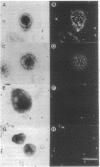
Abstract
Somatostatin and somatostatin receptors are transiently expressed in the immature rat cerebellar cortex but virtually undetectable in the cerebellum of adults. Although somatostatin binding sites have been visualized during the postnatal period in the external granule cell layer, the type of cell that expresses somatostatin receptors has never been identified; thus, the potential function of somatostatin in the developing cerebellum remains unknown. In the present study, we have taken advantage of the possibility of obtaining a culture preparation that is greatly enriched in immature cerebellar granule cells to investigate the presence of somatostatin receptors and the effect of somatostatin on intracellular messengers on cerebellar neuroblasts in primary culture. Autoradiographic labeling revealed the occurrence of a high density of binding sites for radioiodinated Tyr-[D-Trp8]somatostatin-(1-14) on 1-day-old cultured immature granule cells. Saturation and competition studies showed the existence of a single class of high-affinity binding sites (Kd = 0.133 +/- 0.013 nM, Bmax = 3038 +/- 217 sites per cell). Somatostatin induced a dose-dependent inhibition of forskolin-evoked cAMP formation (ED50 = 10 nM), and this effect was prevented by preincubation of cultured immature granule cells with pertussis toxin. Somatostatin also caused a marked reduction of intracellular calcium concentration. These results show the presence of functionally active somatostatin receptors on immature granule cells. Our data suggest the possible involvement of somatostatin in the regulation of proliferation and/or migration of neuroblasts during the development of the cerebellar cortex.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman J. Postnatal development of the cerebellar cortex in the rat. I. The external germinal layer and the transitional molecular layer. J Comp Neurol. 1972 Jul;145(3):353–397. doi: 10.1002/cne.901450305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazeau P., Vale W., Burgus R., Ling N., Butcher M., Rivier J., Guillemin R. Hypothalamic polypeptide that inhibits the secretion of immunoreactive pituitary growth hormone. Science. 1973 Jan 5;179(4068):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4068.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epelbaum J. Somatostatin in the central nervous system: physiology and pathological modifications. Prog Neurobiol. 1986;27(1):63–100. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(86)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez B. J., Leroux P., Bodenant C., Braquet P., Vaudry H. Pharmacological characterization of somatostatin receptors in the rat cerebellum during development. J Neurochem. 1990 Sep;55(3):729–737. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez B. J., Leroux P., Bodenant C., Laquerrière A., Coy D. H., Vaudry H. Ontogeny of somatostatin receptors in the rat brain: biochemical and autoradiographic study. Neuroscience. 1989;29(3):629–644. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez B. J., Leroux P., Boer G. J., Vaudry H. Expression of somatostatin receptors is impaired in the cerebellum of developing Brattleboro rats. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 5;532(1-2):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91750-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez B. J., Leroux P., Laquerrière A., Coy D. H., Bodenant C., Vaudry H. Transient expression of somatostatin receptors in the rat cerebellum during development. Brain Res. 1988 May 1;468(1):154–157. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki S., Shiosaka S., Sekitani M., Noguchi K., Shimada S., Takagi H. In situ hybridization analysis of the somatostatin-containing neuron system in developing cerebellum of rats. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Dec;6(4):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Hescheler J., Ewel C., Rosenthal W., Schultz G., Wittig B. Assignment of G-protein subtypes to specific receptors inducing inhibition of calcium currents. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):43–48. doi: 10.1038/353043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laquerriere A., Leroux P., Gonzalez B. J., Bodenant C., Benoit R., Vaudry H. Distribution of somatostatin receptors in the brain of the frog Rana ridibunda: correlation with the localization of somatostatin-containing neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Feb 15;280(3):451–467. doi: 10.1002/cne.902800310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laquerrière A., Leroux P., Gonzalez B., Bodenant C., Tayot J., Vaudry H. Somatostatin receptors in the human cerebellum during development. Brain Res. 1992 Feb 28;573(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90770-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. F., Manning D., Reisine T. Identification of the subunits of GTP-binding proteins coupled to somatostatin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17885–17897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebow C., Hierowski M., duSapin K. Hormonal control of pancreatic cancer growth. Pancreas. 1986;1(1):44–48. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198601000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebow C., Reilly C., Serrano M., Schally A. V. Somatostatin analogues inhibit growth of pancreatic cancer by stimulating tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2003–2007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundergan C. F., Foegh M. L., Ramwell P. W. Peptide inhibition of myointimal proliferation by angiopeptin, a somatostatin analogue. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991 May;17(6 Suppl B):132B–136B. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(91)90949-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor G. P., Woodhams P. L., O'Shaughnessy D. J., Ghatei M. A., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Developmental changes in bombesin, substance P, somatostatin and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Jan 22;28(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reubi J. C., Horisberger U., Lang W., Koper J. W., Braakman R., Lamberts S. W. Coincidence of EGF receptors and somatostatin receptors in meningiomas but inverse, differentiation-dependent relationship in glial tumors. Am J Pathol. 1989 Feb;134(2):337–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Hescheler J., Hinsch K. D., Spicher K., Trautwein W., Schultz G. Cyclic AMP-independent, dual regulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ currents by LHRH and somatostatin in a pituitary cell line. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1627–1633. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02989.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scambia G., Panici P. B., Baiocchi G., Perrone L., Iacobelli S., Mancuso S. Antiproliferative effects of somatostatin and the somatostatin analog SMS 201-995 on three human breast cancer cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1988;114(3):306–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00405839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel R. A., Tolcsvai L., Rudin M. Partial inhibition of the growth of transplanted dunning rat prostate tumors with the long-acting somatostatin analogue sandostatin (SMS 201-995). Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4651–4655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikant C. B., Patel Y. C. Somatostatin receptors: identification and characterization in rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3930–3934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. E., Bogden A. E., Moreau J. P., Coy D. H. In vitro and in vivo inhibition of human small cell lung carcinoma (NCI-H69) growth by a somatostatin analogue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 31;153(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunoo A., Yoshii M., Narahashi T. Block of calcium channels by enkephalin and somatostatin in neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9832–9836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viguerie N., Tahiri-Jouti N., Ayral A. M., Cambillau C., Scemama J. L., Bastié M. J., Knuhtsen S., Estève J. P., Pradayrol L., Susini C. Direct inhibitory effects of a somatostatin analog, SMS 201-995, on AR4-2J cell proliferation via pertussis toxin-sensitive guanosine triphosphate-binding protein-independent mechanism. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):1017–1025. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villar M. J., Hökfelt T., Brown J. C. Somatostatin expression in the cerebellar cortex during postnatal development. An immunohistochemical study in the rat. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1989;179(3):257–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00326591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R., McIntosh C. H., Buchan A. M., Brown J. C. Central somatostatin systems revealed with monoclonal antibodies. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Aug 8;238(2):169–186. doi: 10.1002/cne.902380205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. L., Bogen C., Reisine T., Dichter M. Somatostatin-14 and somatostatin-28 induce opposite effects on potassium currents in rat neocortical neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9616–9620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Post S. R., Wang K., Tager H. S., Bell G. I., Seino S. Cloning and functional characterization of a family of human and mouse somatostatin receptors expressed in brain, gastrointestinal tract, and kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):251–255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Regulation by secretin, vasoactive intestinal peptide, and somatostatin of cyclic AMP accumulation in cultured brain cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6907–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]