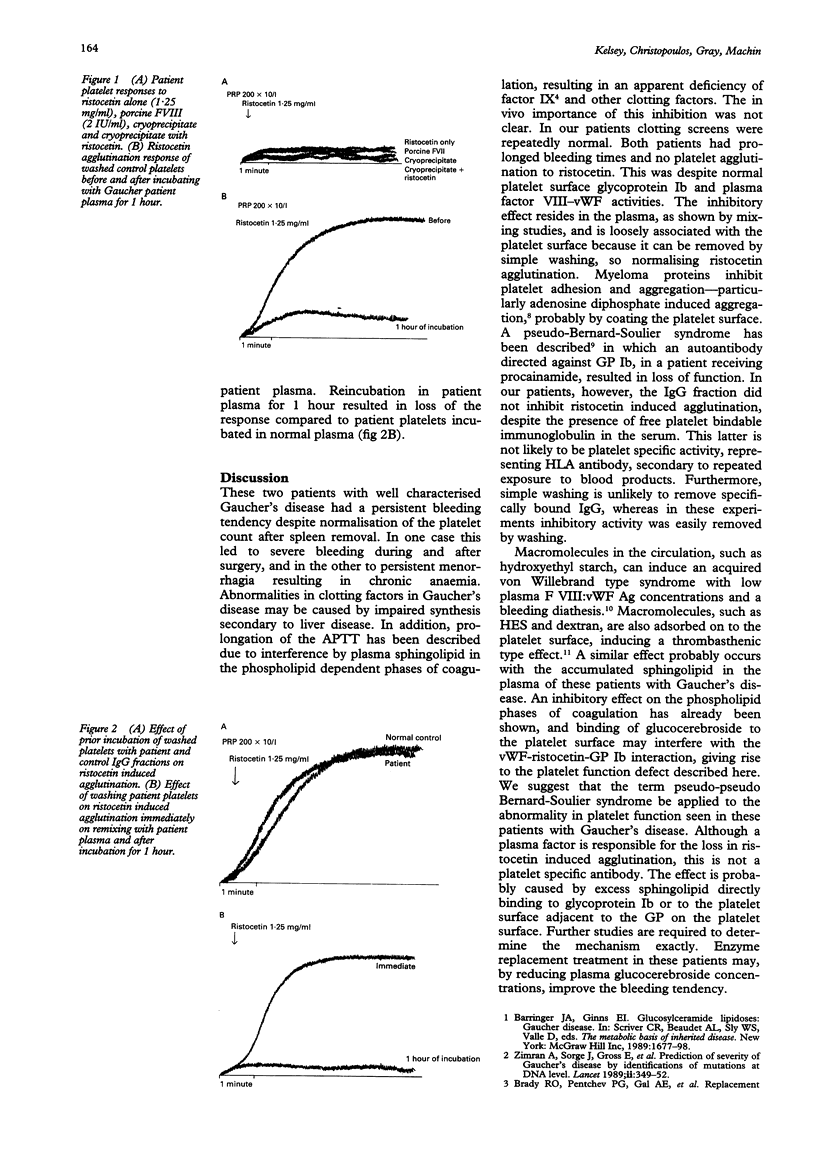
Abstract
AIMS--To investigate the abnormality in platelet function in two patients with type I Gaucher's disease causing a chronic bleeding tendency despite normalisation of the platelet count after spleen removal. METHODS--Routine laboratory methods were used to assess baseline coagulation. Platelet aggregometry was used to assess platelet responses to a range of agonists, and abnormalities were further assessed in mixing experiments using washed platelets and patients' plasma. RESULTS--Platelets from both patients with Gaucher's disease failed to agglutinate to ristocetin, despite normal platelet surface glycoprotein (GP) Ib and plasma von Willebrand factor activity. The agglutination of normal washed platelets was abolished by incubation in patient plasma. The inhibitory activity did not lie in the IgG fraction of patient plasma, and was found to be loosely associated with the patient platelet surface. CONCLUSIONS--The inhibition of ristocetin induced platelet agglutination in patients with Gaucher's disease causes a prolonged skin bleeding time. This could be due to the accumulated glucocerebroside in the plasma coating the platelet membrane. It is suggested that the term pseudo-pseudo Bernard-Soulier syndrome would be appropriate, as on initial screening, the abnormality has the features of Bernard-Soulier syndrome, but further investigation shows normal plasma von Willebrand activity and platelet surface GP Ib concentrations. The inhibitory activity is not due to a platelet specific antibody as is the case in pseudo-Bernard Soulier syndrome.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boklan B. F., Sawitsky A. Factor IX deficiency in Gaucher disease. An in vitro phenomenon. Arch Intern Med. 1976 Apr;136(4):489–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopoulos C. G., Kelsey H. C., Machin S. J. A flow-cytometric approach to quantitative estimation of platelet surface immunoglobulin G. Vox Sang. 1993;64(2):106–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1993.tb02527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine D. V., Currie M. S., Rosse W. F., Greenberg C. S. Pseudo-Bernard-Soulier syndrome: thrombocytopenia caused by autoantibody to platelet glycoprotein Ib. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):428–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood D. N., Bullen C., Machin S. J. A severe coagulopathy following volume replacement with hydroxyethyl starch in a Jehovah's Witness. Anaesthesia. 1988 May;43(5):391–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1988.tb09021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishler J. M., 4th Synthetic plasma volume expanders--their pharmacology, safety and clinical efficacy. Clin Haematol. 1984 Feb;13(1):75–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penny R., Castaldi P. A., Whitsed H. M. Inflammation and haemostasis in paraproteinaemias. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jan;20(1):35–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb00784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimran A., Sorge J., Gross E., Kubitz M., West C., Beutler E. Prediction of severity of Gaucher's disease by identification of mutations at DNA level. Lancet. 1989 Aug 12;2(8659):349–352. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90536-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


