Abstract
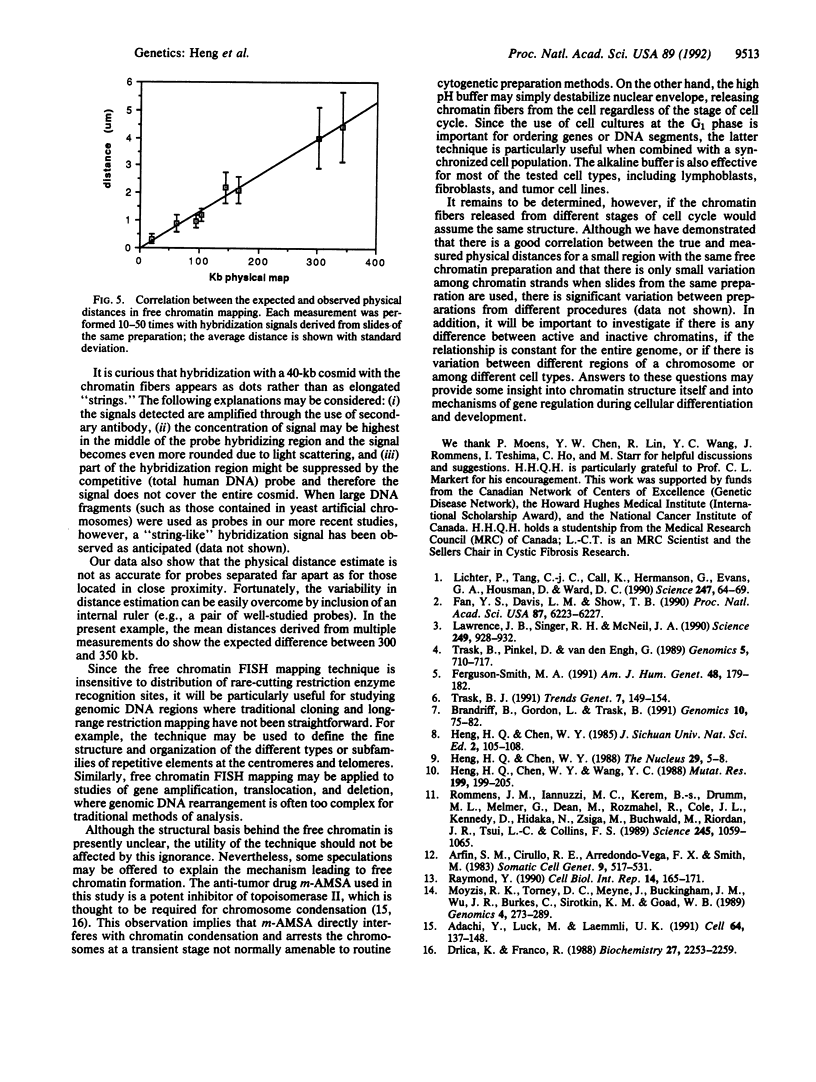
Fluorescence in situ hybridization to metaphase chromosomes or chromatin fibers in interphase nuclei is a powerful technique in mapping genes and DNA segments to specific chromosome region. We have been able to release the chromatin fibers from cells arrested at G1 and G2 phases using different drugs and a simple alkaline lysis procedure. We have also demonstrated specific hybridization of fluorescence-labeled probes to single-copy genomic DNA sequences on the free chromatins. Fluorescence in situ hybridization signals have been detected for sequences separated as close as 21 kilobase pairs and as far as 350 kilobase pairs, with excellent correspondence between the observed and expected distances. The resolution of this technique should approach 10 kilobase pairs and its coverage should span millions of base pairs. Therefore, free chromatin mapping can be generally used to study the structure and organization of mammalian genomes.
