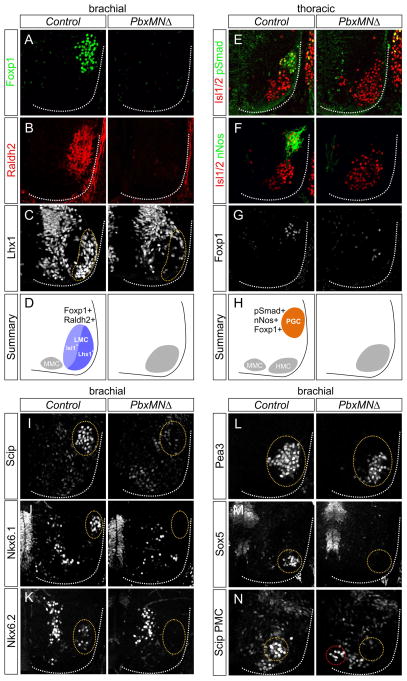
Figure 2. Pbx Genes are Essential for MN Columnar, Divisional, and Pool Specification.
(A,B) Expression of Foxp1 and Raldh2 is reduced in PbxMNΔ mutants at e12.5. (C) Expression of Lhx1 within the lateral division of the LMC is depleted at brachial levels in PbxMNΔ mice. (D) Summary of LMC neuron organization at brachial levels in control and PbxMNΔ mice. (E–G) At thoracic levels there is a loss of nNos, Foxp1, and pSmad expression in PbxMNΔ mutants. (H) Summary of MN organization at thoracic levels in control and PbxMNΔ mice. (I) Loss of Scip expression from median and ulnar MN pools in PbxMNΔ mice (J,K) Loss of Nkx6.1 and Nkx6.2 expression from rostral brachial pools in PbxMNΔ mutants. (L) Expression of Pea3 is detected in PbxMNΔ mice, but mispositioned ventromedially. (M) Loss of the non-LMC Sox5+ pool in PbxMNΔ mice. (N) Expression of Scip in phrenic MNs is reduced and mislocalized (red circle) in PbxMNΔ mice. In panels I–N circled areas discriminate MNs that express indicated factors from other spinal populations. In PbxMNΔ mice circled areas represent position where these pools would be present normally. See also Figure S2.