Abstract
Background
This study sought to investigate crucial genes correlated with diabetic nephropathy (DN), and their potential functions, which might contribute to a better understanding of DN pathogenesis.
Methods
The microarray dataset GSE1009 was downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus, including 3 diabetic glomeruli samples and 3 healthy glomeruli samples. The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified by LIMMA package. Their potential functions were then analyzed by the GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses using the DAVID database. Furthermore, miRNAs and transcription factors (TFs) regulating DEGs were predicted by the GeneCoDis tool, and miRNA-DEG-TF regulatory network was visualized by Cytoscape. Additionally, the expression of DEGs was validated using another microarray dataset GSE30528.
Results
Totally, 14 up-regulated DEGs and 430 down-regulated ones were identified. Some DEGs (e.g. MTSS1, CALD1 and ACTN4) were markedly relative to cytoskeleton organization. Besides, some other ones were correlated with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (e.g. ACTN4, CTNNA1 and ITGB5), as well as complement and coagulation cascades (e.g. C1R and C1S). Furthermore, a series of miRNAs and TFs modulating DEGs were identified. The transcription factor LEF1 regulated the majority of DEGs, such as ITGB5, CALD1 and C1S. Hsa-miR-33a modulated 28 genes, such as C1S. Additionally, 143 DEGs (one upregulated gene and 142 downregulated genes) were also differentially expressed in another dataset GSE30528.
Conclusions
The genes involved in cytoskeleton organization, cardiomyopathy, as well as complement and coagulation cascades may be closely implicated in the progression of DN, via the regulation of miRNAs and TFs.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12882-016-0343-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Diabetic nephropathy, Differentially expressed gene, MicroRNA, Transcription factor, Network
Background
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a complication correlated with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes and is characterized by glomerulosclerosis due to accumulation of extracellular matrix [1]. Despite great attention from both clinicians and basic scientists, the morbidity of end-stage renal disease and glomerulosclerosis in diabetic patients is increasing dramatically [2].
In the past years, many molecules associated with DN have been uncovered. For example, the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex 1 activation has a key role in podocyte dysfunction in diabetic mice [3, 4]. Rooney et al. have shown that connective tissue growth factor/CCN family protein 2 (CTGF/CCN2) can activate the Wnt signaling in mesangial cells through low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6), which may be implicated in the pathogenesis of DN [5]. In diabetic mice, Glo1 (Glyoxalase 1) overexpression completely inhibits diabetes-induced increases in methylglyoxal modification of glomerular proteins, and promotes the development of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) [6]. Furthermore, there is evidence that miR-192 enhances collagen expression by regulating the E-box repressors Zeb1/2, and locked nucleic acid–anti-miR-192 alleviates proteinuria in the diabetic mice [7]. Based on a gene expression profiling of DN, Hans et al. have shown that some genes in glomeruli from patients with DN are down-regulated, such as bone morphogenetic protein 2, fibroblast growth factor 1, vascular endothelial growth factor, nephrin and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2, suggesting that progression of DN might be due to diminished tissue repair ability [8]. However, the pathways which the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) participate in and regulators that target these genes remain unknown.
In this study, the microarray dataset GSE1009 deposited by Hans [8] was used to identify DEGs between diabetic glomeruli samples and healthy controls. Gene Ontology (GO) and pathway enrichment analyses were then performed for the up- and down-regulated DEGs. Furthermore, microRNAs (miRNAs) and transcription factors (TFs) regulating DEGs were predicted, and miRNA-DEG-TF regulatory network was constructed. These findings may contribute to a better understanding of the nosogenesis of DN.
Methods
Affymetrix microarray data
The gene expression profile data of GSE1009 [8] were downloaded from the public database Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/), which was based on the platform of [HG_U95Av2] Affymetrix Human Genome U95 Version 2 Array (GPL8300, Affymetrix Inc., Santa Clara, California, USA). This dataset contained 6 glomeruli samples, including 3 samples from 2 kidneys from patients with diabetes mellitus type 2, and 3 samples from 2 healthy kidneys.
Another gene expression dataset GSE30528 [9] in GEO, which contains a relatively big sample size and has a high data quality, was used for validation. The data in GSE30528 were produced by the platform of [HG-U133A_2] Affymetrix Human Genome U133A 2.0 Array (GPL571, Affymetrix Inc., Santa Clara, California, USA). A total of 9 diabetic glomeruli samples from patients with DKD and 13 healthy glomeruli samples were included in this dataset.
