Abstract
Objectives:
To identify the retention protocols practiced by orthodontists in Saudi Arabia, and the factors affecting retainer choice.
Methods:
This cross-sectional study took place between February and March of 2015 at the College of Dentistry, University of Dammam, Dammam, Saudi Arabia. A previously tested electronic survey of 34 items was sent to all 1,200 orthodontic members of the Saudi Orthodontic Society. The questionnaire elicited data on the subjects’ demographics, orthodontic treatment practices, retention, and post-retention protocols.
Results:
One hundred and sixty-seven (13.9%) responses were received during the study period. The results showed predominant use of Hawley in the maxillary arch (61.3%), and fixed lingual in the mandibular arch (58.5%). Approximately 90.3% recommended full-time maxillary removable retainer wear. Overall, orthodontists who performed fewer extractions tended to use fixed retainers, and those who performed more extractions used removable retainers (p=0.018). Interproximal enamel reduction was used by 28% of the respondents as an adjunct procedure to enhance retention. Approximately 64% practiced a post-retention phase of retainer wear. Participants who used removable retainers most commonly prescribed lifetime retention.
Conclusion:
Hawley in the maxilla, and fixed lingual in the mandible were the most common retention protocols prescribed. Lifetime retention was the most common choice for participants who used removable retainers, especially when extractions were carried out.
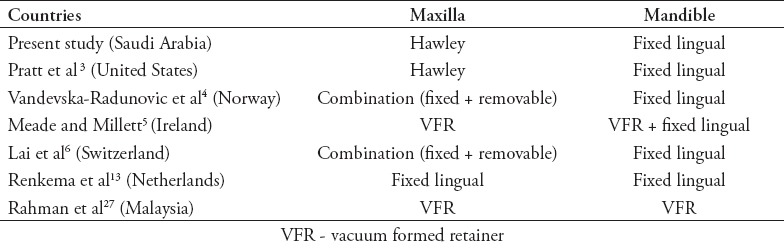
Moyers1 defined retention following orthodontic treatment as “the holding of teeth following orthodontic treatment in the treated position for the period of time necessary for the maintenance of the result.” The rationale for retention includes reorganization of the tissue, minimizing changes caused by growth and allowing neuromuscular adaptation to the corrected tooth position.2 Many forms of retention are used in orthodontic treatment. Bonded retainers, removable acrylic retainers, vacuum formed retainers (VFR), and spring retainers are the most commonly used.1 Orthodontists practice various retention protocols today. Members of the American Association of Orthodontists (AAO) reported predominance in the use of Hawley, or VFR in the maxillary arch and bonded fixed retainers in the mandibular arch.3 In Norway,4 orthodontists used fixed bonded retainers in the mandible, while in the maxilla, they used a combination of bonded retainers and removable retainers. In Ireland,5 a study of 123 eligible orthodontists recommended full-time wear of VFR in the maxillary and mandibular arches followed by part-time wear of removable retainers. Swiss orthodontists preferred using bonded retainers in both arches, except when expansion, or extraction was carried out in the maxillary arch in which a combination of removable and fixed retainers were placed.6
In Saudi Arabia, there are approximately 1,200 orthodontists who are members of the Saudi Orthodontic Society (SOS), a major organization for orthodontists in the country. Members of the SOS must hold active registration with the Saudi Council for Health Specialties. Orthodontic treatment in Saudi Arabia can be provided at no cost by the governmental sector, which results in long waiting lists, or by the private sector, which is privately funded and financed, with the advantage of shorter waiting times. There is a lack of literature regarding retention practices among orthodontists in Saudi Arabia. Therefore, the aim of this study was to survey the retention protocols that are followed by orthodontists in Saudi Arabia, and investigate the factors that affect the retainer choice.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional survey of all orthodontists in Saudi Arabia who are members of the SOS (N=1200 members). The study took place between February and March of 2015 at the College of Dentistry, University of Dammam, Damma, Saudi Arabia. Members were invited to participate and asked to fill out an online questionnaire (Google Forms) of 34 items on their maxillary and mandibular retention practices. The questionnaires were sent to members via email 3 times to maximize response rate. The first electronic mailing was in February 2015, while the second and third sendings were 2 and 4 weeks after the initial sending. Additionally, key members of the SOS were contacted to encourage members to participate in this study. Ethical approval was obtained from the Research Committee at the College of Dentistry, University of Dammam, Dammam, Saudi Arabia and the study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
The questionnaire items were adapted from the study of Valiathan and Hughes.7 Some questions were revised to be suitable for the sample evaluated. The questionnaire elicited the following data: 1) Demographics (gender, year of graduation from an advanced education program in orthodontics, national or international board certification, country from which the orthodontic degree was obtained, socioeconomic status, years in practice, work place/sector). 2) Orthodontic treatment phase (average number of debondings last year, the use of phase-I as part of treatment, extraction rate). 3) Retention phase (this included general questions regarding types of retainers prescribed and duration of retention, in addition to questions specific to retention practices in each arch). 4) Post-retention phase (this included questions on whether, or not the respondent practiced a post-retention follow-up phase described as patients continuing to wear retainers after the hard and soft tissues have completed remodeling following orthodontic treatment, and the length of this phase).
