Abstract
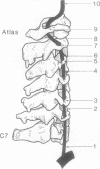
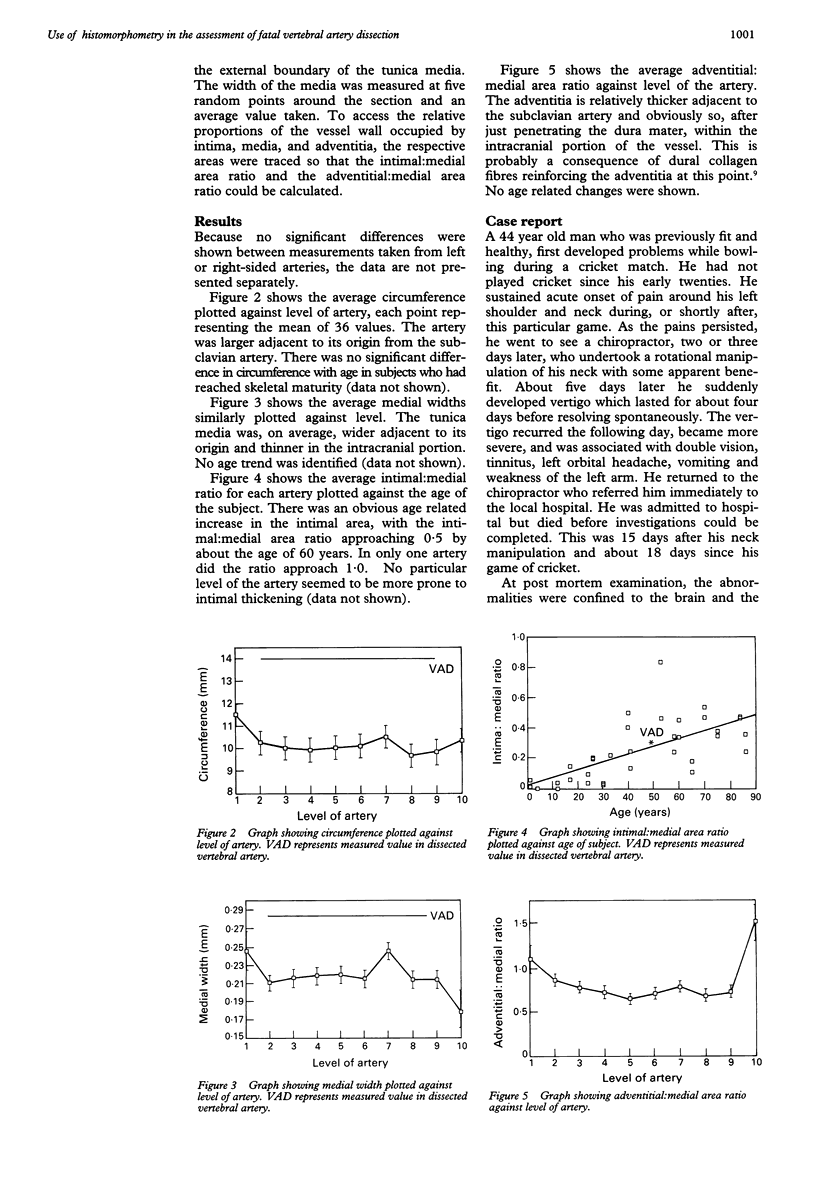
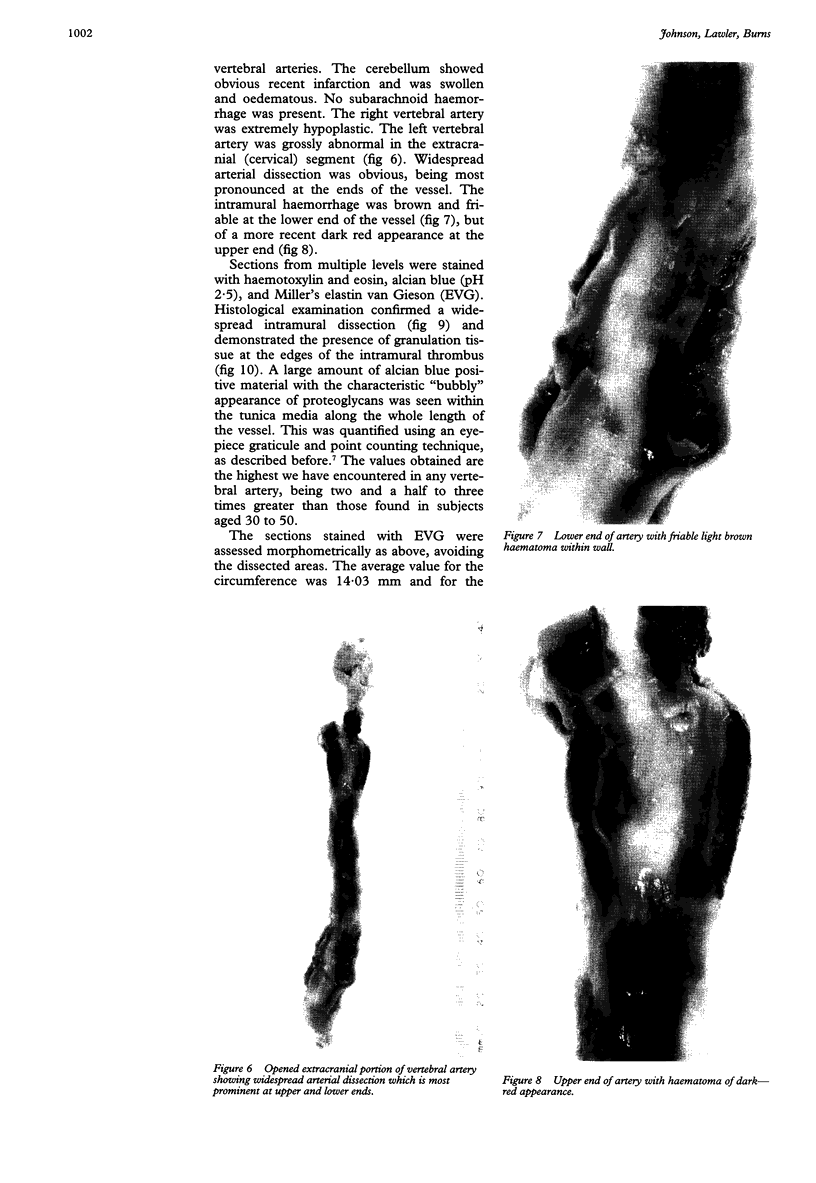
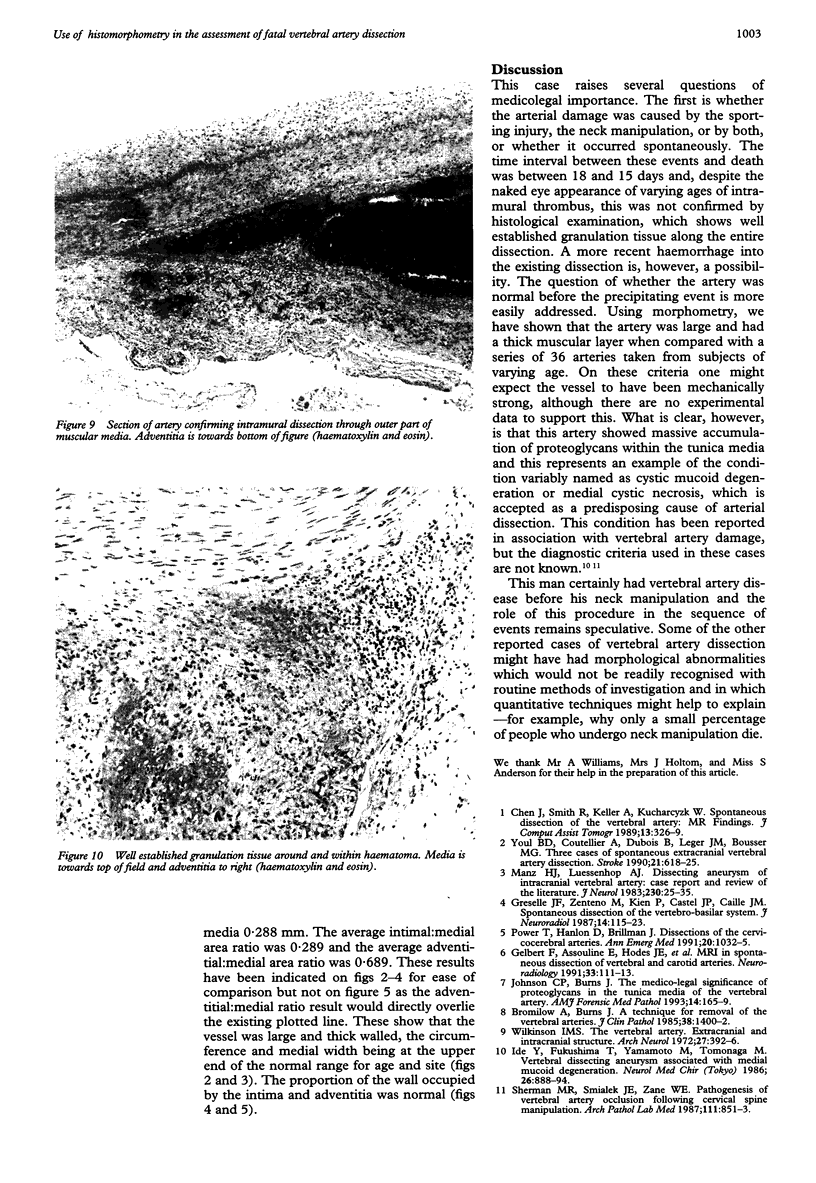
AIM--To assess morphometrically the structural changes, which occur with ageing, along the length of the vertebral artery. METHODS--A series of 36 vessels were removed at necropsy from subjects aged between 9 months and 86 years. Image analysis was used to measure the medial width, the circumference, the intimal: medial area ratio and the adventitial: medial area ratio along each artery. The artery from a case of fatal vertebral artery dissection, which occurred after a game of cricket and then chiropractic neck manipulation, was also examined in the same manner. The proteoglycan accumulation in the media was quantified using an eyepiece graticule. RESULTS--The vertebral arteries were, on average, larger around the origin of the vessel from the subclavian artery, and the adventitia were relatively thicker at this point, and also after piercing the dura mater. The media were much thinner within the intracranial segment and pronounced intimal thickening occurred with increasing age. The dissected artery showed undoubtable pre-existent structural abnormalities, in the form of massive proteoglycan accumulation, which predisposes an artery to dissection. CONCLUSIONS--These data should help pathologists faced with the task of assessing the underlying structural integrity of the vessel wall in cases of vertebral artery injury.