Abstract
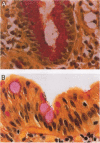
While an association of Helicobacter pylori infection with duodenal mucosa gastric metaplasia has been described, the details and extent of the interaction are lacking. One of the limiting factors has been the lack of a staining technique that allows simultaneous visualisation of the bacteria and gastric metaplasia in the duodenum. This report describes a new stain that allows the simultaneous visualisation of duodenal gastric metaplasia and H pylori and compares the new stain with the component stains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carrick J., Lee A., Hazell S., Ralston M., Daskalopoulos G. Campylobacter pylori, duodenal ulcer, and gastric metaplasia: possible role of functional heterotopic tissue in ulcerogenesis. Gut. 1989 Jun;30(6):790–797. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.6.790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caselli M., Trevisani L., Aleotti A., Bovolenta M. R., Stabellini G. Gastric metaplasia in duodenal bulb and Campylobacter-like organisms in development of duodenal ulcer. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Sep;34(9):1374–1378. doi: 10.1007/BF01538072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. F., Chen C. M. Restoring exhausted Schiff's reagent. Stain Technol. 1970 Mar;45(2):91–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. M., Greene C. Modified Steiner method for the demonstration of spirochetes in tissue. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jan;71(1):109–111. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/71.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khulusi S., Badve S., Patel P., Lloyd R., Marrero J. M., Finlayson C., Mendall M. A., Northfield T. C. Pathogenesis of gastric metaplasia of the human duodenum: role of Helicobacter pylori, gastric acid, and ulceration. Gastroenterology. 1996 Feb;110(2):452–458. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8566592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. I., Rathbone B. J., Dixon M. F., Heatley R. V. Campylobacter pyloridis and acid induced gastric metaplasia in the pathogenesis of duodenitis. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Aug;40(8):841–848. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.8.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. I., Rathbone B. J., Sobala G. M., Shallcross T., Heatley R. V., Axon A. T., Dixon M. F. Gastric epithelium in the duodenum: its association with Helicobacter pylori and inflammation. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Dec;43(12):981–986. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.12.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Zimaity H. M., Graham D. Y., al-Assi M. T., Malaty H., Karttunen T. J., Graham D. P., Huberman R. M., Genta R. M. Interobserver variation in the histopathological assessment of Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Hum Pathol. 1996 Jan;27(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(96)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]