 2016;36(3):179–86. doi: 10.1007/s10875-016-0245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fellmann F, Angelini F, Wassenberg J, et al. IL-17 receptor A and adenosine deaminase 2 deficiency in siblings with recurrent infections and chronic inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 15.Giannelou A, Zhou Q, Kastner DL. When less is more: primary immunodeficiency with an autoinflammatory kick. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;14(6):491–500. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Adenosine HM, Deficiency D. Gene reviews. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zavialov AV, Engstrom A. Human ADA2 belongs to a new family of growth factors with adenosine deaminase activity. Biochem J. 2005;391:51–57. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zavialov AV, Yu X, Spillmann D, et al. Structural basis for the growth factor activity of human adenosine deaminase ADA2. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:12367–12377. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.083527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Savic S, McDermott MF. Clinical genetics in 2014: New monogenic diseases span the immunological disease continuum. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(2):67–8. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zavialov AV, Garcia E, Glaichenhaus N, et al. Human adenosine deaminase 2 induces differentiation of monocytes into macrophages and stimulates proliferation of T helper cells and macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 2010;88:279–290. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1109764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Eltzschig HK, Sitkovsky MV, Robson SC. Purinergic signaling during inflammation. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:2322–2333. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1205750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, et al. 2012 revised international chapel hill consensus conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:1–11. doi: 10.1002/art.37715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ozen S, Pistorio A, Iusan SM, et al. EULAR/PRINTO/PRES criteria for Henoch-Schonlein purpura, childhood polyarteritis nodosa, childhood Wegener granulomatosis and childhood Takayasu arteritis : Ankara 2008. Part II: Final classification criteria. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:798–806. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.116657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