CEL files and the probe annotation files were downloaded, and the gene expression data of all samples were preprocessed via background correction, quantile normalization and probe summarization using the Robust Multi-array Average (RMA) algorithm in Affy software package of Bioconductor (available at http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/affy.html) [10].
DEGs screening
Linear Models for Microarray Data (LIMMA) package [11] of Bioconductor (available at http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/limma.html) was used to identify genes that were differentially expressed in diabetic glomeruli. Only the genes meeting p-value < 0.05 and |log2FC (fold change)| ≥ 1 were chosen as DEGs.
Enrichment analysis for DEGs
To explore the functions of DEGs in diabetic glomeruli samples, the DAVID (Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery) database [12] was used to perform GO and KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) pathway enrichment analyses for DEGs. The p-value < 0.01 and gene count ≥ 2 were set as the cut-off criteria.
Furthermore, the category of enriched GO terms and the gene number were displayed as a histogram which was constructed by WEGO (Web Gene Ontology Annotation Plot) [13] with the cut-off criterion of level = 2.
Construction of miRNA-DEG-TF regulatory network
GeneCoDis (Gene Annotation Co-occurrence Discovery, http://genecodis.cnb.csic.es/) [14], which is a grid-based tool that integrates biological information from different sources to search for biological characteristics (annotations) that frequently co-occur in a series of genes and rank them by statistical significance, was used to identify miRNAs and TFs regulating DEGs with hypergeometric algorithm, and the adjusted p-value < 0.01 was used as the cut-off criteria. The regulatory network consisting of DEGs, miRNAs and TFs were then visualized by Cytoscape (http://cytoscape.org/) [15].
Validation of the expression level of DEGs
The DEGs between DN and control samples in the dataset GSE30528 were identified using the aforementioned methods. The overlapped DEGs in both of GSE30528 and GSE1009 were then identified using the VennDiagram package. Here, if a gene was differentially expressed in both of GSE30528 and GSE1009 with the same expression pattern (up-regulated or down-regulated expression), this gene was identified as an overlapped DEG.
Results
Identification of DEGs
Based on the cut-off criteria, a set of 444 genes were identified to be differentially expressed in the diabetic glomeruli samples, including 14 up-regulated and 430 down-regulated ones, compared with the controls (Additional file 1).
GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of up- and down-regulated DEGs
A total of 111 GO terms for the down-regulated DEGs were generated. Some genes (e.g. MTSS1, CALD1 and ACTN4) were related to cytoskeleton organization, such as actin filament-based process, actin cytoskeleton and cytoskeletal protein binding; some other genes were distinctly enriched in negative regulation of cell proliferation (e.g. AIF1, IGFBP7 and COL4A3) (Table 1). Using WEGO (level = 2), 25 categories of GO terms for down-regulated DEGs were displayed. The majority of genes were enriched in biological processes (BP), such as anatomical structure formation, biological regulation, death and response to stimulus. Moreover, several GO terms in cellular component (CC) were obtained, such as cell part and organelle. Furthermore, three GO terms in molecular function (MF) were enriched by the down-regulated genes, including binding, structural molecule and transporter (Fig. 1). In addition, three up-regulated DEGs (CD69, LGALS2 and FBP1) were significantly enriched in sugar binding.
Table 1.