Data were analyzed using Statistical Package of Social Sciences, version 19 for Windows (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Descriptive analysis was conducted for all variables and frequencies were reported. Chi-square test was used to determine factors affecting the choice of retainers including: gender, years in practice, board certification, number of debonds, Phase-I treatment, extraction rate, and duration of retention. Statistical significance was set at 5%.
Results
One hundred and sixty-seven (13.9%) responses were received. Most of the respondents were male (69%), and more than 46% had 6-15 years of orthodontic experience, Table 1.
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of 167 orthodontists included in the study on retention practices.

When asked regarding the total number of cases debonded within the past year, 65% debonded <150 cases, 25.2% debonded 150-300 cases, and only 9.8% debonded >300 cases. Phase-I (early treatment) was commonly practiced by 83.8% of the orthodontists. The rate of extraction treatment was <1/4th of the cases by 21.5% of the orthodontists, between one quarter and one half of the cases by 66.9%, and between 1/2 and three quarters of the cases by only 11.7%. The types of retainers used in both the maxillary and mandibular arches and the duration of wear are illustrated in Figure 1 and Table 2. In the maxillary arch, the most commonly prescribed type of retainer was Hawley (61.3%). Vacuum formed retainer (VFR) (16%), VFR with fixed lingual (12.9 %), and VFR followed by Hawley (6.1%) were also used by some orthodontists. The least frequently used retainer was the fixed lingual (3.7%). While in the mandible, the most commonly delivered retainer was the fixed lingual (58.5%). Of the orthodontists who used removable retainers, 90.3% recommended full-time maxillary, and 75.3% mandibular removable retainer wear. Of the few who recommended part-time wear only, most instructed patients to wear the retainer for a duration of 16 hours per day. Forty-four percent of the orthodontists indicated that Hawley was the removable retainer type most patients complied with, followed by VFR (28%). The remaining percentage thought there was no difference in compliance with the 2 retainer types.
Figure 1.
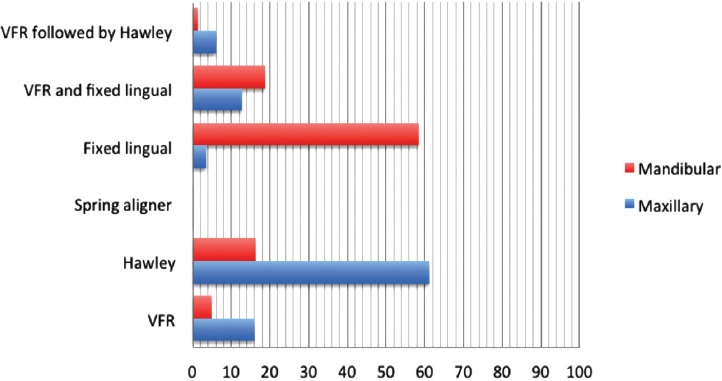
Frequency of maxillary and mandibular retainer use by type. VFR - vacuum formed retainers
Table 2.
Retention and post-retention protocols in the maxillary and mandibular arches.

Most orthodontists (73.5%) stated that whether, or not a patient received extractions as part of his or her orthodontic treatment influenced the type of retainer the orthodontists provided to the patient. Orthodontists who performed fewer extractions tended to use fixed retainers and those who performed more extractions used Hawley retainers (p=0.018). Also, those that debonded fewer cases per year tended to prescribe fixed retainers compared with those that treated more cases (p=0.016). None of the other factors was statistically significant. When asked regarding the use of adjunct procedures to enhance retention, 28% performed interproximal enamel reduction (IPR), a slightly lower percentage (26.8%) performed no adjunct procedure, 26.1% over-corrected the malocclusion, and 19.1% used circumferential supracrestal fibrotomy (CSF).