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bromilow A., Burns J. Technique for removal of the vertebral arteries. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Dec;38(12):1400–1402. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.12.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Smith R., Keller A., Kucharczyk W. Spontaneous dissection of the vertebral artery: MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1989 Mar-Apr;13(2):326–329. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198903000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelbert F., Assouline E., Hodes J. E., Reizine D., Woimant F., George B., Hagueneau M., Merland J. J. MRI in spontaneous dissection of vertebral and carotid arteries. 15 cases studied at 0.5 tesla. Neuroradiology. 1991;33(2):111–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00588245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greselle J. F., Zenteno M., Kien P., Castel J. P., Caillé J. M. Spontaneous dissection of the vertebro-basilar system. A study of 18 cases (15 patients). J Neuroradiol. 1987;14(2):115–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide Y., Fukushima T., Yamamoto M., Tomonaga M. [Vertebral dissecting aneurysm associated with medial mucoid degeneration. Case report and review of literature]. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1986 Nov;26(11):888–894. doi: 10.2176/nmc.26.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. P., Burns J. The medicolegal significance of proteoglycans in the tunica media of the vertebral artery. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 1993 Jun;14(2):165–169. doi: 10.1097/00000433-199306000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manz H. J., Luessenhop A. J. Dissecting aneurysm of intracranial vertebral artery: case report and review of literature. J Neurol. 1983;230(1):25–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00313594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. R., Smialek J. E., Zane W. E. Pathogenesis of vertebral artery occlusion following cervical spine manipulation. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987 Sep;111(9):851–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson I. M. The vertebral artery. Extracranial and intracranial structure. Arch Neurol. 1972 Nov;27(5):392–396. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490170024004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youl B. D., Coutellier A., Dubois B., Leger J. M., Bousser M. G. Three cases of spontaneous extracranial vertebral artery dissection. Stroke. 1990 Apr;21(4):618–625. doi: 10.1161/01.str.21.4.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]