Full text
PDF
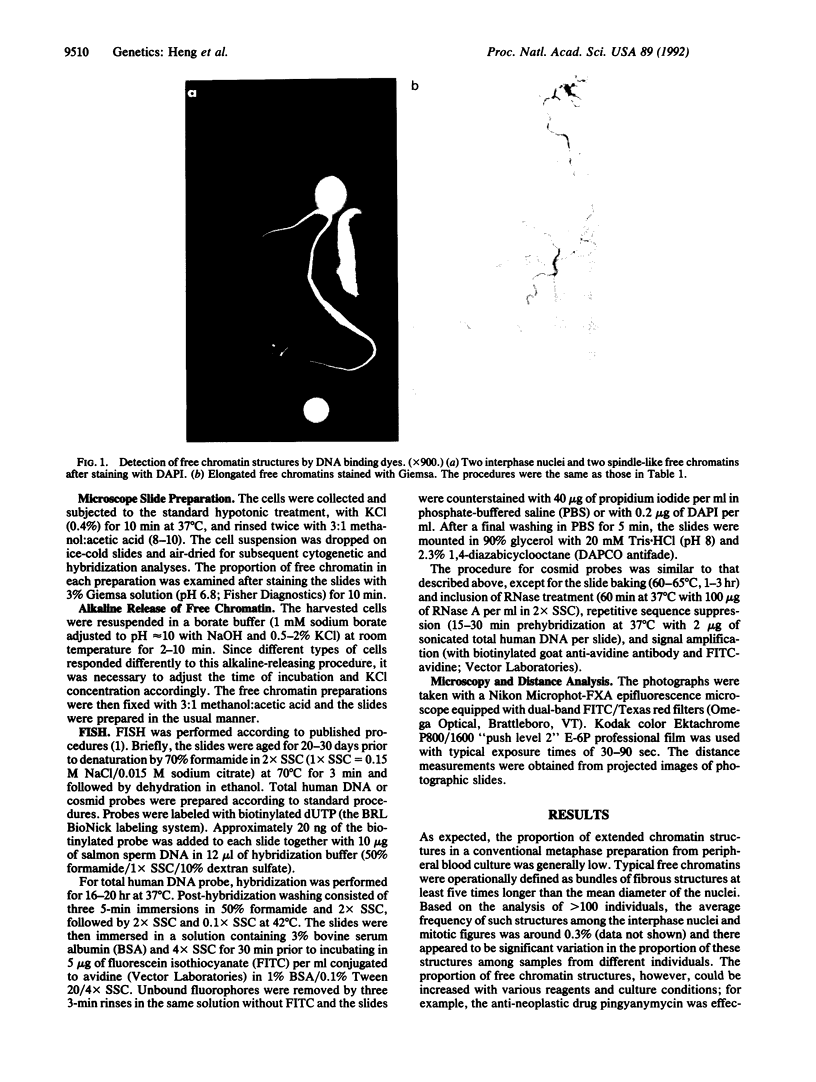


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi Y., Luke M., Laemmli U. K. Chromosome assembly in vitro: topoisomerase II is required for condensation. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90215-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arfin S. M., Cirullo R. E., Arredondo-Vega F. X., Smith M. Assignment of structural gene for asparagine synthetase to human chromosome 7. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 Sep;9(5):517–531. doi: 10.1007/BF01574256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriff B., Gordon L., Trask B. A new system for high-resolution DNA sequence mapping interphase pronuclei. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90486-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Franco R. J. Inhibitors of DNA topoisomerases. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2253–2259. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan Y. S., Davis L. M., Shows T. B. Mapping small DNA sequences by fluorescence in situ hybridization directly on banded metaphase chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6223–6227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Smith M. A. Putting the genetics back into cytogenetics. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Feb;48(2):179–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heng H. Q., Chen W. Y., Wang Y. C. Effects of pingyanymycin on chromosomes: a possible structural basis for chromosome aberration. Mutat Res. 1988 May;199(1):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90246-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H., McNeil J. A. Interphase and metaphase resolution of different distances within the human dystrophin gene. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):928–932. doi: 10.1126/science.2203143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Torney D. C., Meyne J., Buckingham J. M., Wu J. R., Burks C., Sirotkin K. M., Goad W. B. The distribution of interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in the human genome. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):273–289. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90331-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond Y. Differential effect of pH on solubilization of nuclear lamins A/C and lamin B. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1990 Feb;14(2):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(90)90033-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Iannuzzi M. C., Kerem B., Drumm M. L., Melmer G., Dean M., Rozmahel R., Cole J. L., Kennedy D., Hidaka N. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask B. J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization: applications in cytogenetics and gene mapping. Trends Genet. 1991 May;7(5):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask B., Pinkel D., van den Engh G. The proximity of DNA sequences in interphase cell nuclei is correlated to genomic distance and permits ordering of cosmids spanning 250 kilobase pairs. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):710–717. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90112-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]