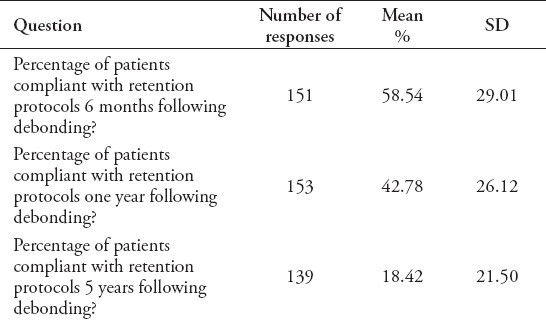
The retention check protocol varied among orthodontists (Table 3). Approximately 42% of the respondents schedule the first retention check at 1-2 months after debonding, while 10% did not schedule any further appointments after appliance debonding and retainer delivery. Eighty-seven percent of the orthodontists did not charge for retention checks, while 13% have a fee schedule and the average fee charged was SAR227 (equivalent to USD60). Reported patient compliance rates at different retention check durations are presented in Table 4.
Table 3.
Retention checks and post-retention protocols in the maxillary and mandibular arches.

Table 4.
Rates of patient compliance with the retention protocols at 6 months, one and 5 years following debonding.
Of the respondents, 63.9% practiced a post-retention phase of retainer wear. Respondents who practiced phase-I (early treatment), and those who did not use any adjunctive retention procedures both instructed a lifetime period of post-retention.
Discussion
Previous evidence has confirmed that retention protocols are case specific in that they take into consideration different factors, such as patient age, type and severity of initial malocclusion, growth potential, and patient compliance.8,9 Yet, common trends exist among orthodontists practicing in different countries that are perhaps influenced by underlying oral health attitudes, behaviors, and practices among treated patients, type of dental care delivery system, as well as the training backgrounds of orthodontists.3,4,6 Hence, it was important to investigate the retention practices of orthodontists in Saudi Arabia. In this study, the most commonly used retainer in the maxilla was the Hawley. This was similar to results found by Pratt et al,3 Keim et al,10 and Valiathan and Hughes.7 Vacuum formed retainer alone was the second most common retainer used in the maxilla in our study, while in Ireland5 it was the first choice, prescribed by 53% of orthodontists. Evidence on the clinical effectiveness of VFR is still limited and variable. One randomized clinical trial11 compared the effectiveness of VFR and Hawely retainers over a 6-month period of retention. The study measured tooth rotations mesial to first permanent molars, little’s irregularity index, and inter-molar, and inter-canine widths. The study found significantly greater changes in irregularity with the Hawley compared to the VFR. Yet, a recent systematic review of 7 studies comparing VFR with Hawley reported insufficient evidence to support the use of one retainer over the other.12 Overall, the preference of prescribing removable retainers in the maxilla may suggest that orthodontists prefer to shift the responsibility of maintaining the results to the patient. A combination of fixed and removable appliances was the most common maxillary retainer favored by orthodontists in Norway4 and Switzerland.6 In our study, it was the third choice. Fixed lingual was the least common retainer used in the maxilla in this study, in contrast to findings by Renkema et al,13 where it was commonly used in the maxilla. Maxillary fixed lingual retainers are associated with greater failure compared with mandibular fixed lingual.14 The success of these retainers is associated with the number of teeth included in the bonded unit, as well as the operator’s experience.14 This may explain their limited use among the sample of our study. In the mandibular arch, fixed lingual was the most commonly used retainer (59%). A similar percentage was reported in the Netherlands13 and in the United States.15 The simplicity of the procedure in terms of direct visibility and good aesthetics seem to be the advantages that explain why mandibular fixed lingual is popular16,17 among orthodontists in Saudi Arabia and elsewhere. A smaller percentage (18.9%) used a combination of fixed lingual and VFR. The most popular retainer combination among Saudi Orthodontists is the maxillary Hawley and the mandibular fixed lingual. According to Hoybjerg et al15 in their study of U.S. orthodontists, maxillary Hawley used with mandibular fixed retainer showed the greatest amount of settling. It is worth stating that 21.4% of the respondents in our study were graduates of North American orthodontic programs and, therefore, might have adapted the same retainer choices used there. In Ireland,5 they preferred to use VFR combined with fixed retainer in the mandibular arch.
In this study, 83.6% of the orthodontists reported that they recommend keeping the fixed lingual retainer in place for a long period of time. Of those, more than one-third instruct removal 2-5 years after debonding. This is consistent with the recommendations of Wong and Freer18 who suggested that a period of retention for more than 2 years is preferred. Although there is no consensus in previous literature on removal times of bonded retainers,19 Zachrisson8 recommended extended use of fixed lingual retainers until after the third molars erupt due to post-pubertal growth and maxillomandibular dental changes that occur during that time,20,21 but only if the patient maintains optimal oral hygiene practices.