The top 5 enriched GO terms with the most low p-value for differentially expressed genes
| Category | Terms | Description | Count | p-value | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP | GO:0030029 | actin filament-based process | 23 | 5.38E-07 | MTSS1, ROCK1, ACTN4, AIF1, CALD1, ARF6, MYH9, CAPZB, TNNT2, ACTG1… |
| GO:0030036 | actin cytoskeleton organization | 22 | 7.32E-07 | MTSS1, ROCK1, ACTN4, AIF1, CALD1, ARPC5, MYH9, CAPZB, TNNT2, ACTG1… | |
| GO:0008285 | negative regulation of cell proliferation | 28 | 1.48E-06 | AIF1, IGFBP7, PTH1R, ING1, COL4A3, BMP2, CTBP1, GAS1, CD164, TGFBR3… | |
| GO:0007010 | cytoskeleton organization | 31 | 2.17E-06 | MTSS1, AIF1, CALD1, ARF6, ACTG1, PAK1, PLS3, ACTN4, ROCK1, MYH9… | |
| GO:0030832 | regulation of actin filament length | 11 | 6.01E-06 | ACTR3, PFN2, CAPZA1, TMSB4X, RDX, ARF6, ARPC5, CAPZB, SPTAN1, DSTN… | |
| CC | GO:0015629 | actin cytoskeleton | 31 | 2.60E-11 | MTSS1, AIF1, CALD1, MYL9, ACTR3, ACTG1, ACTN4, MYO1B, MYH9, CTNNA1… |
| GO:0005938 | cell cortex | 20 | 1.02E-08 | SEPT2, ACTN4, SEPT1, CALD1, ARF6, MYH9, SEPT10, ACTG1, FNBP1, CLIC5… | |
| GO:0005856 | cytoskeleton | 70 | 1.28E-07 | MTSS1, AIF1, CALD1, MYL9, ACTR3, ACTG1, ACTN4, MYO1B, MYH9, CTNNA1… | |
| GO:0044448 | cell cortex part | 13 | 1.78E-06 | SEPT2, ACTN4, SEPT1, CALD1, PRKCI, MYH9, CAPZB, SEPT10, DSTN, ACTG1… | |
| GO:0043232 | intracellular non-membrane-bounded organelle | 104 | 5.54E-06 | SEPT2, ACTN4, SEPT1, CALD1, PRKCI, MYH9, CAPZB, SEPT10, DSTN, ACTG1… | |
| MF | GO:0008092 | cytoskeletal protein binding | 40 | 7.17E-10 | MTSS1, AIF1, TNNC1, CALD1, EZR, TARDBP, ACTN4, MYO1B, SUN2, MYH9… |
| GO:0003779 | actin binding | 30 | 5.79E-09 | MTSS1, AIF1, TNNC1, CALD1, ACTN4, MYH9, PALLD, NEBL, TNNT2, PARVA… | |
| GO:0005520 | insulin-like growth factor binding | 6 | 3.80E-04 | CTGF, HTRA1, IGFBP7, IGFBP2, CRIM1, CYR61 | |
| GO:0005200 | structural constituent of cytoskeleton | 9 | 6.07E-04 | TNNT2, ACTG1, DMD, VIM, AGRN, ARPC5, CD2AP, ADD3, SPTAN1 | |
| GO:0050839 | cell adhesion molecule binding | 6 | 9.18E-04 | EZR, PVRL2, NPTN, CTNNA1, CD2AP, CTNNB1 |
GO Gene Ontology, BP biological process, MF molecular function, CC cellular component
Fig. 1.
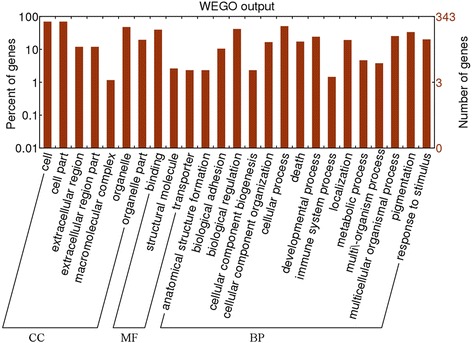
The histogram of the category of enriched GO (Gene Ontology) terms for the down-regulated genes. CC represents cellular component; MF represents molecular function; and BP represents biological process. WEGO represents the tool Web Gene Ontology Annotation Plot
According to KEGG enrichment analysis, the down-regulated DEGs were significantly enriched in 6 pathways, such as arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) (e.g. ACTN4, CTNNA1 and ITGB5), regulation of actin cytoskeleton (e.g. ACTN4, MYL9 and ITGB5) and complement and coagulation cascades (e.g. C1R and C1S). There were no significant pathways for the up-regulated DEGs (Table 2).
Table 2.
