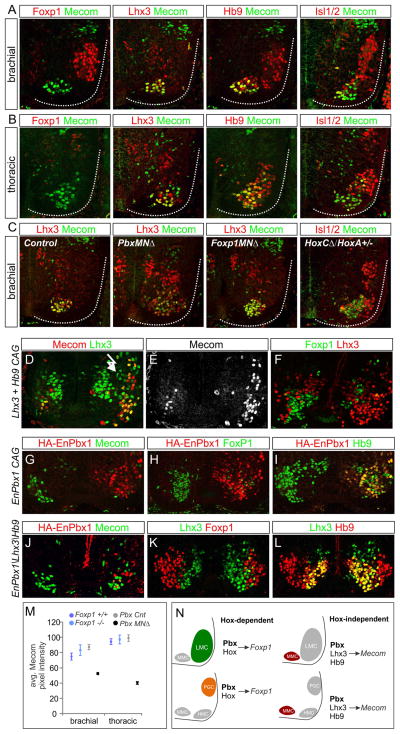
Figure 7. Hox-Independent Regulation of Mecom by Pbx Proteins and Lhx3.
(A) Mecom protein expression at brachial levels at e12.5. Mecom is detected in Lhx3+, Hb9+ MMC neurons but excluded from Foxp1+ LMC neurons. (B) Mecom expression at thoracic levels. Mecom is detected in MMC neurons, a subset of Lhx3−, Hb9+ MNs, but is excluded from Foxp1+ PGC neurons. (C) Analysis of Mecom expression in Pbx, Foxp1, and HoxC mutants. Mecom is reduced in MMC neurons of PbxMNΔ mice, but is unaffected in Foxp1MNΔ and HoxC mutants. (D,E) Chick electroporations at thoracic levels showing Mecom expression is induced after Lhx3 and Hb9 misexpression. (F) Lhx3/Hb9 also represses Foxp1 expression. (G–I) Expression of EnPbx1 represses Mecom and Foxp1 in MNs. (J–L) Coexpression of EnPbx1, Lhx3, and Hb9 fails to generate ectopic Mecom+ MNs. (M) Quantification of Mecom levels in Pbx and Foxp1 mutants. Data are shown as average pixel intensities of Mecom immunofluorescence +/− SEM. (N) Summary MN columnar specification by Pbx proteins. Pbx proteins act in Hox-dependent pathways to induce expression of columnar determinants such as Foxp1. Pbx proteins also act in a Hox-independent manner to regulate expression of MMC-restricted genes including Mecom. See also Figure S7.