Our study found that participants with high extraction rates were more likely to choose the Hawley retainer, while orthodontists with low extraction rates tend to use fixed retainers. This was similar to results from the United States.15 The differences in settling, however, between extraction and non-extraction cases were found to be insignificant.1,3 Similar to the findings of Valiathan and Hughes (84%),7 almost 78% of orthodontists who prescribed lifetime retention in this study used removable retainers in the maxilla.
Most of orthodontists in our study advised full-time removable retainer wear both in the maxilla and the mandible, a smaller percentage did recommend part-time wear. The rational behind instructing full-time versus part-time wear is not known and may need to be explored in future studies. Nonetheless, recent evidence suggested that the 2 year protocols have similar effectiveness in maintaining stability.22
According to the respondents, patients’ compliance was greater with the Hawley compared to the VFR. The occlusal coverage of the VFR may have resulted in speech impairment and, therefore, a lower compliance rate. This factor seemed to have overpowered the demand for an aesthetics appliance, which is one of the advantages of VFR.
Among the available adjunct procedures to enhance retention, IPR was performed more commonly among the orthodontists in Saudi Arabia. It was not clear, however, if IPR was carried out only in the maxillary or mandibular arches, or both. Interproximal enamel reduction has several advantages, including broadening of the interdental contacts, increasing fill of the gingival papilla,23 improving aesthetics, as well as maintaining incisal inclination in non-extraction cases. Aasen and Espeland24 in an earlier study suggested that IPR could be an alternative method to mandibular retainers to maintain lower incisor stability. Our study did not examine whether the IPR was carried out serially, or at one point in time after appliance removal, nor did it investigate the types of cases where IPR was performed. Boese25 recommended the procedure be carried out serially over a 4-6 month period after debonding. In our study, 26.8% reported that no adjunct procedures were practiced, those respondents also tended to prescribe lifetime retention as compared with those who used adjunct methods. This may be explained by their need to compensate for maximum retention. Unexpectedly, 19.1% of the orthodontists stated that they routinely use CSF as an adjunct procedure. The CSF surgical procedure was first described by Edwards,26 and it involves severing of the supra-alveolar fibers to prevent rotational relapse in maxillary and/or mandibular anterior teeth. More studies are needed to determine the sites where this procedure is conducted. Edwards26 found CSF to be less successful in the mandibular anterior region. As well, the long-term stability of the procedure warrants future exploration.
There are a lot of similarities noticed when comparing the current findings to previously published data in the literature. Although orthodontists in the countries reviewed agreed to the use of fixed retention in the mandibular arch with the exception of Malaysian orthodontists who preferred VFR,27 they seem to vary regarding retention in the maxillary arch (Table 5). This reinforces the need for guidelines regarding orthodontic retention in the maxilla.
Table 5.
Comparison of different retention protocols in different countries.
Study limitations
The response rate was low, consequently threatening the validity of the inferences. However, since the questionnaire was sent through the SOS list serve, which is the largest orthodontic association in the country, there is no reason to believe that non-responders differed substantially from responders in this study. Also, there was no information regarding the type of phase-I treatments practiced. Future studies may want to investigate the phase-I treatment practices of orthodontists in the region. Also, the types of retainers prescribed for different malocclusions, such as anterior open bite, warrant future investigation. Finally, since there was no similar study carried out previously in Saudi Arabia, we were not able to learn whether, or not there was a shift in retention practices in the country.
In conclusion, orthodontists in Saudi Arabia reported the most common retention protocol used was Hawley (61.3%) in the maxilla and fixed lingual (58.5%) in the mandible. Respondents who extracted less used fixed retention, while those who extracted more used removable retainers. Lifetime retention was the most common choice for participants who used removable retainers, especially when extractions were carried out. The decline in the use of adjunctive retention procedure was paired with lifetime post-retention.