The results of pathway enrichment analysis for the down-regulated genes
| Category | Pathway Name | Count | p-value | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG_PATHWAY | Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) | 11 | 1.41E-04 |
ACTG1, ATP2A2, ACTN4, DMD, DAG1, CACNB2, ITGB5, ITGA3, CTNNA1, CTNNB1… ACTN4, ROCK1, ITGB5, RDX, ITGA3, ARPC5, MYL12A, MYH9, MYL9, ACTG1… |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 19 | 1.65E-04 | |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) | 9 | 0.00575 | TNNT2, ACTG1, ATP2A2, TNNC1, DMD, DAG1, CACNB2, ITGB5, ITGA3 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | Complement and coagulation cascades | 8 | 0.00641 | CD55, F3, CD46, CD59, C1R, SERPING1, C1S, F2R |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | Dilated cardiomyopathy | 9 | 0.00920 | TNNT2, ACTG1, ATP2A2, TNNC1, DMD, DAG1, CACNB2, ITGB5, ITGA3 |
| KEGG_PATHWAY | Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection | 7 | 0.00956 | ACTG1, EZR, ROCK1, TUBB2A, YWHAQ, ARPC5, CTNNB1 |
KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
Analysis of miRNA-DEG-TF regulatory network
Totally, 896 regulatory relationships between miRNAs, TFs and DEGs were identified to construct the miRNA-DEG-TF regulatory network, including 24 miRNAs, 44 TFs and 275 down-regulated genes (Fig. 2). The transcription factor LEF1 regulated most of genes (degree = 79), such as ITGB5, CALD1, RTN4 and PAK1. Hsa-miR-33a modulated 28 genes, such as C1S and RTN4.
Fig. 2.
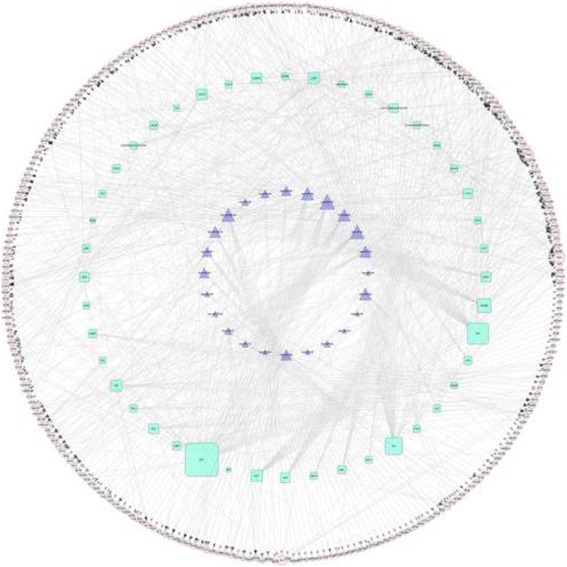
The network consisting of differentially expressed genes, microRNAs and transcription factors. Rounded nodes represent genes; trigonal nodes represent microRNAs; and quadrate nodes represent transcription factors
Besides, no miRNAs were predicted to regulate the up-regulated genes, whereas, two TFs (AML1 and NFKB) were identified to modulate several up-regulated genes. Among them, AML1 regulated CD96 and CYP17A1.
Screening of overlapped DEGs in the two datasets
To validate the expression of the identified DEGs in the dataset GSE1009, another dataset GSE30528 was used. A total of 635 DEGs were identified in GSE30528. Among them, 143 DEGs, including one upregulated gene (TRIM16) and 142 downregulated genes (e.g. MTSS1, ACTN4 and ITGB5), were also differentially expressed in the dataset GSE1009 (Fig. 3), indicating that the expression of the 143 DEGs in GSE1009 identified above were validated by the dataset GSE30528.
Fig. 3.
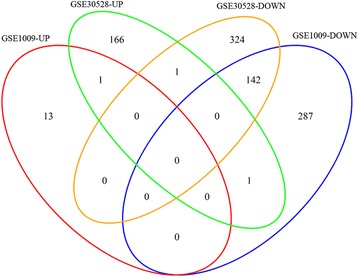
The Venn diagram showing the overlapped differentially expressed genes in the two datasets GSE30528 and GSE1009. “GSE30528-UP” represents the upregulated genes in the dataset GSE30528; “GSE30528-DOWN” represents the downregulated genes in the dataset GSE30528; “GSE1009-UP” represents the upregulated genes in the dataset GSE1009; and “GSE1009-DOWN” represents the downregulated genes in the dataset GSE1009. Arabic numerals in the diagram represent the numbers of the overlapped genes
Discussion
In the present study, a set of 444 DEGs in the dataset GSE1009 were identified from diabetic glomeruli samples, including 14 up-regulated ones and 430 down-regulated ones, compared with healthy glomeruli samples. Among them, the expression of 143 DEGs (one upregulated gene and 142 downregulated genes) were validated by another dataset GSE30528. According to the GO functional enrichment analysis, a set of DEGs were related to the function of cytoskeleton organization, such as MTSS1, ACTN4 and CALD1.
