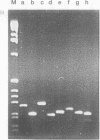
Abstract
AIMS--To test whether human papillomavirus (HPV) variants with large scale sequence alterations to the upstream regulatory region are present in cervical intraepithelial neoplasias (CIN) and cervical carcinomas. METHODS--New PCR based assays were designed specifically to detect large scale insertion/deletion alterations in the upstream regulatory region of HPV 16 and 18. The assays were applied to 24 cases of CIN and 34 cases of cervical carcinoma previously shown to contain these two high risk HPV types. RESULTS--No large scale sequence alterations were found in any of the HPV containing CIN or carcinomas. CONCLUSIONS--These negative findings suggest that major upstream regulatory region variants of HPV 16 and 18 do not contribute to most cervical neoplasms.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arends M. J., Donaldson Y. K., Duvall E., Wyllie A. H., Bird C. C. HPV in full thickness cervical biopsies: high prevalence in CIN 2 and CIN 3 detected by a sensitive PCR method. J Pathol. 1991 Dec;165(4):301–309. doi: 10.1002/path.1711650405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arends M. J., Donaldson Y. K., Duvall E., Wyllie A. H., Bird C. C. Human papillomavirus type 18 associates with more advanced cervical neoplasia than human papillomavirus type 16. Hum Pathol. 1993 Apr;24(4):432–437. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90093-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arends M. J., Wyllie A. H., Bird C. C. Papillomaviruses and human cancer. Hum Pathol. 1990 Jul;21(7):686–698. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., zur Hausen H. Human papillomaviruses in Buschke-Löwenstein tumors: physical state of the DNA and identification of a tandem duplication in the noncoding region of a human papillomavirus 6 subtype. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):963–966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.963-966.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brescia R. J., Jenson A. B., Lancaster W. D., Kurman R. J. The role of human papillomaviruses in the pathogenesis and histologic classification of precancerous lesions of the cervix. Hum Pathol. 1986 Jun;17(6):552–559. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. Y., Ho L., Ong C. K., Chow V., Drescher B., Dürst M., ter Meulen J., Villa L., Luande J., Mgaya H. N. Molecular variants of human papillomavirus type 16 from four continents suggest ancient pandemic spread of the virus and its coevolution with humankind. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2057–2066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2057-2066.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong T., Chan W. K., Bernard H. U. Transcriptional activation of human papillomavirus 16 by nuclear factor I, AP1, steroid receptors and a possibly novel transcription factor, PVF: a model for the composition of genital papillomavirus enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):465–470. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deau M. C., Favre M., Orth G. Genetic heterogeneity among human papillomaviruses (HPV) associated with epidermodysplasia verruciformis: evidence for multiple allelic forms of HPV5 and HPV8 E6 genes. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):492–503. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90419-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasher M. S., Roman A. Characterization of human papillomavirus type 6b DNA isolated from an invasive squamous carcinoma of the vulva. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90676-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulke R., Gross G. E., Pfister H. Duplication of enhancer sequences in human papillomavirus 6 from condylomas of the mamilla. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):284–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90245-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurman R. J., Schiffman M. H., Lancaster W. D., Reid R., Jenson A. B., Temple G. F., Lorincz A. T. Analysis of individual human papillomavirus types in cervical neoplasia: a possible role for type 18 in rapid progression. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Aug;159(2):293–296. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(88)80070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. F., Groff D. E., Chirikjian J. G., Lancaster W. D. Isolation and characterization of a novel human papillomavirus type 6 DNA from an invasive vulvar carcinoma. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):353–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.353-356.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanczuk H., Villa L. L., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. The viral transcriptional regulatory region upstream of the E6 and E7 genes is a major determinant of the differential immortalization activities of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2739–2744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2739-2744.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roossinck M. J., Palukaitis P. Differential replication in zucchini squash of a cucumber mosaic virus satellite RNA maps to RNA 1 of the helper virus. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):371–373. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidy J., Vousden K. H., Mason P., Farrell P. J. A novel deletion within the upstream regulatory region of episomal human papillomavirus type 16. J Gen Virol. 1989 Apr;70(Pt 4):999–1004. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-4-999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Immortalization of human foreskin keratinocytes by various human papillomavirus DNAs corresponds to their association with cervical carcinoma. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):159–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.159-164.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]