Footnotes
References
- 1.Moyers RE. Handbook of orthodontics for the student and general practitioner. 3rd ed. Chicago (IL): Year Book Publishers Inc; 1973. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moorrees CFA. The dentition of the growing child: A longitudinal study of dental development between 3 and 18 years of age. Cambridge (LK): Harvard University Press; 1959. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pratt MC, Kluemper GT, Hartsfield JK, Jr, Fardo D, Nash DA. Evaluation of retention protocols among members of the American Association of Orthodontists in the United States. Am J Ortho Dentofacial Orthop. 2011;140:520–526. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2010.10.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vandevska-Radunovic V, Espeland L, Stenvik A. Retention: type, duration and need for common guidelines. A survey of Norwegian orthodontists. Orthodontics (Chic.) 2013;14:e110–e117. doi: 10.11607/ortho.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Meade MJ, Millett D. Retention protocols and use of vacuum-formed retainers among specialist orthodontists. J Orthod. 2013;40:318–325. doi: 10.1179/1465313313Y.0000000066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lai CS, Grossen JM, Renkema AM, Bronkhorst E, Fudalej PS, Katsaros C. Orthodontic retention procedures in Switzerland. Swiss Dent J. 2014;124:655–661. doi: 10.61872/sdj-2014-06-01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Valiathan M, Hughes E. Results of a survey-based study to identify common retention practices in the United States. Am J Ortho Dentofacial Orthop. 2010;137:170–177. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2008.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zachrisson BU, Buyukyilmaz T. Bonded retainers. In: Graber LW, Vanarsdall RL, Vig KW, editors. Orthodontics: current principles and techniques. 5th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Mosby; 2012. pp. 756–84. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zachrisson BU. Multistranded wire bonded retainers: From start to success. Am J Ortho Dentofacial Orthop. 2015;148:724–727. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2015.07.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Keim RG, Gottlieb EL, Vogels DS, 3rd, Vogels PB. 2014 JCO study of orthodontic diagnosis and treatment procedures, Part 1: results and trends. J Clin Orthod. 2014;48:607–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rowland H, Hichens L, Williams A, Hills D, Killingback N, Ewings P, et al. The effectiveness of Hawley and vacuum-formed retainers: a single-center randomized controlled trial. Am J Ortho Dentofacial Orthop. 2007;132:730–737. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mai W, He J, Meng H, Jiang Y, Huang C, Li M, et al. Comparison of vacuum-formed and Hawley retainers: a systematic review. Am J Ortho Dentofacial Orthop. 2014;145:720–727. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2014.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Renkema AM, Sips ET, Bronkhorst E, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM. A survey on orthodontic retention procedures in The Netherlands. Eur J Orthod. 2009;31:432–437. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjn131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Schneider E, Ruf S. Upper bonded retainers. Angle Orthod. 2011;81:1050–1056. doi: 10.2319/022211-132.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hoybjerg AJ, Currier GF, Kadioglu O. Evaluation of 3 retention protocols using the American Board of Orthodontics cast and radiograph evaluation. Am J Ortho Dentofacial Orthop. 2013;144:16–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2013.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Espeland LV, Stenvik A. Perception of personal dental appearance in young adults: relationship between occlusion, awareness, and satisfaction. Am J Ortho Dentofacial Orthop. 1991;1001:234–241. doi: 10.1016/0889-5406(91)70060-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zachrisson BU. Long-term experience with direct-bonded retainers: update and clinical advice. J Clin Orthod. 2007;41:728–737. quiz 749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wong PM, Freer TJ. A comprehensive survey of retention procedures in Australia and New Zealand. Aust Orthod J. 2004;20:99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Booth FA, Edelman JM, Proffit WR. Twenty-year follow-up of patients with permanently bonded mandibular canine-to-canine retainers. Am J Ortho Dentofacial Orthop. 2008;133:70–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.10.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Richardson ME, Gormley JS. Lower arch crowding in the third decade. Eur J Orthod. 1998;20:597–607. doi: 10.1093/ejo/20.5.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Thilander B. Dentoalveolar development in subjects with normal occlusion. A longitudinal study between the ages of 5 and 31 years. Eur J Orthod. 2009;31:109–120. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjn124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Littlewood SJ, Millett DT, Doubleday B, Bearn DR, Worthington HV. Retention procedures for stabilising tooth position after treatment with orthodontic braces. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(1):CD002283. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002283.pub4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zachrisson BU. Interdental papilla reconstruction in adult orthodontics. World J Orthod. 2004;5:67–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Aasen TO, Espeland L. An approach to maintain orthodontic alignment of lower incisors without the use of retainers. Eur J Orthod. 2005;27:209–214. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cji012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Boese LR. Fiberotomy and reproximation without lower retention, nine years in retrospect: part I. Angle Orthod. 1980;50:88–97. doi: 10.1043/0003-3219(1980)050<0088:FARWLR>2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Edwards JG. A surgical procedure to eliminate rotational relapse. Am J Orthod. 1970;57:35–46. doi: 10.1016/0002-9416(70)90203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rahman NB, Low TFINS. A survey on retention practice among orthodontists in Malaysia. Korean J Orthod. 2016;46:36–41. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2016.46.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