MTSS1 encodes metastasis suppressor 1, which is also known as MIM (missing in metastasis). It is an actin and membrane binding protein that was originally identified as a potential tumor metastasis suppressor [16]. MTSS1 can induce actin-rich protrusions at the plasmalemma and promote disintegration of actin stress fibers [17], indicating that it may be crucial in regulating cytoskeletal dynamics. Renal tubular cell and podocyte apoptosis is an inevitable event in the progression of glomerulosclerosis [18, 19], and major modifications of the cytoskeleton are involved in the apoptosis progress, including dynamic membrane blebbing, nuclear disintegration, chromatin condensation and cell fragmentation [20]. Therefore, MTSS1 may play a pivotal role in DN, via participation in the regulation of cytoskeleton organization. ACTN4 encodes an actinin, which participates in cytoskeleton action. Previous studies have been reported that mutations in ACTN4 cause focal segmental glomerulosclerosis [21–23]. There is evidence that two single-nucleotide polymorphisms in ACTN4 are associated with DN in women [24]. Moreover, the up-regulation of ACTN4 was observed during the proteinuria stage [25]. Thereby, ACTN4 may be also important in the progression of DN. CALD1 encodes a caldesmon that plays a key role in the regulation of smooth muscle and nonmuscle contraction [26]. A previous study has shown that CALD1 is over-expressed in fibroblasts from the diabetic patients with nephropathy, compared with those from the controls [27]. Conway et al. have demonstrated that caldesmon is a candidate susceptibility gene for DN [28]. In this study, CALD1 was found to be regulated by several TFs, such as LEF1. LEF1 (lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1) is a nuclear transcription factor modulated by Wnt, and it expedites epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) when its activity is activated by β-catenin [29]. Rooney et al. have reported that overexpression of CCN2 during the progression of DN likely results in the activation of Wnt signaling and subsequent initiation of TCF/LEF transcription [5]. Collectively, CALD1 may play an essential role in the development of DN likely through the regulation of LEF1.
Furthermore, a series of downregulated DEGs were discovered to be enriched in the pathways of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in our study, such as ITGB5. Diabetic cardiomyopathy is a frequent event in diabetic patients due to hyperglycemia [30]. ITGB5 encodes integrin beta 5 [31], and it has been found to be differentially expressed in DKD glomeruli and tubuli [9]. Furthermore, integrins are the primary receptors for intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1), which has been reported to have a close relationship with DN [32]. Additionally, in our study, ITGB5 was also regulated by LEF1. These results suggest that ITGB5 may have a significant function in the development of DN, via participating in cardiomyopathy pathways.
Additionally, a set of genes were markedly enriched in complement and coagulation cascades, such as C1S and C1R. These two genes both encode members of the human complement subcomponent C1, which is involved in immune response [33]. Migration of immune cells into the renal is a feature of early DN, and it is implicated in the development of this complication [34–37]. Previous studies also have found C1S and C1R to be differentially expressed in DN [38, 39]. In our study, C1S and C1R were regulated by LEF1 and hsa-miR-33a. MiR-33a has been reported to be implicated in diabetes due to its regulation of insulin signaling and fatty acid metabolism [40, 41]. Therefore, C1S and C1R may be crucial in the development of DN.
However, this study has some limitations. For example, these predictions were not validated by experiments. The number of samples used for analysis is small. In further studies, more samples will be analyzed, and the predictions will be validated by experimental data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a total of 14 up-regulated genes and 430 down-regulated ones were identified. Some DEGs related to cytoskeleton organization (e.g. MTSS1, ACTN4 and CALD1), cardiomyopathy (e.g. ITGB5) and immune response (e.g. C1S and C1R), as well as some regulators (e.g. LEF1 and hsa-miR-33a) might play pivotal roles in the progression of DN. These findings may contribute to our better understanding of DN pathogenesis, and provide a theoretical basis for further experimental studies.
Acknowledgement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Funding
None.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
ZKW and ZXW participated in the design of this study, and they both performed the statistical analysis. ZZ carried out the study, collected important background information, and drafted the manuscript. YR conceived of this study, and participated in the design and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
None.
Competing interests
The Authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ARVC
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
- BP
biological processes
- CC
Cellular component
- DEGs
Differentially expressed genes
- DKD
Diabetic kidney disease
- DN
Diabetic nephropathy
- EMT
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition
- GO
Gene Ontology
- ICAM1
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1
- LIMMA
Linear Models for Microarray Data
- MF
Molecular function
- mTOR
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- RMA
Robust Multi-array Average
- TFs
Transcription factors
- WEGO
Web Gene Ontology Annotation Plot
Additional file
The list of differentially expressed genes. (XLSX 30 kb)
Contributor Information
Zhikui Wang, Email: wangzhikuily@163.com.
Zhaoxia Wang, Phone: +86-0539-8216273, Email: zhaoxiazhzhh@163.com.
Zhongqi Zhou, Email: zhouzhongqi7@163.com.
Yueqin Ren, Email: nerenxueqin@163.com.
References
- 1.Schor N, Ichikawa I, Rennke HG, Troy JL, Brenner BM. Pathophysiology of altered glomerular function in aminoglycoside-treated rats. Kidney Int. 1981;19(2):288–96. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Inoki K, Corradetti MN, Guan K-L. Dysregulation of the TSC-mTOR pathway in human disease. Nat Genet. 2004;37(1):19–24. doi: 10.1038/ng1494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Inoki K, Mori H, Wang J, Suzuki T, Hong S, Yoshida S, et al. mTORC1 activation in podocytes is a critical step in the development of diabetic nephropathy in mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(6):2181–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI44771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gödel M, Hartleben B, Herbach N, Liu S, Zschiedrich S, Lu S, et al. Role of mTOR in podocyte function and diabetic nephropathy in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(6):2197–209. doi: 10.1172/JCI44774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rooney B, O’Donovan H, Gaffney A, Browne M, Faherty N, Curran SP, et al. CTGF/CCN2 activates canonical Wnt signalling in mesangial cells through LRP6: implications for the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(3):531–38. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Giacco F, Du X, D’Agati VD, Milne R, Sui G, Geoffrion M, et al. Knockdown of glyoxalase 1 mimics diabetic nephropathy in nondiabetic mice. Diabetes. 2014;63(1):291–99. doi: 10.2337/db13-0316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Putta S, Lanting L, Sun G, Lawson G, Kato M, Natarajan R. Inhibiting microRNA-192 ameliorates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23(3):458–69. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011050485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Baelde HJ, Eikmans M, Doran PP, Lappin DW, de Heer E, Bruijn JA. Gene expression profiling in glomeruli from human kidneys with diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43(4):636–50. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2003.12.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Woroniecka KI, Park ASD, Mohtat D, Thomas DB, Pullman JM, Susztak K. Transcriptome analysis of human diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes. 2011;60(9):2354–69. doi: 10.2337/db10-1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Seo J, Hoffman EP. Probe set algorithms: is there a rational best bet? BMC Bioinformatics. 2006;7(1):395. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Smyth GK. Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol. 2004;3:Article3. doi: 10.2202/1544-6115.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Da Wei Huang BTS, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2008;4(1):44–57. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mayes S, Ferrone M. Fentanyl HCl patient-controlled iontophoretic transdermal system for the management of acute postoperative pain. Ann Pharmacother. 2006;40(12):2178–86. doi: 10.1345/aph.1H135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nogales-Cadenas R, Carmona-Saez P, Vazquez M, Vicente C, Yang X, Tirado F, et al. GeneCodis: interpreting gene lists through enrichment analysis and integration of diverse biological information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(Web Server issue):W317–22. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kohl M, Wiese S, Warscheid B. Data Mining in Proteomics. New York: Springer; 2011. Cytoscape: software for visualization and analysis of biological networks; pp. 291–303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lee YG, Macoska JA, Korenchuk S, Pienta KJ. MIM, a potential metastasis suppressor gene in bladder cancer. Neoplasia. 2002;4(4):291–4. doi: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Woodings J, Sharp S, Machesky L. MIM-B, a putative metastasis suppressor protein, binds to actin and to protein tyrosine phosphatase delta. Biochem J. 2003;37:463–71. doi: 10.1042/bj20021962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Erkan E, Garcia CD, Patterson LT, Mishra J, Mitsnefes MM, Kaskel FJ, et al. Induction of renal tubular cell apoptosis in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: roles of proteinuria and Fas-dependent pathways. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16(2):398–407. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2003100861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shankland S. The podocyte’s response to injury: role in proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2006;69(12):2131–47. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ndozangue-Touriguine O, Hamelin J, Bréard J. Cytoskeleton and apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;76(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kaplan JM, Kim SH, North KN, Rennke H. Mutations in ACTN4, encoding α-actinin-4, cause familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet. 2000;24(3):251–56. doi: 10.1038/73456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dai S, Wang Z, Pan X, Wang W, Chen X, Ren H, et al. Functional analysis of promoter mutations in the ACTN4 and SYNPO genes in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2010;25(3):824–35. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Choi HJ, Lee BH, Cho HY, Moon KC, Ha IS, Nagata M, et al. Familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis associated with an ACTN4 mutation and paternal germline mosaicism. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;51(5):834–8. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ihalmo P, Wessman M, Kaunisto M, Kilpikari R, Parkkonen M, Forsblom C, et al. Association analysis of podocyte slit diaphragm genes as candidates for diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia. 2008;51(1):86–90. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0854-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nakatani S, Kakehashi A, Ishimura E, Yamano S, Mori K, Wei M, et al. Targeted proteomics of isolated glomeruli from the kidneys of diabetic rats: sorbin and SH3 domain containing 2 is a novel protein associated with diabetic nephropathy. Exp Diabetes Res. 2011;2011:979354. doi: 10.1155/2011/979354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Novy RE, Lin J, Lin J. Characterization of cDNA clones encoding a human fibroblast caldesmon isoform and analysis of caldesmon expression in normal and transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(25):16917–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Millioni R, Iori E, Lenzini L, Puricelli L, Caroccia B, Arrigoni G, et al. Caldesmon over-expression in type 1 diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 2011;25(2):114–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2010.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Conway BR, Maxwell AP, Savage DA, Patterson CC, Doran PP, Murphy M, et al. Association between variation in the actin-binding gene caldesmon and diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004;53(4):1162–65. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.4.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kim K, Lu Z, Hay ED. Direct evidence for a role of beta-catenin/LEF-1 signaling pathway in induction of EMT. Cell Biology Int. 2002;26(5):463–76. doi: 10.1006/cbir.2002.0901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cai L, Kang YJ. Oxidative stress and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2001;1(3):181–93. doi: 10.1385/CT:1:3:181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.McLean JW, Vestal D, Cheresh D, Bodary S. cDNA sequence of the human integrin beta 5 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(28):17126–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gu HF, Ma J, Gu KT, Brismar K. Association of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1) with diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2012;3:179. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schumaker VN, Hanson DC, Kilchherr E, Phillips ML, Poon PH. A molecular mechanism for the activation of the first component of complement by immune complexes. Mol Immunol. 1986;23(5):557–65. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Galkina E, Ley K. Leukocyte recruitment and vascular injury in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(2):368–77. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005080859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Navarro-González JF, Mora-Fernández C, de Fuentes MM, García-Pérez J. Inflammatory molecules and pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7(6):327–40. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2011.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wada J, Makino H. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Clin Sci. 2013;124(3):139–52. doi: 10.1042/CS20120198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lim AK, Tesch GH. Inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. Mediat Inflamm. 2012;2012:146154. doi: 10.1155/2012/146154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang Z, Peng H, Chen J, Chen X, Han F, Xu X, et al. MicroRNA-21 protects from mesangial cell proliferation induced by diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. FEBS letters. 2009;583(12):2009–14. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 39.Fechete R, Heinzel A, Perco P, Mönks K, Söllner J, Stelzer G, et al. Mapping of molecular pathways, biomarkers and drug targets for diabetic nephropathy. PROTEOMICS-Clinical Applications. 2011;5(5–6):354–66. doi: 10.1002/prca.201000136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dávalos A, Goedeke L, Smibert P, Ramírez CM, Warrier NP, Andreo U, et al. miR-33a/b contribute to the regulation of fatty acid metabolism and insulin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2011;108(22):9232–37. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102281108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nikpour P, Miranzadeh-Mahabadi H, Emadi-Baygi M, Kelishadi R. Association of rs8066560 variant in the sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1) and miR-33b genes with hyperglycemia and insulin resistance. J Pediatr Endocr Met. 2014;27(7–8):611–5. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2014-0115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.


